The Russell 2000 ETF is a popular choice among traders looking to tap into the growth potential of smaller U.S. companies. Often viewed as a barometer of the American small-cap sector, it provides a unique window into the more agile, entrepreneurial side of the equity market. While large-cap stocks often dominate the headlines, small-caps can offer higher growth opportunities—alongside a higher degree of volatility.
What Is the Russell 2000 Index?
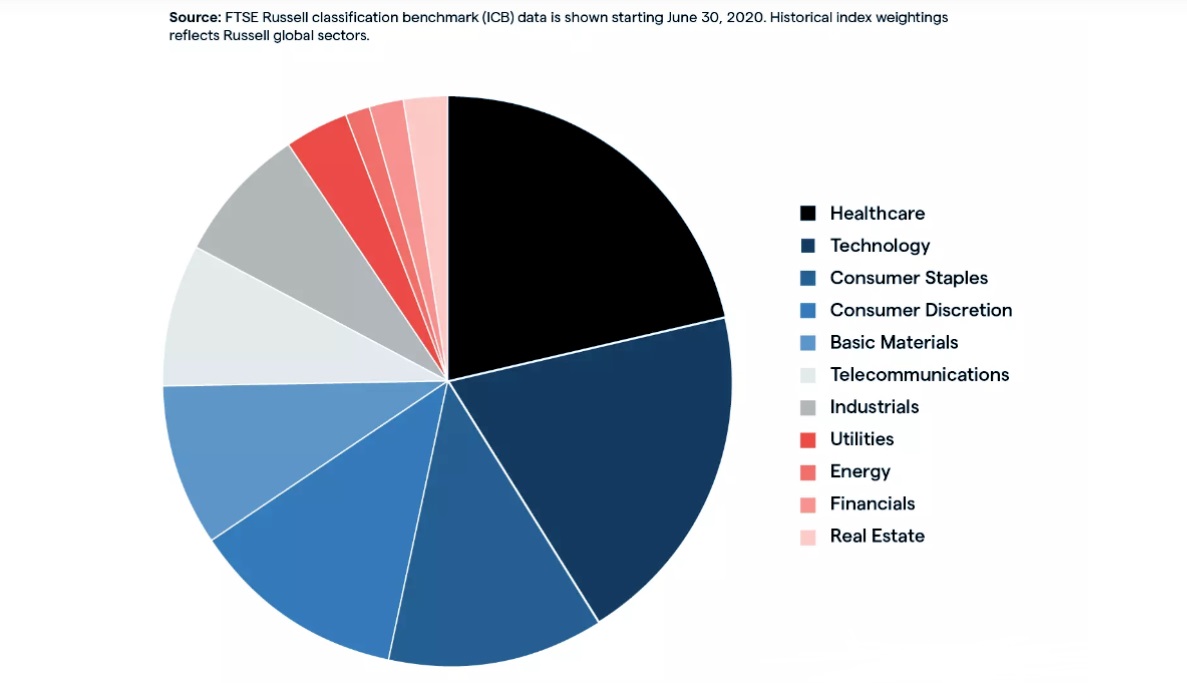
The Russell 2000 Index is a small-cap stock market index composed of 2.000 of the smallest companies in the Russell 3000 Index, which itself represents the 3.000 largest publicly traded U.S. companies. Launched in 1984 by FTSE Russell, the index is widely regarded as the benchmark for small-cap U.S. equities.
These companies typically have market capitalisations ranging from $300 million to $2 billion, making them significantly smaller than the blue-chip firms found in the S&P 500. Sectors such as healthcare, industrials, technology, and consumer discretionary are often heavily represented, though the exact weightings can shift over time.
Unlike actively managed indices that are curated by committees, the Russell 2000 uses a rules-based approach, rebalancing annually in June to ensure only the most relevant companies are included. This keeps the index fresh and reflective of changes in the small-cap space.
The Russell 2000 is widely used by fund managers, financial analysts, and traders as a gauge of U.S. economic strength, especially because smaller companies tend to be more sensitive to changes in domestic conditions, interest rates, and consumer demand.
How the Russell 2000 ETF Works
A Russell 2000 ETF is an exchange-traded fund designed to track the performance of the Russell 2000 Index as closely as possible. Rather than picking and choosing stocks, these ETFs aim to replicate the index by investing in either all or a representative sample of its 2.000 constituent companies.
Here's how they work in practice:
Passive Management: Most Russell 2000 ETFs are passively managed, meaning they follow the index automatically rather than trying to outperform it. This helps keep fees relatively low.
Daily Liquidity: ETFs trade on stock exchanges like regular shares, allowing you to buy or sell them during market hours. This is in contrast to mutual funds, which only price once per day.
Dividend Income: Many of the companies in the Russell 2000 pay dividends. These are typically collected by the ETF provider and distributed to shareholders, either quarterly or semi-annually.
Diversification: Buying one ETF gives you exposure to a wide range of small-cap stocks across different industries, helping to spread risk.
Some ETFs try to hold all 2.000 stocks in the index (known as full replication), while others use sampling techniques, selecting a subset that closely mirrors the index's performance. The choice of strategy can affect tracking accuracy and operating costs.
Key Benefits of Investing in Small-Cap ETFs
Russell 2000 ETFs offer several advantages, particularly for traders seeking long-term growth. Here are some of the most compelling reasons to consider them:
Small-cap firms are often in earlier stages of development, meaning they have more room to grow. While not all will succeed, those that do can deliver impressive returns.
Because smaller firms tend to operate domestically, they're highly sensitive to the health of the U.S. economy. This makes the Russell 2000 a good way to gauge and capitalise on economic recovery cycles.
The index includes companies across various sectors, with no single one dominating. This built-in diversification helps mitigate the risk of sector-specific downturns.
In certain periods, small-cap stocks have been more resilient during inflationary cycles, especially when domestic consumption is strong.
However, traders should also be aware of the risks:
Higher Volatility: Small-caps tend to fluctuate more in price, which can mean larger short-term losses.
Limited Liquidity: Some constituent companies may not trade as frequently, especially in times of market stress.
Business Fragility: Smaller firms may struggle during economic downturns or face difficulties securing financing.
Understanding these risks is essential before making an investment decision.
Popular Russell 2000 ETFs to Know
If you're looking to invest in the Russell 2000 Index, there are several ETF options available, each with its own features and cost structure. Here are the most notable:
iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM)
Vanguard Russell 2000 ETF (VTWO)
Issuer: Vanguard
Assets Under Management: Over $10 billion
Expense Ratio: 0.10%
Overview: Known for its low fees, VTWO is an excellent option for cost-conscious traders planning to hold for the long term.
SPDR Russell 2000 ETF (TWOK)
Issuer: State Street
Assets Under Management: More modest compared to IWM and VTWO
Expense Ratio: Typically similar to peers
Overview: Offers similar exposure but is less popular in terms of trading volume.
Each ETF offers exposure to the same index but may differ in how closely they track it, how often they rebalance, and what costs they pass on to the trader. Be sure to compare liquidity, spread, and tracking error before choosing.
Is the Russell 2000 ETF Right for You?
Whether a Russell 2000 ETF belongs in your portfolio depends largely on your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance.
You might consider investing in it if:
You're aiming for long-term capital growth and are comfortable with short-term volatility.
You want to diversify beyond large-cap and international stocks.
You believe that U.S. small-cap firms are well-positioned for an economic upswing.
You want exposure to the innovation and entrepreneurship of younger companies.
On the other hand, if your priority is income stability, or if you're approaching retirement and prefer less market turbulence, you may want to allocate a smaller portion of your portfolio to small-cap ETFs—or avoid them altogether.
A balanced approach might involve combining the Russell 2000 ETF with other asset classes, such as large-cap stocks, bonds, or international equities, to reduce volatility while still capturing growth potential.
Final Thought
The Russell 2000 ETF can be a valuable addition to an trader's toolkit, offering broad exposure to the dynamic U.S. small-cap sector. While it carries more risk than large-cap-focused ETFs, it also holds the potential for higher returns, particularly in growth-oriented markets. As with any investment, understanding the structure, benefits, and risks is the first step toward making informed decisions.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.