The full form of ICT in trading is "Inner Circle Trader". This term originated from the online trading mentorship founded by Michael J. Huddleston, who taught thousands of traders worldwide about institutional trading methods.
In trading circles, the term ICT often sparks curiosity, especially among beginner and intermediate traders aiming to refine their market approach.
In this guide, we'll explore what ICT means in trading, its role in a trader's development, its core strategies, and how it's used in real-world scenarios.
What Is ICT Full Form in Trading?
As mentioned above, ICT stands for "Inner Circle Trader", which refers both to a trader education brand created by Michael J. Huddleston and to a unique style of market analysis that emphasises institutional trading concepts.
The ICT trading methodology relies on the idea that institutional players, like banks, hedge funds, and market makers, manipulate financial markets, and that understanding their tactics provides retail traders with a strategic advantage.
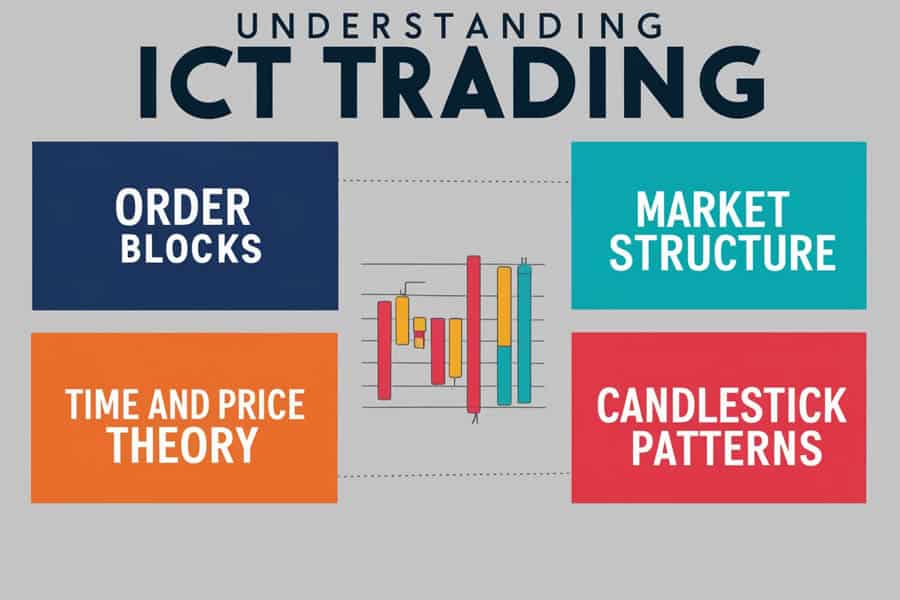
Key Components of ICT Concepts:
Understanding market structure shifts
Identifying liquidity pools
Recognising smart money concepts like displacement, order blocks, and fair value gaps
Applying time-based trading windows
The Role of ICT in Modern Trading
ICT plays a dual role as a market education framework and a practical trading approach. We can break down its role in modern trading into three main points:
1) Market Clarity:
ICT aids traders in analysing charts more effectively, identifying high-probability setups rather than relying on arbitrary indicators.
2) Risk Management Discipline:
Strategies include tight stop-losses and specific entry zones, which help control risk effectively.
3) Confidence Building:
By learning how institutions operate, traders feel more confident in following price action instead of getting shaken out by false moves.
ICT in Different Trading Markets
Forex
ICT strategies are extremely popular in the Forex market due to its deep liquidity and strong institutional participation. Typical Forex applications include:
Identifying liquidity sweeps before major economic news
Trading order blocks during the London/New York overlap
Using fair value gaps for retracement entries
Stock and Index
Stock and index traders also benefit from ICT principles, particularly when dealing with major indices such as the S&P 500 or DAX.
Patterns such as order blocks and liquidity grabs frequently appear around market openings and closings.
Crypto
The volatile nature of cryptocurrencies makes ICT particularly valuable, as liquidity grabs and fair value gaps appear frequently due to lower liquidity compared to Forex and stocks.
Core ICT Trading Strategies
While ICT covers a wide range of concepts, some strategies stand out for their effectiveness and clarity.
1. Market Structure Shifts (MSS)
ICT emphasises reading price action in terms of higher highs, higher lows, lower highs, and lower lows. A market structure shift signals a potential reversal or continuation, providing a clear roadmap for entries and exits.
2. Order Blocks
An order block is the last bullish or bearish candle before a strong market move. These zones represent institutional buying or selling and act as high-probability entry points.
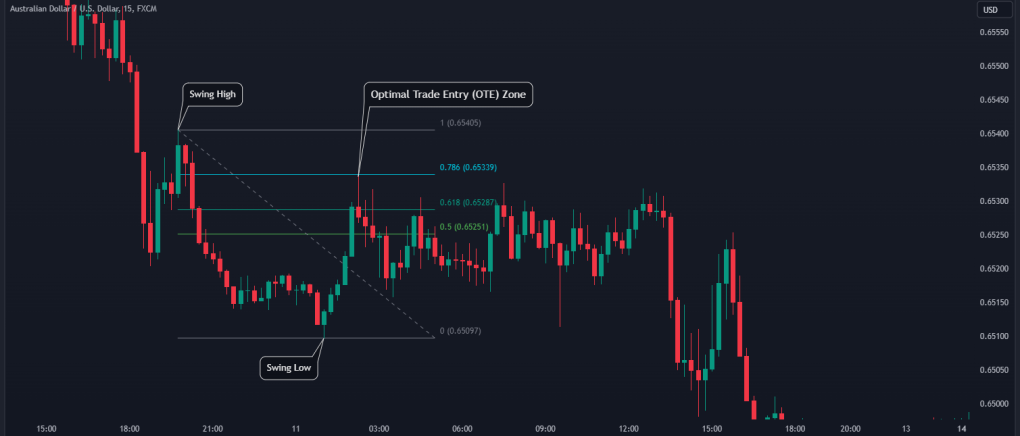
3. Fair Value Gaps (FVG)
Fair value gaps occur when there's an imbalance in the market, leaving an area of inefficiency between candles. Price often returns to these zones before continuing in its original direction.
4. Liquidity Grabs
Institutions frequently manipulate prices beyond crucial levels to trigger stop losses before reversing. Traders who recognise this pattern can avoid being caught in these traps.
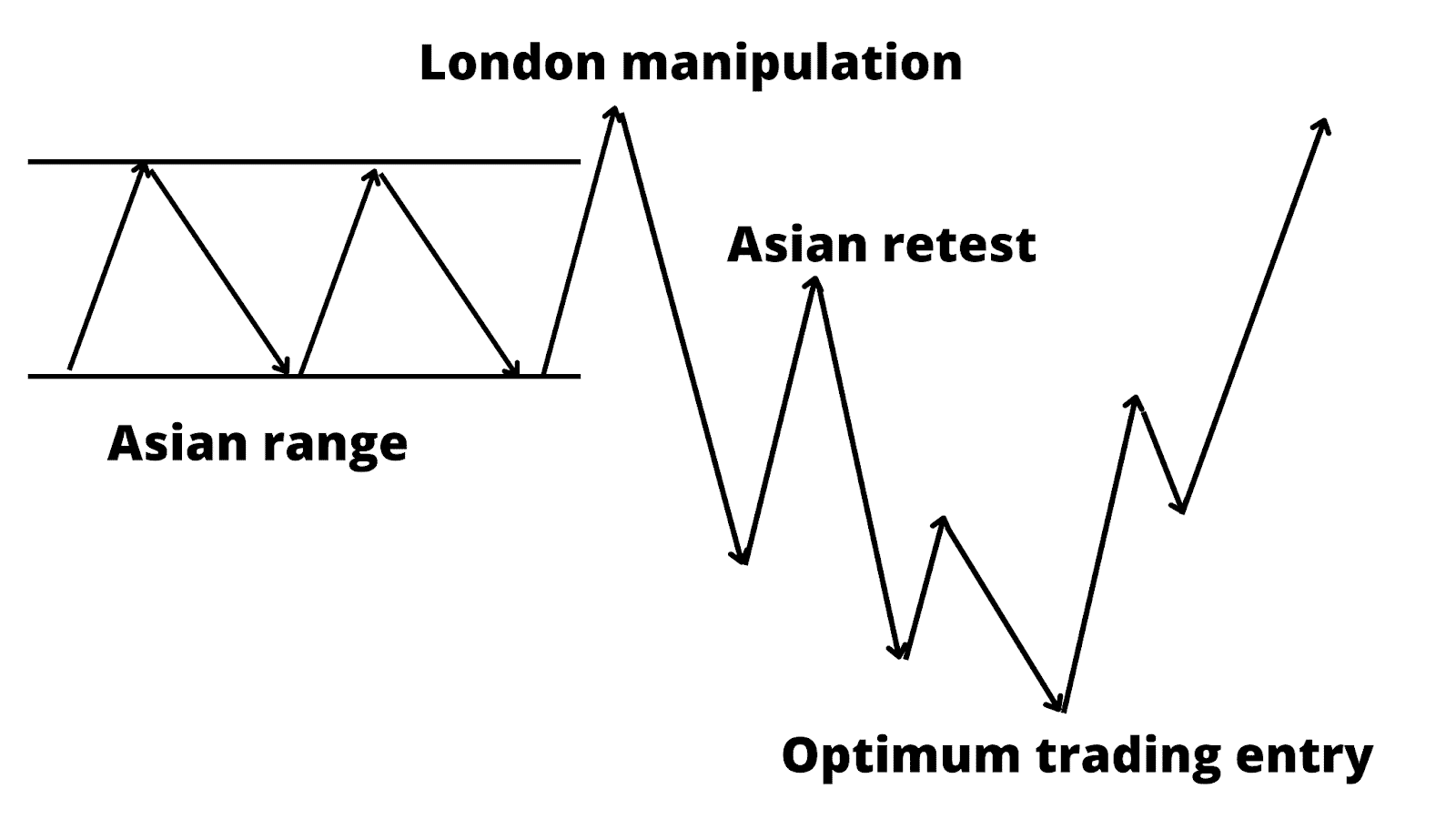
5. Time of Day Trading
ICT strategies often focus on specific market segments, such as:
London Open: High volatility and trend formation
New York Open: Continuation or reversal moves
Asian Session: Consolidation and setup formation
Advantages and Risks of Using ICT Strategies
| Advantages |
Risks |
| Clear, rule-based entries and exits |
Steep learning curve for beginners |
| Focus on institutional concepts |
Can lead to over-analysis |
| High reward-to-risk potential |
Requires strong discipline |
| Works in multiple asset classes |
Market conditions may reduce accuracy |
| Encourages risk management |
Not a guaranteed profit method |
Common Mistakes When Using ICT Strategies
Even with a solid strategy, traders can still make mistakes:
1) Overcomplication:
Trying to apply every ICT concept to every chart leads to confusion.
2) Ignoring Market Context:
A legitimate setup can collapse if executed during times of low liquidity.
3) Risking Too Much Per Trade:
ICT promotes strict risk control; violating this principle often leads to drawdown.
4) Lack of Patience:
ICT setups often require waiting for the market to reach key zones, a challenge for some traders.
Tips for Mastering ICT Trading
Focus on one or two core setups before expanding your knowledge.
Always use a trading journal to track performance.
Pair ICT concepts with economic calendar awareness to avoid high-impact news whipsaws.
Use higher timeframes for bias and lower timeframes for entry precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is ICT Trading Suitable for Beginners?
Yes, beginners can use ICT trading, but it comes with a steep learning curve. Beginning with market structure, a couple of setups, and risk management is advisable before delving into advanced concepts.
2. How Do I Start Learning ICT Trading Strategies?
Begin by studying market structure shifts, identifying liquidity zones, and mastering setups such as order blocks. Use demo trading to practice before moving to a live account.
3. What Is the Main Advantage of ICT Trading Methods?
The primary benefit of ICT methods is accuracy, as they help traders identify high-probability setups with tight risk control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the full form of ICT signifies more than merely a title. It's a complete methodology that focuses on trading alongside institutional market flow rather than against it.
By mastering ICT strategies such as market structure shifts, order blocks, liquidity grabs, and fair value gaps, traders can improve their accuracy, risk management, and market confidence.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.