The USD, or United States dollar, is the official currency of the United States and the most used currency in global trade and finance. It is accepted, saved, borrowed, and traded more than any other currency in the world.
For traders, the USD matters because it sits at the center of the forex market, appears in most major currency pairs, and often moves first when global news hits.
Definition

In trading, USD refers to the value of the US dollar compared with other currencies or assets. It is the base or quoted currency in most forex pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. Because of this, changes in USD strength affect a wide range of markets at the same time.
Traders see USD everywhere. It appears in currency quotes, economic calendars, interest rate decisions, and market news. Central banks, hedge funds, importers, exporters, and retail traders all watch the USD closely.
When the dollar moves, it often pulls other currencies, commodities, and even stock markets with it.
What Affects The Changes In USD Value
The value of the USD does not stay still. It moves based on clear forces that traders can track.
Interest rates: When US interest rates rise, USD often strengthens because investors can earn more by holding dollar assets. When rates fall, USD may weaken.
Economic data: Strong jobs reports or steady inflation tend to support USD. Weak growth data can pressure it lower.
Risk mood: When markets feel nervous, money often flows into USD as a safe place. When confidence returns, money may move out into higher risk assets.
Federal Reserve signals: Comments and decisions from the US central bank can move USD quickly, even without an actual rate change.
How USD affects your trades
USD has a direct effect on trade timing, cost, and risk. Because it is so widely traded, USD pairs often have high liquidity, meaning many buyers and sellers are active. This usually leads to tighter spreads and smoother order execution.
At the same time, USD can move sharply around major news events. That can create opportunity, but it can also increase risk. Entries taken just before key data may face sudden price jumps. Exits can be filled at worse prices if volatility spikes.
Good situation: Calm market conditions, steady spreads, clear trend in USD.
Bad situation: Major US news releases, sudden shifts in risk mood, fast spread widening.
Simple number example
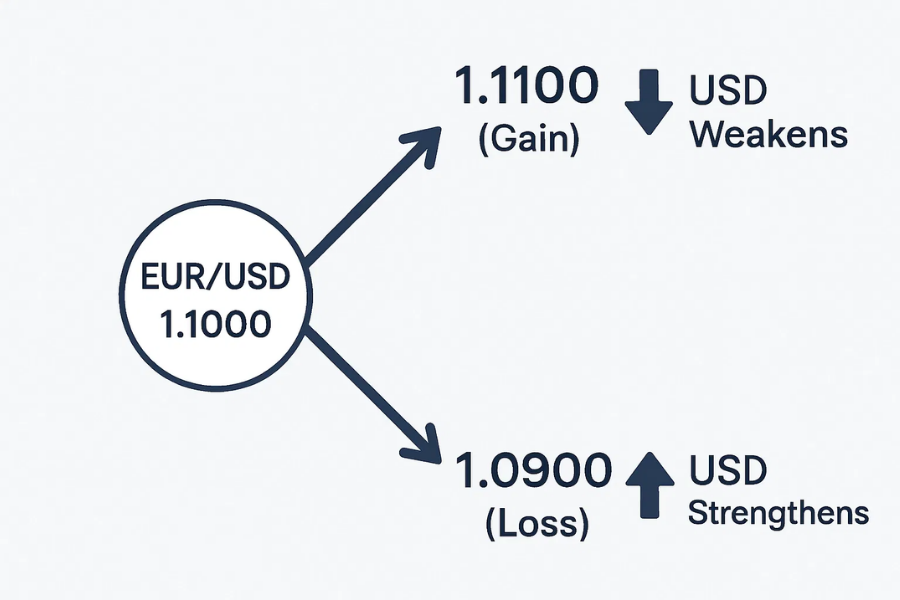
Assume EUR/USD is trading at 1.1000. This means one euro costs 1.10 US dollars. A trader buys at 1.1000, expecting USD to weaken. If USD does weaken, EUR/USD may rise to 1.1100. On a small position, that 100-point move produces a clear gain.
Now imagine strong US jobs data being released. USD strengthens quickly. EUR/USD falls to 1.0900 instead. The same trade now shows a loss. The only change was USD strength, not the euro itself. This shows how central the dollar is. Even when trading another currency, USD often decides the result.
How To Check Before You Trade
Before entering a trade, traders should take a few simple steps to judge USD conditions.
Check the economic calendar for US data such as inflation, jobs, or interest rate meetings.
Look at a USD index or major USD pairs to see if the dollar is trending or ranging.
Watch spread behavior on USD pairs. Sudden widening can signal risk.
Read recent Federal Reserve comments to understand market expectations.
A simple habit is to review USD conditions at the start of each trading session and again before major US news.
Common Mistakes While Trading USD
Ignoring Fed news: Major data can move USD fast and surprise unprepared traders.
Assuming USD always rises in crises: While often true, it does not happen every time.
Overtrading USD pairs: High activity can lead to rushed decisions.
Forgetting correlation: Many USD pairs can move together, increasing hidden risk.
Holding through key releases without a plan: This can lead to large, sudden losses.
Related Terms
EUR/USD: The most traded currency pair, showing USD strength against the euro.
USD Index (DXY): A measure of USD value against a basket of major currencies.
Federal Reserve: The US central bank that sets interest rates influencing USD.
Safe-haven currency: A currency investors prefer during market stress, often USD.
Interest rates: The return on holding a currency, a key driver of USD value.
Liquidity: How easily USD can be traded without large price changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why is the USD used so much in forex trading?
The USD is trusted globally and used in trade, finance, and reserves. This makes it highly liquid, with many buyers and sellers at all times. High liquidity usually means lower trading costs and smoother price movement.
2. Does USD always move after US news?
USD often reacts to major US data, but the size and direction depend on expectations. If the data matches what the market expects, the move may be small. Surprises tend to cause stronger reactions.
3. Is trading USD pairs good for beginners?
Many beginners start with USD pairs because they are liquid and widely covered in news. This can make them easier to follow and understand. However, beginners still need risk control, especially around news events.
4. Where can I trade USD?
You can trade the USD through regulated brokers that offer forex and CFD markets, where it is available in major currency pairs and USD-based instruments. EBC Financial Group provides access to USD trading across key markets, with pricing and execution designed for active and long-term traders.
Summary
The USD sits at the center of global trading and plays a leading role in the forex market. Its value is shaped by US interest rates, economic conditions, and shifts in global risk sentiment.
When understood and managed well, the USD provides deep liquidity and reliable market signals. When overlooked or traded without preparation, it can introduce unexpected risk into any trade.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.























