Emerging markets have long been seen as an area of growth potential for investors seeking higher returns and greater diversification. The EEM ETF, formally known as the iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF, offers exposure to a broad basket of equities from developing countries. This includes companies based in China, India, Brazil, Taiwan and other major emerging economies.
With global shifts in economic power and rising consumer bases in these regions, the EEM ETF presents an attractive option for those looking beyond developed markets. However, it also comes with its own set of risks and volatility.
This article explores the structure, benefits and considerations of the EEM ETF to help determine whether it is a suitable addition to your investment portfolio.
What Is the EEM ETF?
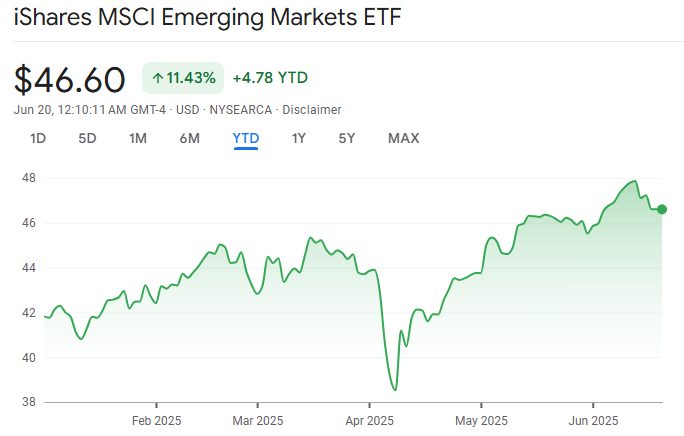
The EEM ETF tracks the MSCI Emerging Markets Index, which consists of large- and mid-cap companies from over 20 emerging market nations. It was launched by iShares, a subsidiary of BlackRock, and is one of the most widely traded emerging market ETFs globally.
The EEM ETF offers a convenient and liquid way for investors to gain diversified exposure to these markets without having to invest in individual foreign stocks or navigate unfamiliar exchanges.
It includes sectors ranging from financials and technology to energy and consumer goods, providing a cross-section of economic growth across developing regions.
Why Consider the EEM ETF?
One of the main reasons to consider the EEM ETF is its potential for long-term capital appreciation. Emerging markets often experience faster economic growth than developed economies, driven by expanding workforces, industrial development and rising consumer demand. This growth can translate into higher returns for investors willing to accept more volatility.
The EEM ETF also offers diversification. Many portfolios are heavily weighted toward developed markets such as the United States and Europe. Adding exposure to regions with different economic cycles and demographic trends can reduce overall portfolio risk and enhance return potential over time.
Performance and Volatility
While the EEM ETF can deliver significant returns during bull markets, it is also subject to higher volatility compared to developed market ETFs. Political instability, currency fluctuations and slower-than-expected reforms can negatively affect returns in emerging markets.
Additionally, the EEM ETF has substantial exposure to certain regions—particularly Asia. For example, China often represents a large portion of the fund's holdings. As a result, geopolitical tensions or regulatory crackdowns in key countries can impact the ETF's performance disproportionately.
Investors need to consider their risk tolerance and investment horizon when evaluating whether the EEM ETF fits their strategy. Those with a long-term outlook and the ability to endure short-term fluctuations may benefit most from this exposure.
Cost and Structure
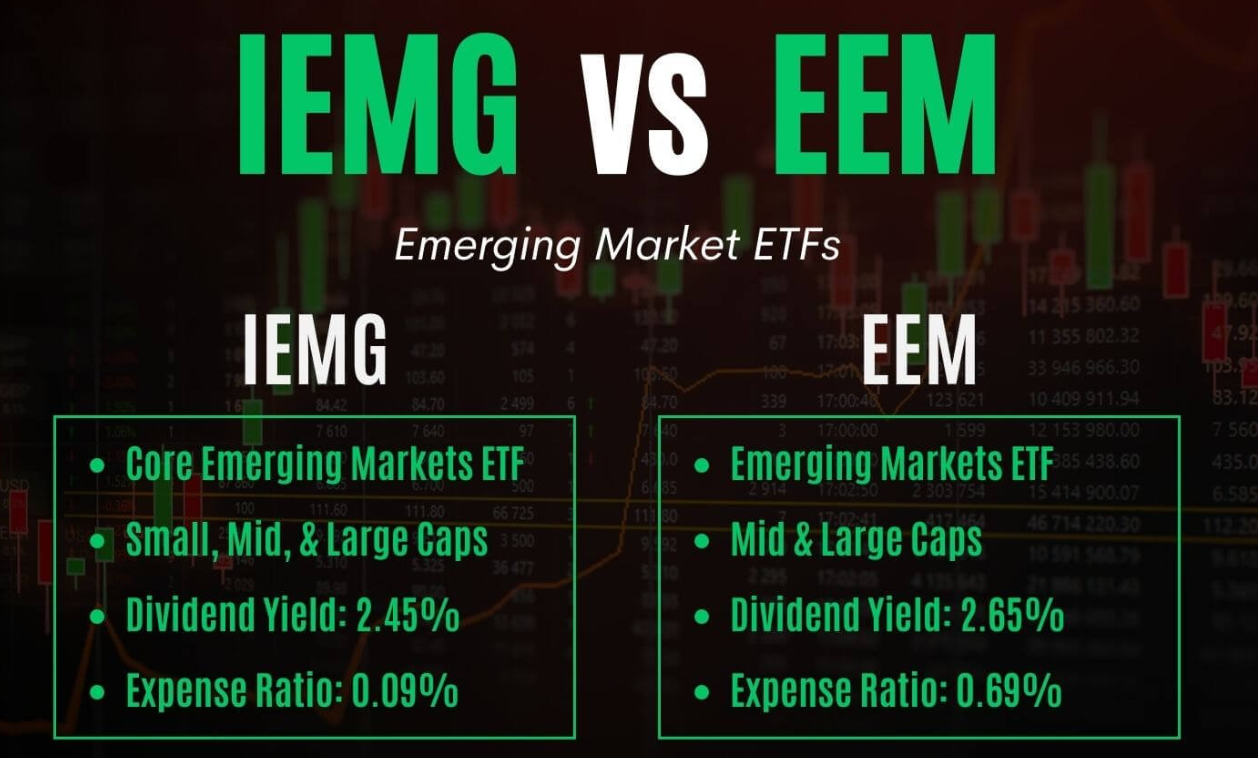
The EEM ETF has a management fee (expense ratio) of around 0.68%, which is higher than some broad market ETFs but fairly typical for international funds. It trades on US exchanges and is available through most brokerage platforms, offering flexibility and liquidity.
For cost-conscious investors, there are alternative emerging market ETFs with lower fees, such as the iShares Core MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (IEMG). However, the EEM ETF remains popular due to its liquidity and long track record, making it suitable for both retail and institutional investors who prioritise ease of trading.
Risks to Consider
Investing in the EEM ETF involves several risks. Currency risk is significant, as the performance of foreign currencies relative to the investor's base currency can impact returns. Political and regulatory uncertainty in emerging markets can also create instability. In addition, corporate governance standards may differ from those in developed countries, affecting transparency and investor protection.
The EEM ETF is also affected by global economic trends, commodity prices and capital flows. For example, higher interest rates in developed markets can lead to capital outflows from emerging economies, pressuring local markets and affecting the ETF's value.
Is the EEM ETF Right for You?
The decision to invest in the EEM ETF depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance and investment timeframe. For investors seeking growth and willing to accept volatility, the EEM ETF can be a valuable component of a globally diversified portfolio. It may also appeal to those looking to hedge against inflation or gain exposure to non-correlated assets.
However, it should not be seen as a core holding for conservative investors. Instead, it works best as a satellite allocation within a broader investment strategy, complementing other ETFs focused on developed markets, fixed income or sectors like technology and healthcare.
Conclusion
The EEM ETF offers a straightforward way to invest in emerging market equities through a single, liquid instrument. With its broad diversification, exposure to growing economies and potential for long-term returns, it can enhance portfolio diversification and growth prospects. However, it also carries higher risk, and investors should approach it with a clear understanding of the volatility and geopolitical factors involved.
For those willing to ride out the fluctuations and stay invested over the long term, the EEM ETF could prove to be a rewarding addition to an investment portfolio.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.