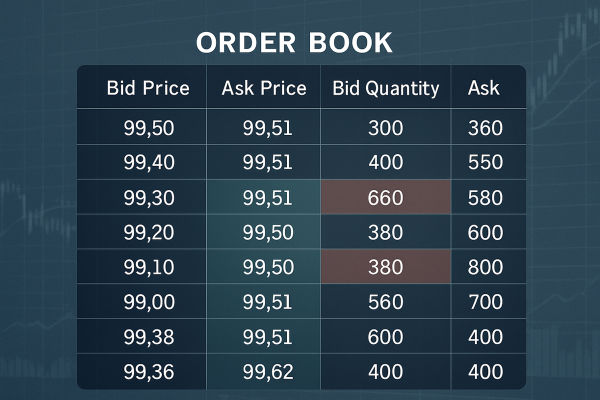
An order book is an electronic list of buy and sell orders for a security or asset, organised by price level. It's essentially a live record of all purchase and sell orders for a particular asset, such as a stock, currency pair, commodity, or cryptocurrency.
In simple terms, the order book answers the question: Who is buying, who is selling, and at what price? The order book provides traders with a clear view of supply and demand dynamics by displaying the number of buyers and sellers, with their associated prices.
This guide explains what an order book is, its types, how it works, and effective strategies for its use.
What Is an Order Book in Trading?
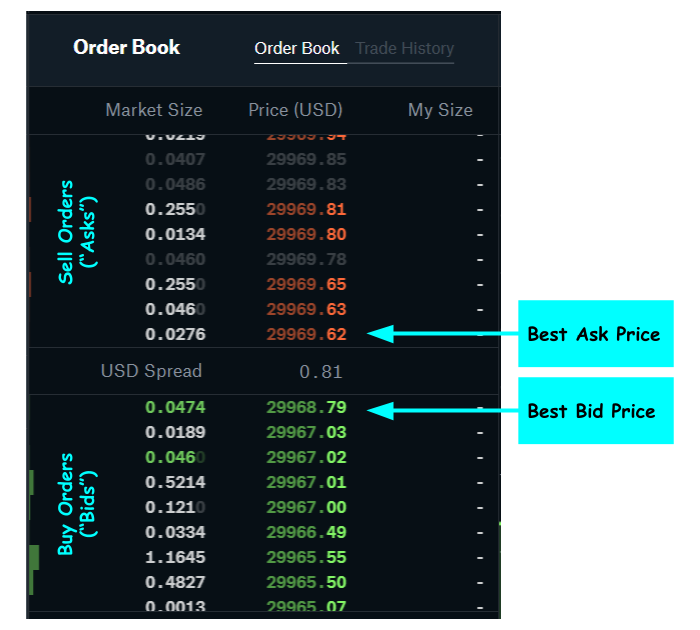
As mentioned above, the order book provides a live view of market sentiment and liquidity, displaying who is looking to buy or sell at which prices.
The two main sides of the order book are:
The point at which the highest bid meets the lowest ask is the market price or last traded price.
Why Order Books Matter:
Understanding market depth (liquidity)
Spotting large buy or sell walls
Anticipating short-term price movements
Identifying potential support and resistance levels
How an Order Book Works
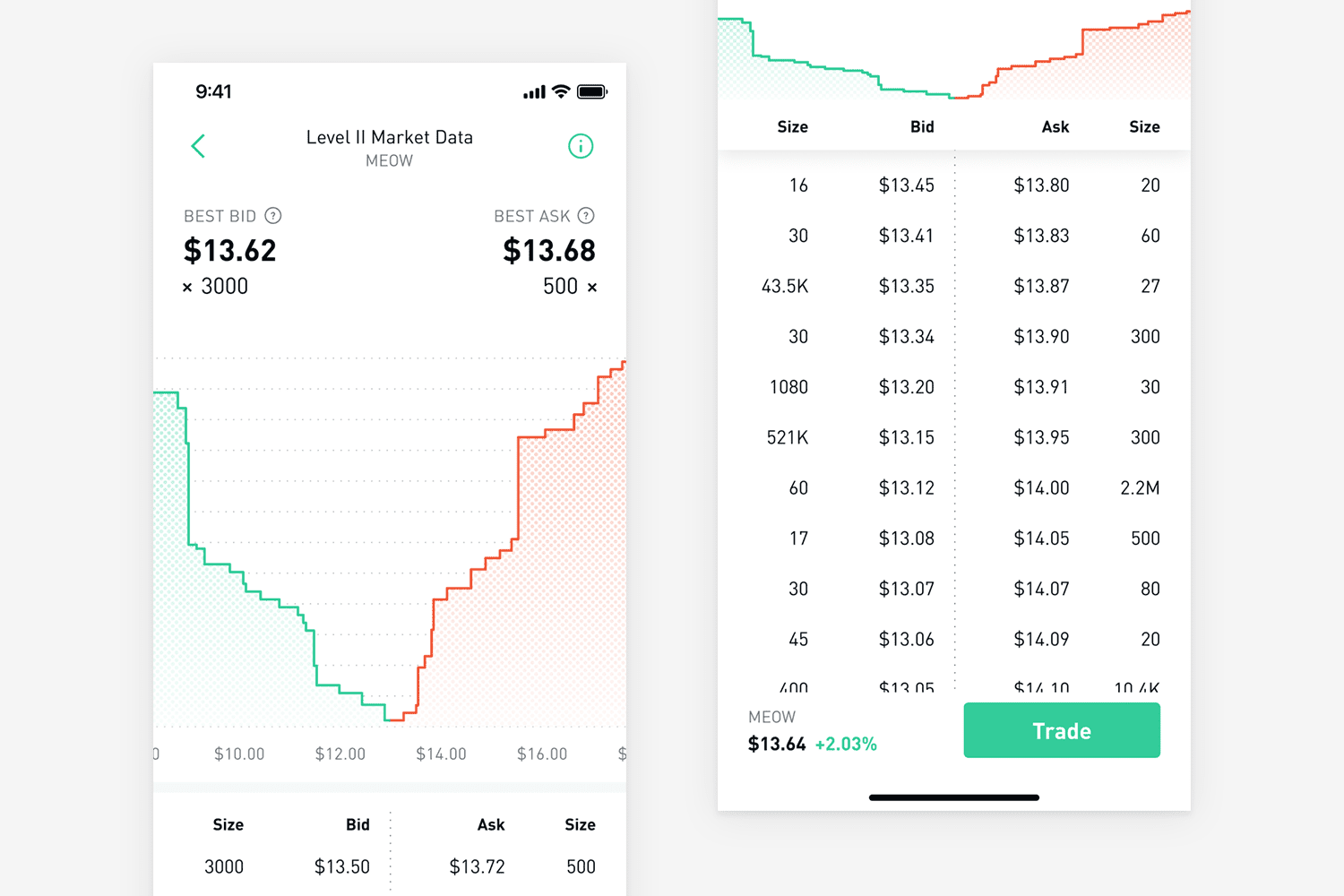
When traders place orders through their broker or trading platform, the broker or trading platform sends these orders to the exchange. The exchange then adds them to the order book until it matches them with opposite orders.
Key Components of an Order Book
Bid Price & Quantity: The price and number of units buyers are willing to purchase.
Ask Price & Quantity: The price and number of units sellers are offering.
Order Size: The number of shares, contracts, or units in each order.
Market Depth: The total volume of buy and sell orders at different price levels.
Example
When the top bid for a stock is ₹500 and the minimum ask is ₹502, the market price will probably fluctuate within that range until a transaction occurs.
Types of Order Books
1. Level 1 Order Book
A Level 1 order book displays solely the top bid and top ask prices. It's simpler and ideal for beginners, but lacks in-depth information.
2. Level 2 Order Book (Market Depth)
A Level 2 order book displays multiple bid and ask levels, providing insight into overall market liquidity and where large traders might be positioned.
How to Read an Order Book Effectively and Implement Trading Strategies
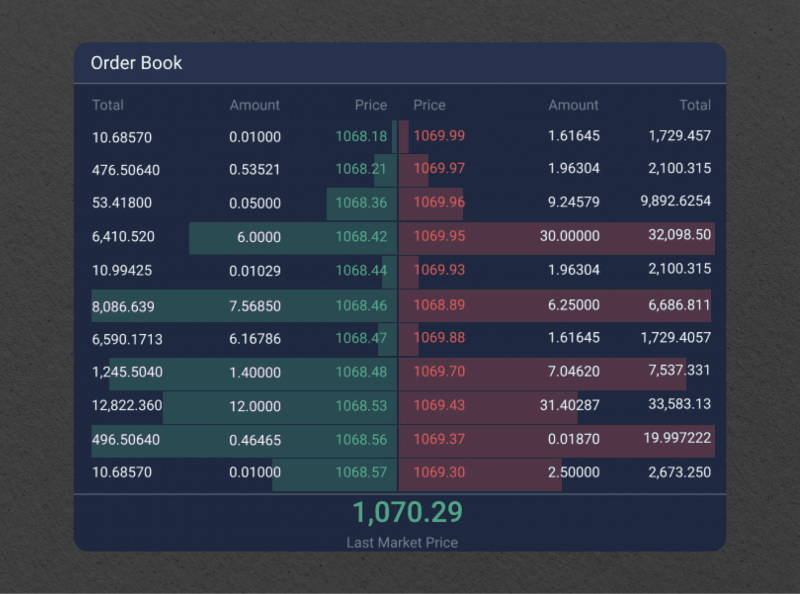
Identify the Best Bid and Ask: This tells you where the market is currently tradin
Look for Large Buy/Sell Walls: Big orders at certain prices can act as support or resistance.
Watch Order Flow Changes: If traders consistently add buy orders at higher prices, it may signal bullish sentiment.
Monitor Spread Size: A tight spread indicates high liquidity; a wide spread suggests low liquidity.
After learning how to read, traders can implement such strategies:
Support and Resistance Identification
Significant groupings of buy orders beneath the market price may suggest robust support, whereas substantial sell orders above indicate resistance.
Order Flow Trading
By monitoring changes in order book levels, traders can gauge buying or selling pressure and enter trades accordingly.
Fade Large Orders
Sometimes, big orders are used to mislead the market. Advanced traders may "fade" these orders by taking positions in the opposite direction when they suspect manipulation.
How to Use Order Book in Different Markets
In Stock Trading
Order books show institutional and retail demand for shares. Day traders often use them for scalping and short-term plays.
In Forex Trading
While Forex is decentralised, some brokers provide synthetic order books based on their liquidity providers.
In Cryptocurrency Trading
Crypto order books provide a high level of transparency, and users frequently utilise them to monitor whale activities and significant liquidity pools.
Order Book Limitations
While order books are powerful, they are not perfect:
Spoofing Risk: Traders can place large orders without executing to influence prices.
Partial Visibility: Not all trades and orders are visible, especially in dark pools.
High Volatility: Fast-moving markets can change order book data within seconds.
Final Tips
Start with a Level 1 order book before moving to Level 2.
Combine order book analysis with technical indicators.
Avoid over-relying on a single large order, as it may be fake.
Practice in a demo account to build confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Is an Order Book In Trading?
An order book is a real-time list of all buy and sell orders for a specific asset, organised by price level. It helps traders see market depth, liquidity, and current supply-and-demand dynamics.
Q2. Can Order Books Be Manipulated?
Yes. Some traders use spoofing, placing large orders without intending to execute them to mislead the market. This is why traders should combine order book data with other analysis tools.
Q3. Is the Order Book Available in All Markets?
Order books are common in stock and cryptocurrency markets. In Forex, since the market is decentralised, brokers often provide synthetic order books based on their liquidity providers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the order book is one of the most efficient tools for traders to get a clear view of supply and demand dynamics through the number of buyers, sellers, and their associated prices.
Whether you're trading stocks, Forex, or cryptocurrencies, mastering the order book can transform your market analysis and help you make more informed decisions.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.