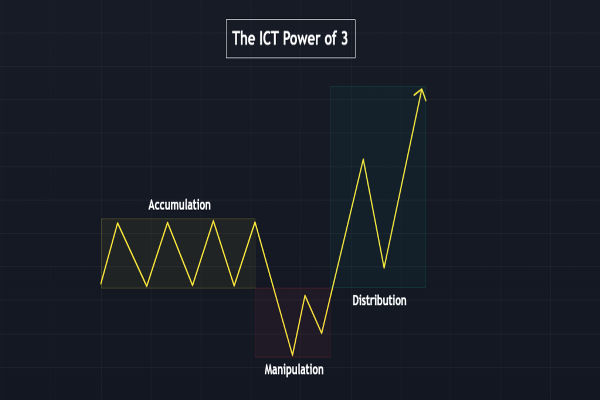
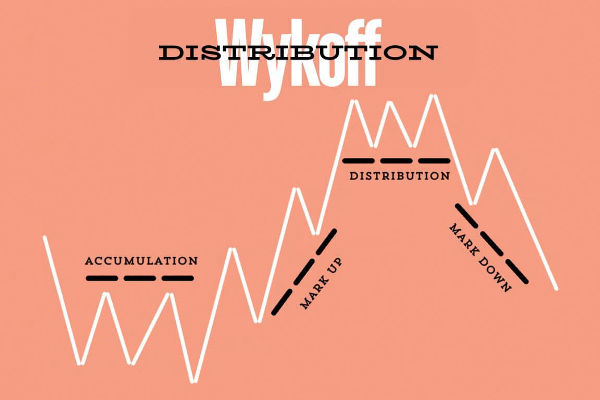
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) have become a powerful framework for understanding market structure, price manipulation, and institutional trading strategies.
Popularised among forex, stock, and crypto traders, SMC is rooted in the idea that "smart money" — large institutions, banks, and hedge funds — control market movements. These players don't trade like retail traders; they leave behind clues in the form of price action.
In this guide, you'll learn what smart money is, the core concepts of SMC, how to spot it, practical SMC trading strategies, examples, and tips to master this approach.
What Is Smart Money in Trading?

Smart money refers to the capital controlled by professional traders, institutional investors, market makers, and banks. These participants' significant resources, insider knowledge, and advanced algorithms give them an edge over retail traders.
Smart Money Concepts (SMC) is a trading methodology based on price action that seeks to track and trade with major market players rather than against them.
SMC in Forex vs Stocks
| Market |
How SMC Applies |
| Forex |
Highly liquid, institution-driven — ideal for order blocks and liquidity sweeps |
| Stocks |
Works well on large caps and indices — volume and structure matter |
SMC vs Traditional Trading Approaches
| Traditional Retail Trading |
Smart Money Concepts |
| Uses indicators (RSI, MACD) |
Relies on price action and market structure |
| Follows breakouts blindly |
Waits for liquidity grabs and manipulations |
| Trendlines and patterns |
Focuses on OBs, FVGs, and CHOCH
|
| Trades what is visible |
Trades what institutions are doing |
Core Elements of Smart Money Concepts
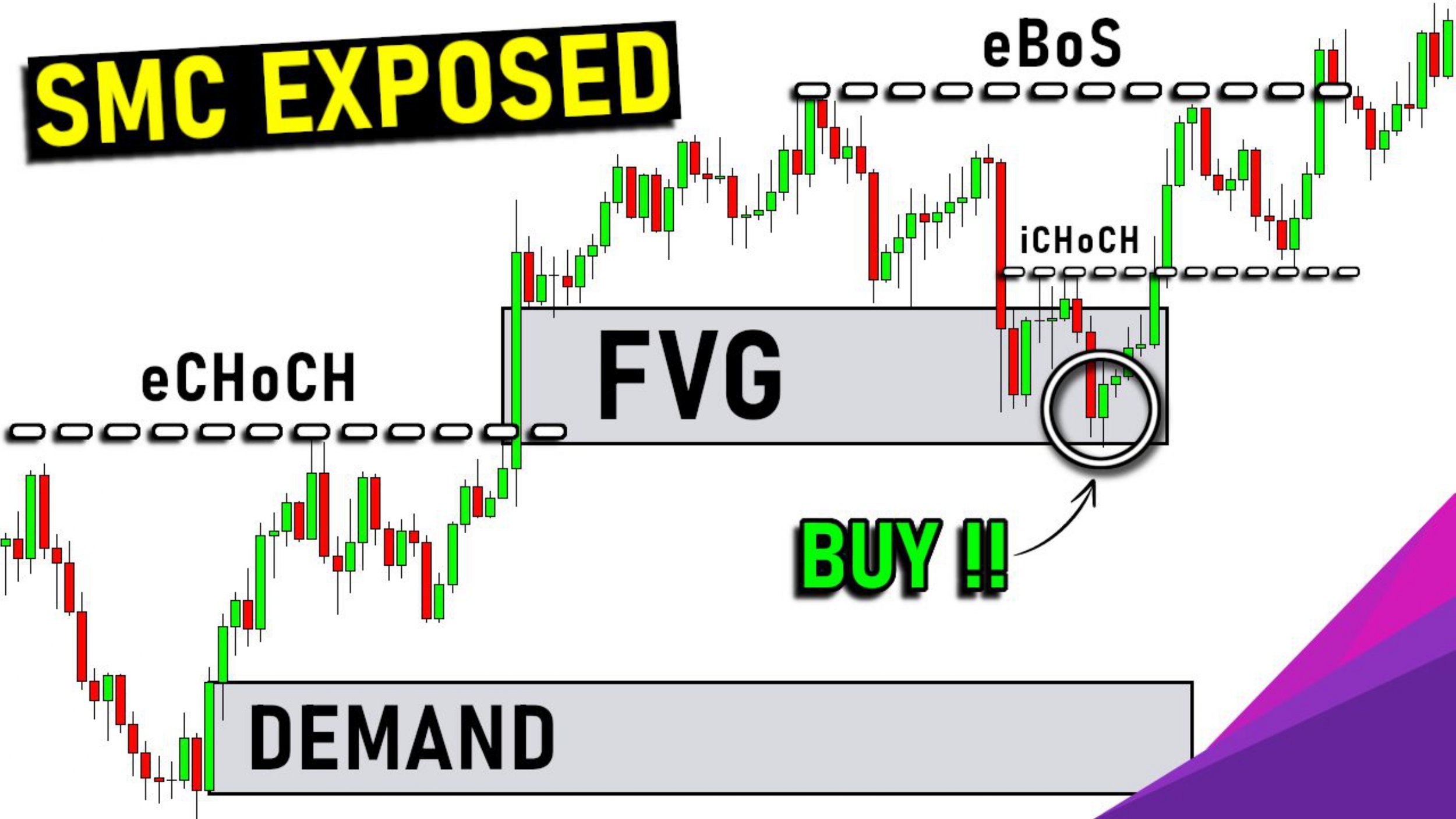
1. Market Structure
SMC relies heavily on market structure to determine trend direction, strength, and potential reversals.
Key Phases:
Higher Highs (HH) and Higher Lows (HL) = Bullish market
Lower Lows (LL) and Lower Highs (LH) = Bearish market
break of structure (BOS): Confirmed trend continuation
Change of Character (CHOCH): Signals a potential trend reversal
Understanding market structure allows traders to trade with the dominant trend and time entries precisely.
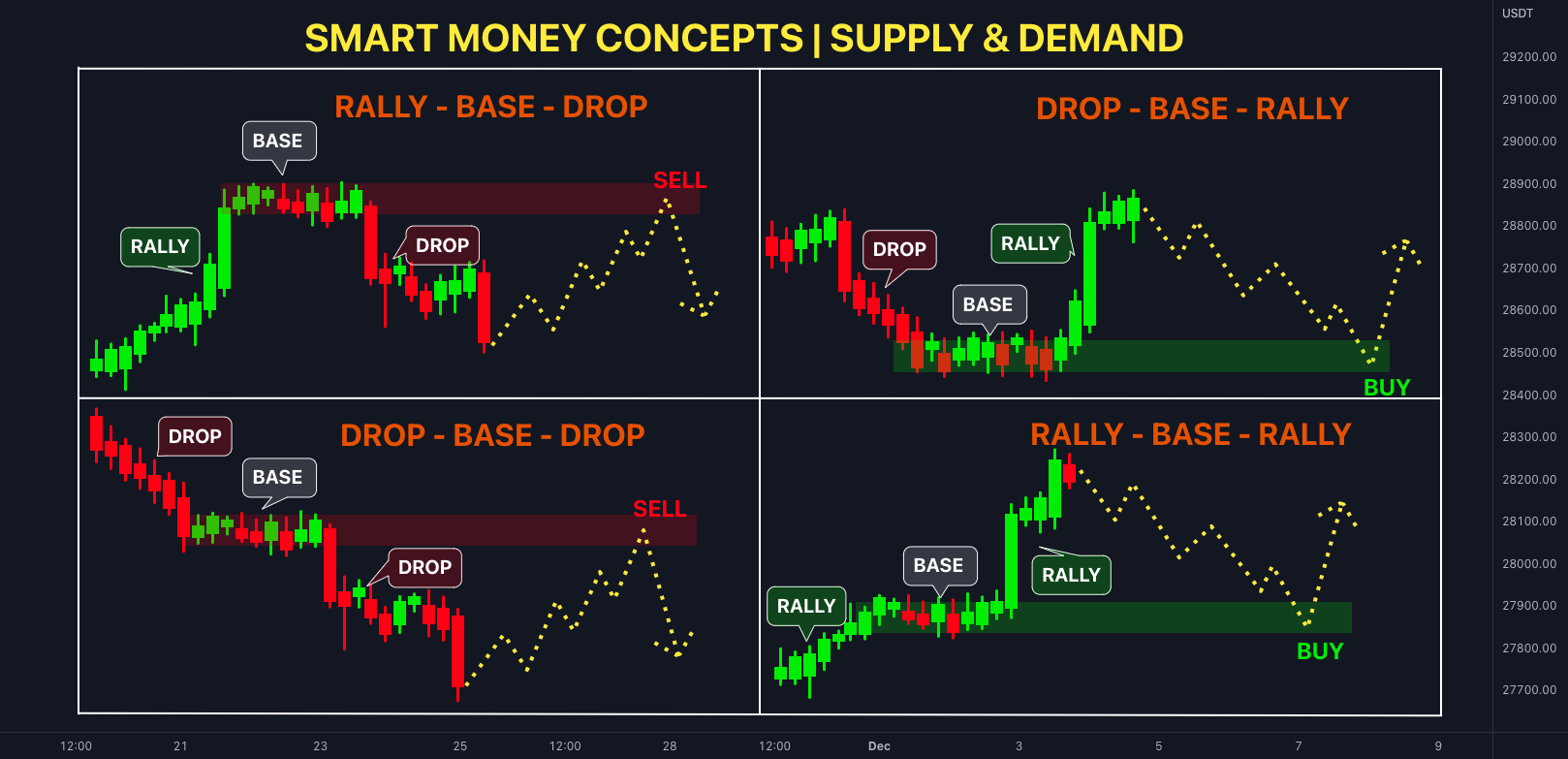
2. Liquidity Pools
Liquidity is where most orders lie. Smart money needs liquidity to fill large positions, so they:
Types of liquidity:
Equal highs/lows = Double tops and bottoms, prime targets for liquidity grabs
Trendline liquidity = Stops above/below trendlines
Session highs/lows = Often manipulated for liquidity collection
Smart money hunts these areas before making the true move.
3. Order Blocks (OB)
An order block is the last bullish or bearish candle before a significant price reversal or break of structure. It represents an area where smart money placed large institutional orders.
Types:
Traders use order blocks as potential entry zones, often paired with confirmations.
4. Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
Also known as imbalances, FVGs are price inefficiencies where one side of the market (buyers or sellers) dominates with little opposition. These often get retested or filled.
An FVG is a gap between:
Price often returns to this area before continuing the trend, giving traders a chance to enter at better prices.
5. Change of Character (CHOCH)
CHOCH marks the first sign of a potential trend reversal. It occurs when:
This early warning sign helps traders anticipate a shift in momentum before the broader market reacts.
6. Mitigation Blocks
Mitigation is when smart money closes previous positions or reduces drawdown by entering a trade in the opposite direction. Mitigation blocks often overlap with order blocks and act as strong zones for price reactions.
Why Smart Money Concepts Matter?
Most retail traders lose because they chase breakouts, follow lagging indicators, or trade randomly. Smart money, however, operates with:
Liquidity awareness
Price manipulation tactics
Market structure knowledge
Long-term planning and precision entries
SMC helps traders anticipate these moves by identifying where and why institutional traders are entering and exiting positions.
How to Trade Using Smart Money
Step 1: Identify the Market Structure
Use the 1H, 4H, or daily chart to spot the overall trend. Are we forming HH and HL (bullish) or LH and LL (bearish)
Step 2: Look for Liquidity Zones
Mark out equal highs/lows, trendlines, or previous session highs and lows. These are often targets for smart money.
Step 3: Wait for Liquidity Grab
Look for a stop hunt or liquidity sweep followed by a reversal, often indicated by a strong engulfing candle or break of structure (BOS).
Step 4: Confirm with Order Block or FVG
Once the market shifts, wait for a retest of the order block or Fair Value Gap in the new direction.
Step 5: Use CHOCH for Early Reversals
If the trend changes and a CHOCH occurs, it signals an early switch in direction.
Example
Scenario: EUR/USD is in a downtrend on the 4H chart.
Liquidity Pools Identified: Double top at 1.0800
Liquidity Grab: Price breaks above 1.0800, stops out buyers, then sharply reverses
CHOCH: 1H chart forms a new lower low — trend shift begins
Order Block: A bullish 1H candle at 1.0815 becomes the mitigation zone
Entry: Short position at the OB retest
Target: Next liquidity pool at 1.0700
Stop Loss: Just above the OB
This high-probability setup shows how smart money "traps" retail and then moves in the opposite direction.
Benefits of SMC
| Benefit |
Explanation |
| High-probability entries |
SMC focuses on institutional footprints |
| Better risk-reward ratios |
Entries near OBs and FVGs offer small SL, large TP |
| Avoiding retail traps |
SMC teaches traders to think opposite of retail sentiment |
| Price action-based |
No indicators needed — clean charts and logic-driven |
| Works across markets |
Effective in forex, crypto, stocks, and indices |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Smart Money Concepts unlock a deeper understanding of market behaviour — from structure and liquidity to manipulation and institutional strategy. By trading with the flow of smart money instead of against it, you can dramatically improve your edge.
However, SMC takes time and discipline to master, but once understood, it becomes one of the most crucial approaches in a trader's toolbox.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.