In this era of international trade, buyers and sellers are faced with transaction challenges that span thousands of miles. Sellers are worried that buyers will not pay after the goods are sent, while buyers are worried that sellers will not deliver the goods after payment is made. In the midst of this uncertainty, the emergence of the letter of credit brings a sense of security and a foundation of trust to both parties. It serves as a guarantee from the bank to ensure that the transaction is carried out safely, so that both buyers and sellers can rest assured that the money is paid with one hand and the goods are delivered with the other, realizing true equality of transactions and safety and security. Now we will take a closer look at the international trade payment security, letter of credit classification, and operation process.
What is a Letter of Credit?
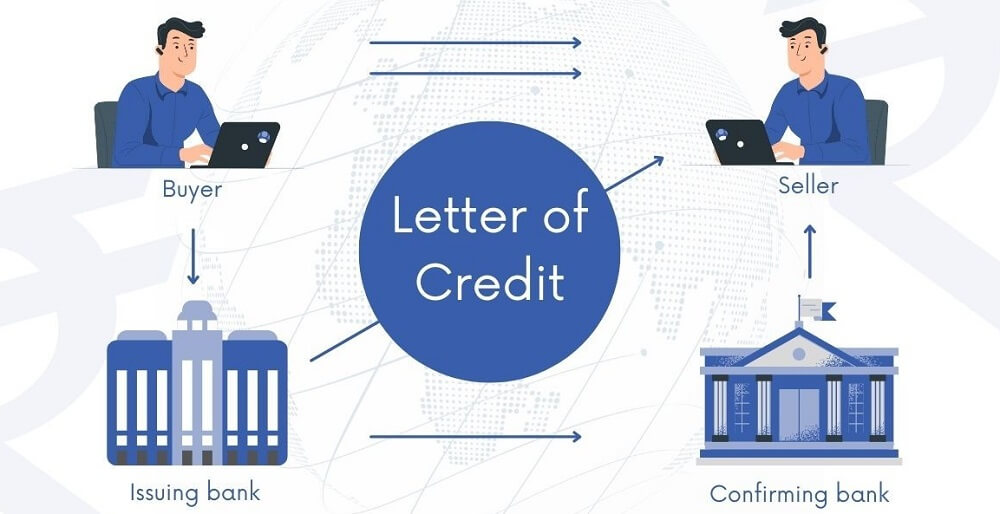
L/C, for short, the full name of the Letter of Credit, is a financial instrument issued by the bank or other financial institutions according to the buyer's application, used in international trade or domestic trade, to ensure the security of payment and delivery between the buyer and seller. It provides a guarantee of payment for the seller; that is, after the seller submits the documents in line with the terms of the letter of credit, the bank will pay on behalf of the buyer to the seller.
A written document issued by the bank that promises to pay according to certain conditions is one of the most important payment methods in international trade. Its principle is similar to secured transactions, that is, the bank as the issuing bank, after the agreement between the buyer and seller, to the seller's commitment to pay the money in accordance with the terms.
First of all, the buyer will provide the content of the transaction and requirements in the form of an application submitted to the bank. The bank will accept the application to open a letter of credit, which will be delivered to the seller's location at the bank. The seller ships the goods according to them and hands over the documents representing the goods to the local bank. The bank verifies that there is no error and pays the seller for the goods. And the buyer can take delivery of the goods on the basis of the documents after the bank has redeemed them.
As a financial instrument independent of the trade contract, it provides an independent guarantee of payment for both the buyer and the seller. Unlike a trade contract, it is issued by the buyer's bank (the issuing bank) and guarantees to the seller that payment will be made subject to the terms. As such, it is executed independently of the trade contract and can be relied upon by the buyer and seller to carry out the transaction.
It is important to note that it is based on the documents and not the goods themselves. Banks make payments in accordance with the requirements of the prescribed documents and not by directly inspecting or handling the actual goods. This means that the bank is concerned with the accuracy and conformity of the documents to ensure that the transaction between the buyer and the seller under the terms of the contract is successfully completed as agreed. The actual condition and quality of the goods are agreed upon and are the responsibility of the buyer and seller in the underlying transaction contract, and they are not directly related to the bank's role therein.
When the seller submits compliant documents, the bank must make payment in accordance with the terms, which is a core principle in a letter of credit transaction. The terms specify in detail the type of documents the seller must provide, quantity, quality standards, shipment location, payment terms, and other specific requirements.
When dealing with it, the bank's main concern is the completeness and conformity of the documents rather than the actual delivery or quality of the goods. This arrangement helps to protect the rights and interests of both the seller and the buyer and ensures that the transaction is carried out in accordance with the contractual agreement, while at the same time minimizing disputes arising from non-conformity of the quality or quantity of the goods. As a result, the seller only needs to ensure that the documents meet its requirements in order to obtain payment from the bank, which makes it one of the most widely used secure payment instruments in international trade.
In practical application, the importer (buyer) can ensure that the supplier will receive payment only after delivery and submission of qualified documents by opening a letter of credit, which reduces the risk of early payment. The exporter (seller) can be sure of the security of the payment after receiving it and ensure that it can receive payment from the bank after submitting qualified documents. At the same time, the bank, as an intermediary, is able to earn commission income through this settlement business and, at the same time, promote trade activities between customers.
It greatly facilitates both buyers and sellers. With the bank's guarantee, both parties no longer have to worry about credit problems, even with distant and unfamiliar customers. Buyers can buy with confidence because it guarantees that they will only pay if they meet the conditions of the contract. For the seller, it is not just a guarantee of payment but an important tool to ensure that payment can be recovered in a timely manner, as valuable as an actual cash transaction.
A reliable letter of credit can even be used as collateral for a bank loan, which facilitates the liquidity of the seller. Its existence makes trade more reliable and efficient, especially when it comes to large transactions or cross-border trade. Its role is particularly significant. It not only simplifies the transaction process between buyers and sellers but also greatly reduces the risk of the transaction, allowing global trade to proceed more smoothly.
However, although it plays an important role in international trade, it also comes with certain risks. Banks are only responsible for checking the compliance of documents when advancing payment for goods without involving the actual verification of specific goods. This opens up the possibility for the seller to make a mistake by falsifying documents, failing to ship goods, or shipping counterfeit goods, all of which can lead to significant financial losses for the buyer.
Similarly, if the buyer maliciously tampers with or falsifies the terms, for example, by intentionally altering the amount or the period of validity, this may also result in the seller ultimately failing to receive payment for the goods and thus suffering a loss of both the money and the goods. These situations emphasize the importance of prudent practices and strict adherence to contractual terms by both parties when using letters of credit in international trade. Effective contract management and the use of rules to follow for the reduction and management of potential risks are essential to ensuring the safety and reliability of trade transactions.
In conclusion, the letter of credit plays an indispensable role in international trade as a payment guarantee instrument provided by banks. It effectively reduces the payment risk in cross-border transactions by replacing commercial credit and ensuring the rights and safety of buyers and sellers in the transactions. It is not only a kind of payment guarantee but also an important trade financing tool that ensures the smooth progress of the transaction and the safe flow of funds through the intervention and guarantee of the bank.
Operation Process of a Letter of Credit
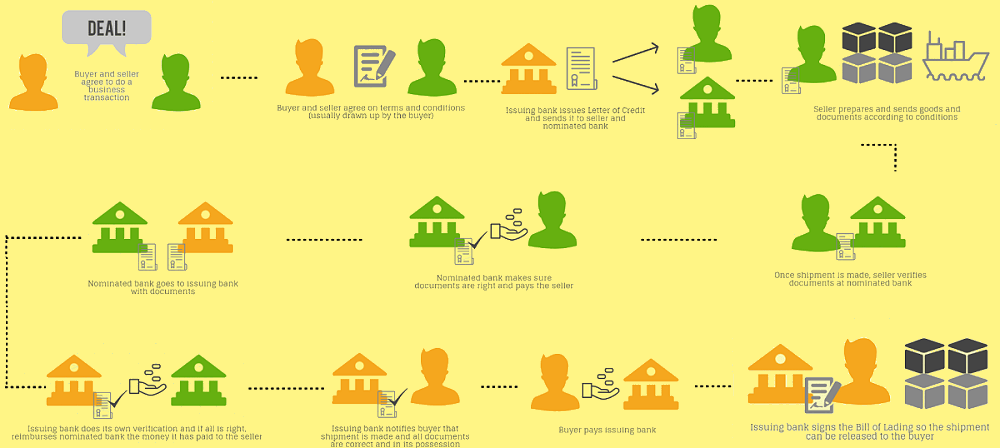
Its complete operation process should include key steps such as application, issuance, delivery of documents, submission of documents, examination of documents, and payment. The buyer first submits an application to the issuing bank, setting out the transaction conditions and requirements in detail. The issuing bank opens a letter of credit based on the application and notifies the seller and the notifying bank.
The seller then completes the delivery of goods according to the requirements, prepares the relevant documents, submits them to the notifying bank for review, and forwards them to the issuing bank. The issuing bank examines the completeness and conformity of the documents and pays the seller if they meet the requirements; otherwise, the seller is required to modify or supplement the documents. This process ensures the rights and interests of both parties in international trade and payment security.
Specifically, when the buyer, after reaching a trade agreement with the seller, can make a request to its bank (the issuing bank), Submit detailed transaction conditions and requirements, such as a description of the goods, quantity, price, shipment period, and other relevant information, and provide the necessary security documents. Upon receiving the application, the issuing bank will review and evaluate it to ensure that the application complies with international trade norms and requirements. Once the issuing bank confirms that the application is correct, it will open a letter of credit and notify the seller's bank (the notifying bank), thus initiating the execution of the transaction and the payment process for the goods.
Once the seller receives the L/C issued by the buyer's bank (the issuing bank), it needs to deliver the goods as required. Typically, it will detail specific requirements such as the description of the goods, quantity, quality standards, place, and time of shipment. The seller must ensure that the goods are shipped and delivered in accordance with these requirements.
At the same time, the seller also needs to prepare the relevant documents in accordance with the terms, such as bills of lading (maritime transportation documents), invoices, insurance documents, packing lists, and so on. These documents must be in full conformity with the requirements, and any non-conformity may lead to delay or refusal of payment. Therefore, the seller must take great care in the preparation of these documents to ensure that every detail is in order in order to secure payment.
The completeness and accuracy of the documents in this process are crucial to the successful completion of the transaction; they are not only the basis for the buyer to pay for the goods but also the basis for the bank to make a payment judgment. Therefore, the seller should fully understand the requirements of the letter of credit when delivering the goods and preparing the documents, and ensure that the delivery of the goods and the preparation of the documents are completed within the specified shipment period.
Once the seller has prepared the relevant documents (such as bills of lading, invoices, insurance policies, etc.) in accordance with the requirements of the letter of credit, the next step is to submit these documents to the designated notifying bank. The notifying bank will audit these documents to confirm their consistency and completeness with the terms and conditions.
After passing the audit, the notifying bank will send the documents to the issuing bank. Upon receipt of the documents, the issuing bank will double-check whether the documents comply with the requirements of the letter of credit. If everything meets the requirements, the issuing bank will promise to pay the seller on time according to the terms. This means that the preparation and submission of the documents are of utmost importance to the seller, because only documents that meet the requirements can ensure smooth payment.
In submitting documents, the seller usually needs to ensure that they are accurate and complete, avoiding any errors or inconsistencies that could lead to a denial of payment. This includes confirming that the description and quantity of the goods are accurate, that the invoice amount is consistent with the contract, and that the shipping information on the bill of lading is in order. By strictly following the terms and submitting compliant documents in a timely manner, the seller can effectively manage and control the risks of the transaction and ensure its successful completion.
Once the seller has prepared the corresponding documents (e.g., bill of lading, invoice, insurance policy, etc.) according to the requirements, these documents will be strictly audited by the issuing bank. The issuing bank's review process includes a detailed examination of the contents of the documents to ensure that they are in full compliance with all terms and conditions set forth in the voucher. The issuing bank will check the accuracy of the description of the goods, the consistency of the quantities, the conformity of the unit price, the reasonableness of the shipment period, and the completeness of all other required documentation.
In addition, the issuing bank will also ensure that the format of the documents conforms to the requirements of international trade practices and applicable laws, so as to avoid any errors that may lead to payment delays or refusal of payment. Only when the issuing bank confirms that all documents are in order and in full compliance with the terms and conditions will it continue with the payment process to ensure that payment is made to the seller on time.
Payment is the last step in the letter of credit transaction; the key to the issuing bank is for the seller to submit documents for review. Once the issuing bank confirms that the documents comply with all the requirements and terms of the rewritten letter, including but not limited to the accuracy of the description of the goods, the consistency of the quantity, and the unit price in line with the reasonableness of the shipment period, the issuing bank will pay the seller the payment for the goods as required.
This means that the issuing bank assumes responsibility for payment, and even if the buyer fails to fulfill its payment obligations, the seller can still rely on it to claim payment from the issuing bank. If there are discrepancies in the documents, the issuing bank will return the documents and require the seller to make corrections or additions to ensure that the documents ultimately meet all requirements. This rigorous review process ensures the security and reliability of the transaction while protecting the rights and interests of both buyer and seller and avoiding possible payment disputes and delays.
Types of Letters Of Credit
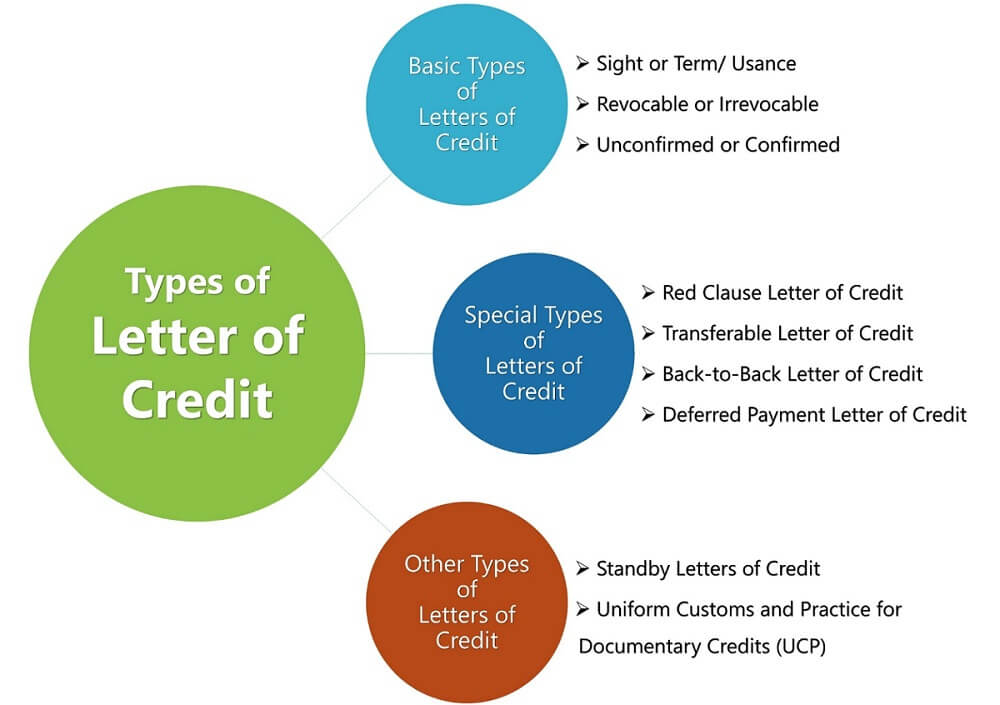
It can be divided into several types based on different conditions and purposes. For example, based on payment terms, there are spot and forward transactions. According to revocation conditions, there are two main types: revocable and irrevocable. Depending on whether there is a guarantee from other banks, it can be classified as confirmed or unconfirmed. Based on usage, there are two types: commercial and standby. Finally, according to payment methods, there are payment, acceptance, and negotiation.
A sight L/C requires the issuing bank to pay the seller for the goods immediately upon receipt of documents in accordance with the terms and conditions. It ensures that the seller is able to obtain payment for the goods quickly and effectively reduces payment risks and delays in the transaction. For the buyer, its use ensures timely access to the purchased goods while enhancing the reliability and efficiency of the transaction. It is widely used in international trade because of its real-time nature and payment guarantee role, and it is especially suitable for scenarios where transactions and payments need to be completed quickly.
Forward L/C, on the other hand, requires the bank to make payment in accordance with the agreed period of time, such as 30 days, 60 days, 90 days, etc., upon receipt of documents in compliance with the terms and conditions. It allows the buyer to have a longer period of time to pay for the goods, thus providing flexibility in arranging funds, and is suitable for international trade transactions with long lead times.
Irrevocable L/C refers to the fact that it cannot be changed or canceled without the consent of all relevant parties (including the issuing bank, the beneficiary, and the applicant) and therefore provides a high degree of security and stability and is widely used in international trade. A revocable letter of credit (revocable L/C) can be changed or canceled by the issuing bank or the applicant without the consent of the beneficiary due to the higher risk of the actual application.
A confirmed letter of credit (confirmed L/C) is issued in addition to the issuing bank; another bank (confirming bank) also bears the responsibility of payment. It provides a double guarantee for the seller and enhanced security. It is usually used when the seller does not fully trust the credit status of the issuing bank or the buyer's national credit status is poor to ensure the smooth completion of the transaction. Unconfirmed L/C is only the issuing bank's responsibility to pay; no other bank is required to provide additional guarantees. It carries a higher risk because the seller can only rely on the credit of the issuing bank to ensure payment.
The commercial letter of credit (Commercial L/C) is used in general transactions for the purchase and sale of goods and is the most common form in international trade. It serves as a payment tool for both buyers and sellers to ensure that the seller can obtain payment in a timely manner after the provision of documents in line with the requirements, thus promoting the security and smooth progress of the transaction.
Standby L/C is used as a kind of guarantee tool, which is mainly used to ensure that the applicant fulfills the contractual obligations. Usually, when the applicant fails to fulfill the terms of the contract, defaults, or other problems arise, the beneficiary can obtain payment on demand. It is usually used in international trade involving services, construction projects, bid bonds, and other needs to ensure the performance of the occasion. Under normal circumstances, it is not used to pay for the goods but as a means to ensure payment and the performance of the contract.
A payment letter of credit (Payment L/C) requires the beneficiary to submit documents in line with the terms and conditions of the issuing bank to pay immediately. It ensures that the seller, in the delivery of documents in line with the requirements of the goods, can be quickly paid; it is usually used in the immediate payment of trade transactions.
The acceptance letter of credit (Acceptance L/C) is issued by the issuing bank to the beneficiary to submit documents in line with the terms of acceptance of the beneficiary to open a forward bill of exchange and in the bill of exchange on the maturity date of payment. It allows the buyer to pay for the goods on an agreed-upon date in the future and is usually used in transactions that require deferred payment.
A negotiation L/C is a negotiating bank (usually a bank or trade finance institution of the beneficiary's own choosing) that purchases documents submitted by the beneficiary in accordance with the terms and conditions of the negotiation and pays the beneficiary in advance for the goods. The negotiating bank then seeks payment from the issuing bank. It provides the beneficiary with flexible payment options and is particularly suited to situations where quick access to funds is required.
In addition to this, there are revolving, back-to-back, and advance types of letters of credit, depending on the payment method. They provide a variety of options according to the specific needs and payment arrangements in a trade transaction, providing greater flexibility and security for both buyers and sellers in international trade.
Characteristics of letters of credit
| Features |
Description |
Remarks |
| Payment security |
Bank guarantee for seller payment. |
Enhance transaction security. |
| Independence |
Concerns only documentary compliance. |
Avoid contract disputes. |
| Conditional |
Payment depends on document compliance. |
Requires a strict document audit. |
| Irrevocability |
Most are irrevocable and unchangeable. |
Provide high security. |
| Bank Guarantees |
Issued and guaranteed by the bank. |
Provide additional credit. |
| Financing tools |
Can be used for trade finance. |
Improve the seller's cash flow. |
| Instrumentality |
Based on documents rather than goods. |
Reduce cargo disputes. |
| Risk Management |
Controls payment risk in cross-border deals. |
Needs cooperation and contracts. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.