The Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) has long held the title of the world's most valuable currency, consistently trading over USD 3.26 per dinar.
Although many believe this is solely due to Kuwait's oil riches, the truth is more complex, grounded in years of careful economic oversight, a consistent currency framework, and well-planned fiscal strategies.
In this updated edition, we'll explain why the Kuwaiti Dinar remains so strong, what risks could test it, and whether its strength will last in the years ahead.
The Kuwaiti Dinar Today: Still the World's Highest-Valued Currency
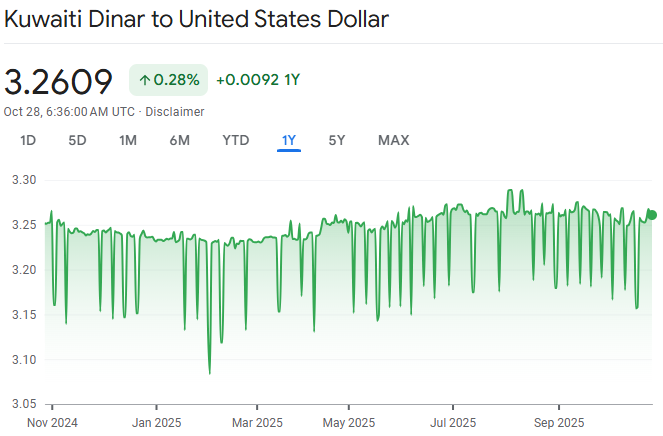
As of October 2025, the Kuwaiti Dinar trades at around:
Despite global inflation and shifting oil prices, KWD continues to outperform nearly all other currencies. Unlike dollar-pegged Gulf currencies, Kuwait maintains a managed peg to a basket of major currencies, giving it both stability and flexibility.
Comparison with Other Strong Currencies
Although many international currencies vary with interest rate changes or inflation trends, the Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) has stayed impressively stable and consistently retains the highest currency value.
| Currency |
USD Value (Oct 2025) |
Peg Regime |
Main Strengths |
| Kuwaiti Dinar (KWD) |
3.26–3.27 |
Pegged to currency basket |
Oil wealth, large fiscal reserves, diversified peg |
| Bahraini Dinar (BHD) |
2.65 |
USD peg |
Oil-backed economy, macro stability, small population |
| Omani Rial (OMR) |
2.60 |
USD peg |
Oil & gas support, prudent budget control |
| British Pound (GBP) |
~1.34 |
Float |
Financial hub, economic diversity |
| Swiss Franc (CHF) |
~1.24 |
Float |
Safe-haven status, strong banking sector |
| US Dollar (USD) |
1.00 (base) |
Float |
Global reserve currency, unmatched liquidity |
Listed above are the currencies lagging behind the dinar.
Why Is the Kuwaiti Dinar So Strong?

1. Oil Wealth: The Core Driver Behind KWD's Strength
Kuwait holds approximately 6-7% of the world's proven oil reserves and produces around 2.7 million barrels per day. Oil exports account for over 92% of government revenue, providing a steady inflow of foreign currency reserves. [1]
When oil prices remain high, as they have for much of 2025, Kuwait's trade surplus supports demand for KWD and boosts its external balance.
However, while oil wealth is crucial, Kuwait's currency strength is also built on how it manages this wealth, not just the revenue itself.
2. The Managed Peg System: A Cushion Against Volatility
Since 2007, Kuwait has pegged its currency to a basket of major currencies rather than the US dollar alone.
This basket includes the USD, euro, yen, and others, weighted according to trade patterns.
Why this matters:
When the US dollar fluctuates sharply, the dinar stays more stable.
The Central Bank of Kuwait (CBK) can adjust its policy to maintain competitiveness in exports and imports.
It provides greater resilience against global inflation and exchange-rate shocks.
The CBK's strong reserves, estimated at above USD 45 billion, allow it to defend this peg confidently.
3. Fiscal Discipline and Sovereign Wealth Power
Kuwait's General Reserve Fund (GRF) and the Future Generations Fund (FGF), overseen by the Kuwait Investment Authority (KIA), remain vital foundations of dinar stability.
Combined, these funds are believed to exceed $1 trillion, making KIA one of the largest sovereign wealth funds globally.
These funds ensure:
Liquidity during downturns (when oil prices dip or spending rises).
Confidence in the dinar's stability for global investors.
A long-term safety net for post-oil diversification.
Even though fiscal deficits have re-emerged in recent years, Kuwait's financial buffers remain robust enough to prevent currency stress.
4. Balanced Monetary Policy and Controlled Inflation
Inflation in Kuwait has stayed moderate, averaging 2.3–2.4% in 2025, thanks to effective monetary policy and government subsidies that stabilise prices for essentials.
The Central Bank adjusts interest rates in accordance with the US Federal Reserve while preserving some independence through its peg.
This disciplined monetary approach reassures both citizens and investors that KWD's purchasing power remains steady.
5. Political and Economic Stability
Kuwait remains one of the most politically stable nations in the Middle East, underpinned by a constitutional monarchy, a long-standing parliamentary system, and a strong rule of law.
While regional tensions continue to affect nearby economies, Kuwait has largely maintained internal peace and balanced diplomacy, particularly in navigating disputes among Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) members.
This stability continues to attract global investors, reinforcing confidence in the Kuwaiti Dinar and the broader financial system.
According to the World Bank's 2025 governance indicators, Kuwait ranks among the top GCC countries in political stability and government effectiveness.
6. Attractive Investment and Business Environment
Kuwait maintains a tax-free environment for individuals, featuring no personal income tax, along with one of the lowest corporate tax rates in the GCC, primarily applicable to foreign enterprises.
This remains a key attraction for expatriates, investors, and multinational firms establishing operations in the region.
In recent years, there has been a surge in foreign direct investment (FDI), particularly after the introduction of the New Kuwait 2035 Vision, which aims to diversify the economy away from oil by enhancing infrastructure, logistics, and technological initiatives.
Projects such as:
Silk City (Madinat Al-Hareer)
Kuwait Metro and port modernisation
Digital government transformation efforts
They are strengthening Kuwait's position as a financial and commercial hub in the northern Gulf. Together, these policies and projects enhance investor confidence and underpin the Kuwaiti Dinar's long-term resilience.
Fiscal Challenges Emerging Beneath the Surface
However, beneath the surface of this currency success story, Kuwait faces fiscal challenges that could test its long-term strength.
Latest Fiscal Updates (2025)
S&P Global expects Kuwait's fiscal deficit to average 8.9% of GDP between 2025 and 2028, primarily due to rising public sector spending and heavy reliance on oil income.
Still, with large sovereign reserves and no significant external debt, the short-term risk to KWD's stability remains low.
Will the Kuwaiti Dinar Stay Strong in 2026 and Beyond?

Looking ahead, analysts expect the Kuwaiti Dinar to retain its leading position in the global foreign exchange market through 2026 and beyond.
While oil revenues remain the backbone of Kuwait's wealth, the country has accelerated diversification under its Vision 2035 strategic plan, focusing on logistics, finance, tourism, and clean energy.
Recent policy shifts underscore this transition:
The Public Debt Law, passed in early 2025, set a borrowing limit of KD 30 billion (~$97 billion), Kuwait's first sovereign debt authorisation in nearly a decade.
The new funds will support key infrastructure projects, including the Mubarak Al-Kabeer Port, Kuwait International Airport Terminal 2, and the Silk City megaproject.
These initiatives aim to create alternative income sources while preserving fiscal discipline and long-term currency stability.
According to Fitch Ratings (2025), Kuwait maintains an "AA-" credit rating with a stable outlook, supported by strong sovereign assets and prudent fiscal management. [3]
Should diversification initiatives and fiscal reforms progress effectively, the Kuwaiti Dinar is set to remain not only the globe's most valuable currency but also one of its most stable.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Currencies Be "Too Strong" for Their Economy?
While a strong currency is a point of pride and economic strength, it can make exports less competitive.
2. Will the KWD's Value Fall if Oil Prices Drop?
Oil downturns do pressure the economy, but Kuwait's enormous financial buffers and the KIA's investments cushion and stabilise the dinar, as seen in previous oil price cycles.
3. Is the Dinar's Value Just Policy, or Does It Reflect Real Economic Fundamentals?
Both. Policy sets the nominal strength, but oil wealth, reserves, and prudent governance give that value real-world backing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Kuwaiti dinar's strength is neither an accident nor merely a matter of policy arrogance. Instead, it's the result of decades of prudent governance, enormous oil wealth, fiscal discipline, and a uniquely managed exchange rate regime.
In 2025, as the world watches currencies swing with inflation and monetary policies, the KWD stands nearly alone in its stability and strength.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.
Sources
[1] https://en.majalla.com/node/327473/business-economy/kuwaits-budget-deficit-shrinks-without-public-spending-cuts
[2] https://www.arabnews.com/node/2613093/business-economy
[3] https://www.fitchratings.com/research/sovereigns/fitch-affirms-kuwait-at-aa-outlook-stable-05-09-2025