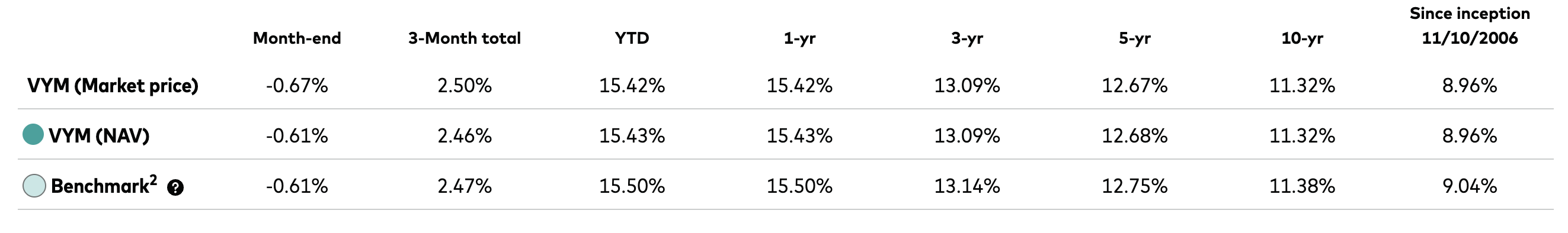The Enduring Appeal of the VYM Dividend Yield in a Volatile Market
Income investing has quietly reasserted itself as one of the most rational strategies in modern portfolio construction. After a decade dominated by growth-at-any-price narratives, investors are again prioritizing cash flow, balance-sheet strength, and valuation discipline.
Few instruments capture that shift as cleanly as the VYM dividend strategy, which combines scale, diversification, and consistency into a single vehicle. The VYM dividend yield is not designed to dazzle. Its power lies in durability.
This article examines how the VYM dividend works, what drives the VYM dividend yield, and why the structure remains highly relevant for long-term investors navigating inflation, interest rate uncertainty, and uneven equity markets. Rather than focusing on short-term performance, our analysis centers on income reliability, portfolio construction logic, and the strategic role VYM plays in serious capital allocation.
What Is VYM and Why Dividend Investors Gravitate Toward It
VYM is the ticker symbol for the Vanguard High Dividend Yield ETF, one of the largest dividend-focused exchange-traded funds globally. It is issued by Vanguard, a firm synonymous with low-cost investing and long-term discipline.
The fund tracks an index composed of U.S. companies with above-average dividend yields, excluding real estate investment trusts. The result is a portfolio tilted toward mature, cash-generative businesses with established payout policies rather than speculative growth profiles.
At its core, VYM is not a high-risk income play. It is a broad-based equity income instrument designed to provide steady dividends while maintaining exposure to long-term equity appreciation.
Key structural characteristics include:
Exposure to several hundred U.S. dividend-paying stocks
Sector diversification with emphasis on financials, healthcare, consumer staples, and energy
A rules-based methodology that avoids discretionary stock picking
Ultra-low expense ratio, preserving net income for shareholders
This structure explains why the VYM dividend has become a default holding for income-oriented portfolios across retail and institutional channels.
Understanding the VYM Dividend Yield in Practical Terms
The VYM dividend yield reflects the fund’s trailing twelve-month distributions divided by its current market price. Historically, the yield has fluctuated in a range that typically exceeds the broader U.S. equity market while remaining below highly concentrated income strategies.
That balance is intentional. VYM seeks sustainability, not yield maximization.
Several factors influence the VYM dividend yield at any given time:
1. Corporate payout behavior
Because VYM holds companies with established dividend policies, changes in aggregate payouts tend to be gradual rather than abrupt.
2. Market price movements
As equity prices rise, the yield compresses. During market pullbacks, the yield expands, often creating attractive entry points for income-focused investors.
3. Sector composition
VYM’s heavier exposure to traditionally higher-yielding sectors supports a yield premium without excessive leverage or payout risk.
4. Dividend growth trends
Many VYM holdings prioritize modest but consistent dividend growth, reinforcing long-term income stability.
Unlike bond yields, the VYM dividend yield is not fixed. That variability introduces market risk, but it also offers inflation resilience that fixed-income instruments often lack.
VYM Dividend Consistency and the Power of Compounding
One of the most underappreciated aspects of the VYM dividend is its consistency over time. While quarterly distributions can vary slightly, the annual income stream has demonstrated resilience across economic cycles.
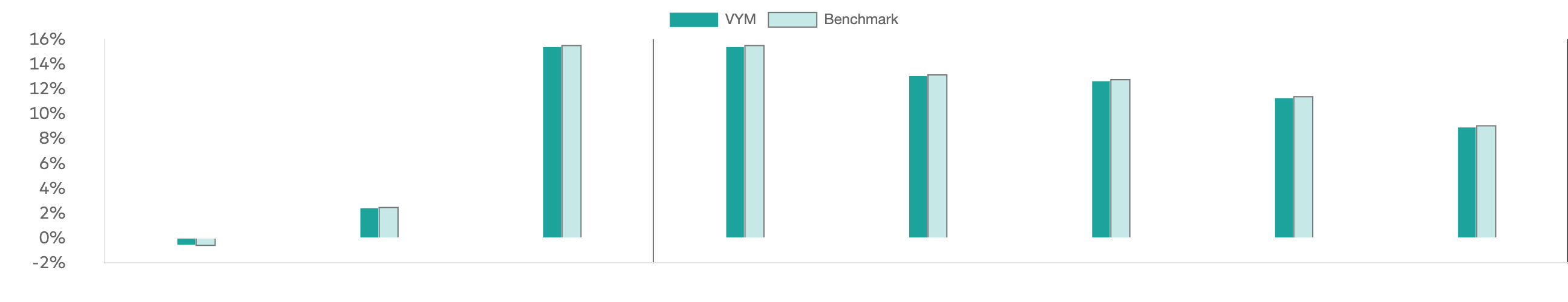
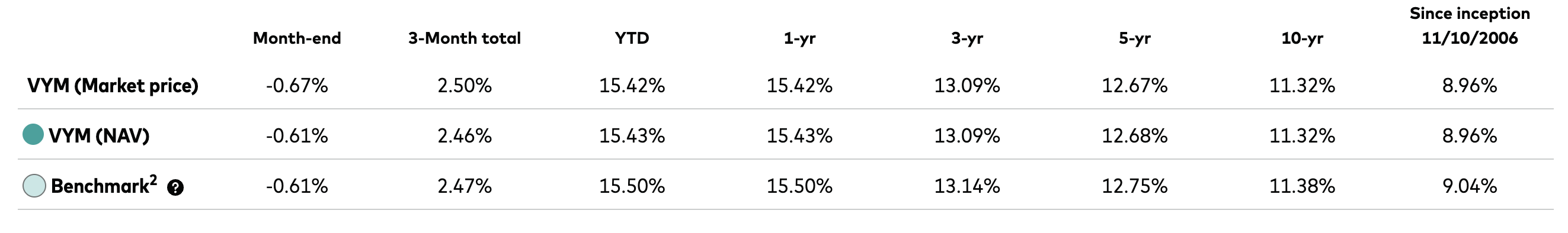
For long-term investors, reinvested dividends materially alter total return outcomes. When distributions are reinvested during market downturns, additional shares are accumulated at lower prices, increasing future income potential. Over multi-decade horizons, this compounding effect often rivals or exceeds capital appreciation as a driver of total returns.
Importantly, VYM avoids excessive exposure to companies that maintain dividends through leverage or deteriorating fundamentals. Dividend cuts within the portfolio tend to be offset by increases elsewhere, smoothing aggregate income.
Sector Allocation and Its Impact on VYM Dividend Yield
VYM’s sector composition plays a central role in shaping both yield and risk characteristics.
Financials contribute meaningfully to income, benefiting from normalized interest rate environments and strong capital buffers.
Healthcare offers defensive cash flow supported by demographic trends and recurring demand.
Consumer staples provide stability through economic cycles, reinforcing dividend reliability.
Energy introduces cyclicality but also boosts yield during periods of elevated commodity prices.
The absence of REITs reduces sensitivity to interest rate fluctuations, while the underweight to high-growth technology dampens volatility. This composition reflects a deliberate income-first philosophy rather than an attempt to track headline market performance.
How VYM Compares to Other Dividend Strategies
The VYM dividend yield often sits between broad-market ETFs and aggressive high-yield equity funds. That middle ground is precisely what makes it compelling.
Compared with dividend aristocrat strategies, VYM sacrifices some payout growth potential in exchange for higher current income. Relative to high-yield equity funds, it avoids excessive concentration and balance-sheet risk.
VYM’s competitive advantages include:
Scale-driven cost efficiency
Broad diversification reduces single-stock risk.
Transparent methodology with minimal turnover
Strong tax efficiency for a dividend-focused product
For investors seeking predictable income without complex strategy overlays, VYM remains one of the cleanest implementations available.
The Role of VYM in a Modern Portfolio
VYM fits naturally into several portfolio frameworks:
As a core income holding for retirees, prioritizing cash flow
As a stabilizing equity allocation alongside growth assets
As a dividend reinvestment vehicle for long-term wealth accumulation
As a defensive tilt during periods of valuation compression
Crucially, VYM works best when investors align expectations with its mandate. It is not a momentum trade or a yield trap. It is an income-oriented equity allocation built for patience.
Tax Treatment and Distribution Mechanics
VYM distributions are primarily qualified dividends, which often receive favorable tax treatment relative to ordinary income. This enhances after-tax yield, particularly for taxable accounts.
The fund distributes income quarterly, allowing predictable cash flow planning. For investors using dividend reinvestment plans, this cadence supports disciplined accumulation without timing decisions.
As with all ETFs, capital gains distributions are generally minimal due to the fund’s structure and low turnover.
Long-Term Outlook for the VYM Dividend Yield
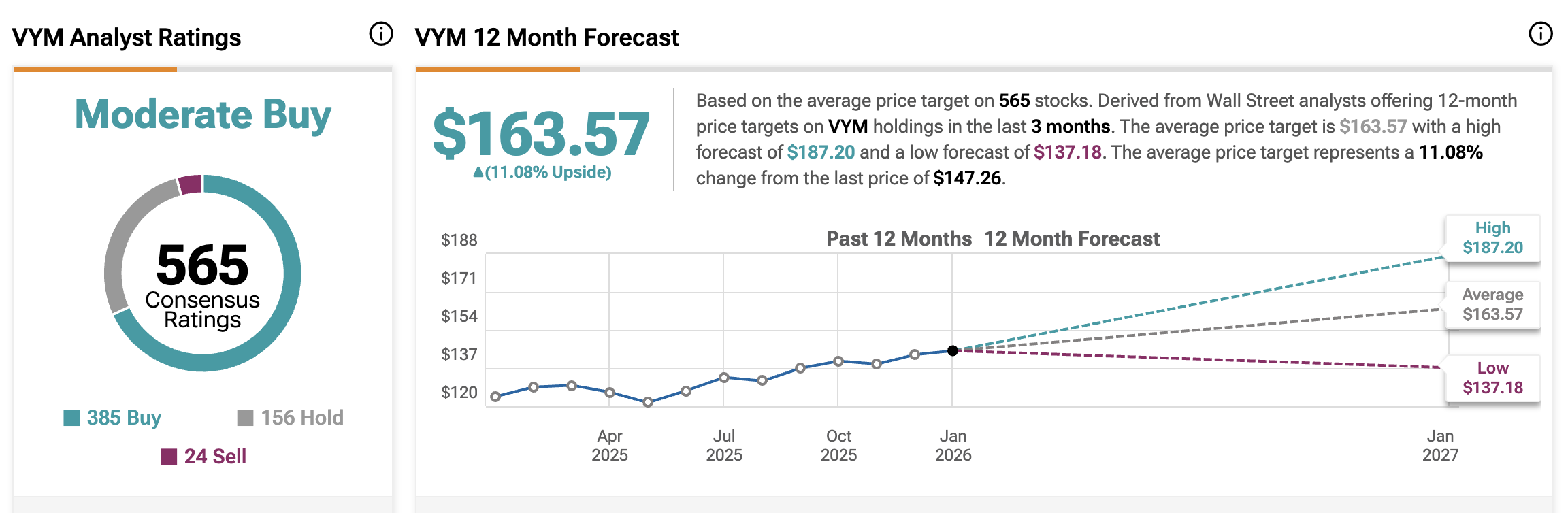
Looking ahead, the VYM dividend yield is likely to remain competitive relative to both equities and fixed income. Structural forces support this outlook:
Aging demographics are increasing the demand for income assets.
Corporate preference for dividends as a shareholder return mechanism
Ongoing emphasis on balance-sheet strength among large-cap firms
Persistent inflation risks favor real asset-linked cash flows.
While yields will fluctuate with market conditions, the underlying income engine remains intact.
Risk Management Considerations for VYM Investors
Equity market risk: VYM is an equity ETF, so its market price fluctuates with broader stock market conditions despite relatively stable dividend income.
Dividend risk: Dividends are not guaranteed and depend on corporate earnings and payout decisions. Broad diversification helps reduce reliance on any single company.
Sector concentration risk: Higher exposure to financials, healthcare, consumer staples, and energy can lead to periods of underperformance during sector-specific downturns.
Interest rate sensitivity: Rising interest rates can pressure dividend stock valuations as fixed-income alternatives become more attractive, though earnings resilience helps offset this over time.
No leverage risk: VYM does not use leverage, reducing the risk of amplified losses during market stress.
Portfolio fit: VYM is most effective when paired with growth assets and fixed income to balance volatility, income stability, and long-term return potential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is the VYM dividend guaranteed or fixed?
No. The VYM dividend is not guaranteed or fixed. Dividend payments depend on the cash distributions of the underlying dividend-paying companies held within the fund. However, VYM’s broad diversification across hundreds of large-capitalization U.S. stocks significantly reduces dependence on any single issuer. This structure helps stabilize income over time and mitigates the impact of individual dividend cuts.
2. How often does VYM pay dividends to investors?
VYM pays dividends on a quarterly basis. This regular distribution schedule provides predictable income, making the ETF well-suited for investors seeking consistent cash flow, including retirees and income-focused portfolios. Quarterly payouts also support systematic dividend reinvestment strategies.
3. Is the VYM dividend yield higher than the S&P 500?
Historically, the VYM dividend yield has exceeded that of the S&P 500. This yield premium reflects VYM’s deliberate focus on established companies with above-average dividend payouts, rather than growth-oriented firms that reinvest earnings instead of returning capital to shareholders. As a result, VYM is often favored by investors prioritizing income over maximum capital appreciation.
4. Can VYM be used as a reliable retirement income investment?
Yes. VYM is commonly used as a core equity income holding within retirement portfolios. Its combination of diversified dividend income, low expense ratio, and exposure to financially mature companies makes it a practical complement to bonds, annuities, and other income-producing assets. While not immune to market fluctuations, VYM offers a balance between income generation and long-term equity participation.
5. Does VYM increase its dividend over time?
VYM does not promise annual dividend growth, but its long-term distribution trend has generally moved upward alongside corporate earnings growth. Many companies within the fund have established dividend growth policies, which can support rising income over full market cycles. Dividend growth, when combined with reinvestment, enhances the compounding potential of the VYM dividend strategy.
Conclusion
In an investment landscape crowded with complexity, the VYM dividend strategy stands out for its clarity. The VYM dividend yield is not engineered for headlines or short-term outperformance. It is designed for investors who value income consistency, cost efficiency, and disciplined exposure to high-quality dividend-paying companies.
As markets oscillate between optimism and fear, strategies grounded in cash flow tend to endure. VYM exemplifies that principle. For investors seeking a reliable equity income foundation, the VYM dividend remains one of the most thoughtfully constructed options available, quietly compounding wealth while others chase noise.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.