In the fast-paced world of financial markets, clarity and precision are essential. With thousands of companies listed on exchanges around the globe, traders and investors need a quick and reliable way to identify each one. That's where stock symbols come in.
A stock symbol — sometimes called a ticker symbol — is a short series of letters or numbers that uniquely represents a publicly traded company's shares. It acts like a shorthand label, making it easier to track prices, place trades, and follow financial news. Whether you're glancing at a trading screen or reading a business report, stock symbols help cut through complexity and point directly to the company in question.
Understanding how these symbols work, why they matter, and how they're assigned gives investors a clearer view of the markets — and helps avoid costly mistakes.
Definition of a Stock Symbol (Ticker Symbol)

A stock symbol, often referred to as a ticker symbol, is a unique series of letters assigned to a publicly traded company's shares. It serves as an abbreviated name for the company on a stock exchange, acting as a quick reference for traders and investors when buying or selling shares.
For instance, Apple Inc. trades under the stock symbol AAPL, while Microsoft Corporation is represented as MSFT. These identifiers simplify the process of tracking and trading shares, eliminating the need to type out or search for the full company name, which may vary or be used by multiple entities across markets.
While the term "ticker symbol" is commonly used in the United States, it is also widely understood internationally, even in markets that prefer "stock code" or "stock number."
Purpose and Importance
The primary purpose of a stock symbol is identification. On trading platforms and financial systems where thousands of companies are listed, having a standardised and unique code allows for:
Speed and efficiency in trading execution.
Avoidance of confusion between companies with similar or identical names.
Streamlined communication between brokers, analysts, and investors.
Efficient indexing, enabling the creation of automated systems and financial tools such as ETFs and stock screeners.
Stock symbols also improve data entry accuracy and help in the automation of real-time trading systems, making them a vital part of the market's infrastructure.
Exchange Formats and Character Rules
The structure and length of stock symbols can vary depending on the stock exchange. These character limits and formatting conventions are often determined by the country and the governing body of the exchange.
Here are a few common formats:
New York Stock Exchange (NYSE): Typically uses up to three letters (e.g., IBM, T for AT&T).
NASDAQ: Often uses four or five letters (e.g., GOOG, AMZN, AAPL).
London Stock Exchange (LSE): Uses a ticker and a market identifier (e.g., VOD.L for Vodafone Group).
Hong Kong Stock Exchange (HKEX): Uses numeric stock codes (e.g., 0700.HK for Tencent Holdings).
Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE): Also uses numeric codes (e.g., 7203.T for Toyota).
The variation in format highlights the importance of understanding where the stock is traded, as this affects how you identify it across platforms.
How Symbols Are Assigned
Stock symbols are not assigned randomly; there is a formal process, and companies often have some influence over their selection — especially for those going public for the first time.
When a company plans to list its shares on a stock exchange, it typically submits a request for a preferred ticker symbol. If that symbol is already in use or reserved, the exchange may suggest an alternative. In many cases, companies select symbols that closely resemble their brand or name to strengthen investor recognition. For example:
Stock exchanges maintain a centralised database to ensure no duplication of active symbols, although delisted or dormant symbols may be reused after a cooling-off period.
Extensions and Class Identifiers
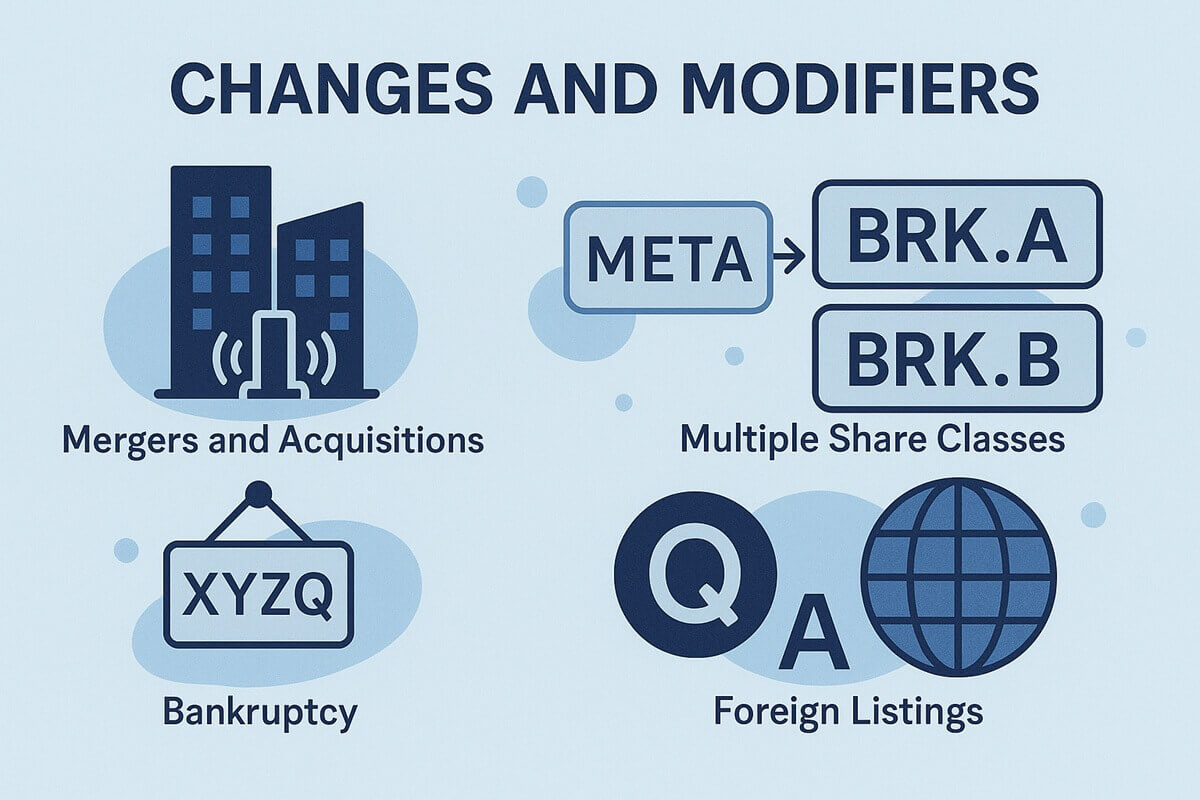
Sometimes a stock symbol may include additional characters or suffixes to indicate a particular class of share or a special condition related to the company. These extensions are important for accurate trading and analysis.
Common suffixes and identifiers include:
Berkshire Hathaway trades under BRK.A (Class A) and BRK.B (Class B).
"L" – Indicates the London Stock Exchange (e.g., BP.L).
"Q" – In the US, this indicates the company is in bankruptcy proceedings.
"Y" – Denotes American Depository Receipts (ADRs) for foreign companies trading on US exchanges.
"K" or "F" – May denote foreign listings or share types under some exchanges.
These identifiers are essential for ensuring that investors are trading the correct instruments — particularly when companies offer multiple classes of stock or operate across borders.
Examples in Practice
To bring all of this theory into practical context, here are a few well-known examples and what they represent:
AAPL – Apple Inc., listed on NASDAQ. Common shares.
GOOG vs. GOOGL – Both represent Alphabet Inc. (Google's parent), with GOOGL offering voting rights and GOOG not.
HSBA.L – HSBC Holdings, listed on the London Stock Exchange.
TSLA – Tesla Inc., listed on NASDAQ.
0700.HK – Tencent Holdings, listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
Each of these ticker symbols uniquely identifies a company's shares and links directly to their market activity, financial data, and performance charts on trading platforms.
Conclusion
A stock symbol is far more than just a few letters or numbers. It is a crucial element of the modern financial system, ensuring transparency, accuracy, and efficiency in global trading. From simplifying transactions to identifying companies across borders and exchanges, stock symbols empower investors and professionals alike to operate within a clearly defined framework.
As markets become increasingly interconnected and digital, the role of stock symbols remains foundational — allowing the seamless buying, selling, tracking, and analysis of securities with just a glance.
Whether you are buying your first share or managing a diversified portfolio, having a solid understanding of stock symbols gives you a clearer lens through which to interpret the financial world.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



























