Understanding the term "pip" is essential for anyone beginning their journey in forex trading. Whether you're analysing currency pairs, setting stop-losses, or calculating profits and losses, pips are a fundamental building block.
Thus, this step-by-step guide will describe its meaning in forex, its function in currency trading and calculation, and its importance to your trading strategy. By the end, you'll be able to interpret pip movements and make smarter trading decisions.
Understanding Pips in Forex: Step-by-Step Guide
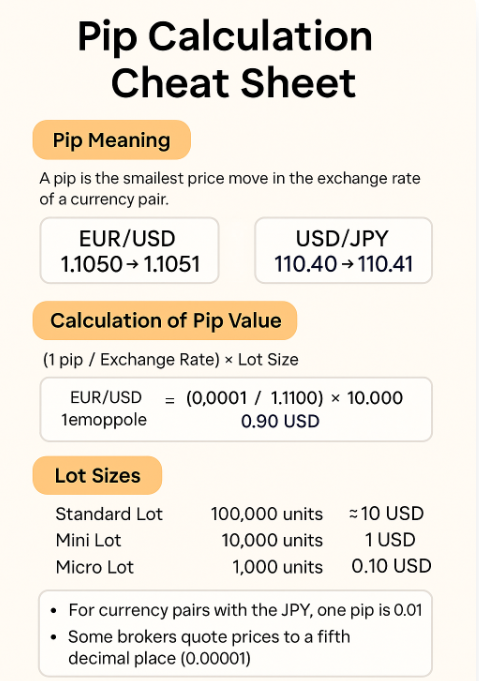
1) Pip Meaning in Forex Explained
A pip stands for "percentage in point" or "price interest point". It is the smallest price move that a given currency pair can make based on market convention.
In most currency pairs, 1 pip = 0.0001 (fourth decimal place).
Example:If EUR/USD moves from 1.1000 to 1.1001, that's a 1-pip movement.
Note: For currency pairs involving the Japanese Yen (such as USD/JPY), 1 pip equals 0.01 (the second decimal place).
Pipettes and Fractional Pips
A pipette is one-tenth of a pip (0.00001 in most currency pairs). Some brokers quote prices to 5 decimal places to provide more precision.
Example:If GBP/USD moves from 1.31235 to 1.31240, that's a 0.5 pip movement or 5 pipettes.
Scalpers and high-frequency traders mainly used Pipettes than other traders.
2) How to Calculate Pip Value
Pip value depends on:
The currency pair you're trading
The lot size (standard, mini, micro)
The exchange rate
Lot Sizes:
Standard Lot = 100,000 units (pip value ≈ $10)
Mini Lot = 10,000 units (pip value ≈ $1)
Micro Lot = 1,000 units (pip value ≈ $0.10)
Formula:
Example:For EUR/USD at 1.1000 and a mini lot (10,000 units): Pip Value = (0.0001 / 1.1000) × 10,000 = $0.91
3) Examples of Pip Movements
Example 1: EUR/USD
Entry: 1.1234
Exit: 1.1244
Movement: +10 pips
Example 2: USD/JPY
Entry: 110.25
Exit: 110.05
Movement: -20 pips
Tracking pip movements helps traders gauge performance and adjust position sizing.
4) Pips in Different Currency Pairs
Different base and quote currencies can affect pip size and value.
Major Pairs:
EUR/USD, GBP/USD, AUD/USD: 1 pip = 0.0001
USD/JPY, EUR/JPY: 1 pip = 0.01
Cross Currency Pairs:
Exotics:
Always check your broker's pip conventions for each pair.
5) Pips and Profit/Loss Calculation
Your profit or loss in a trade is directly linked to the number of pips gained or lost.
Example: You buy 1 standard lot of GBP/USD at 1.3000 and close at 1.3030.
If the trade went the other way, the loss would also amount to $300.
6) Pips vs Points vs Ticks
Pips:
Points:
Ticks:
Smallest possible movement in futures or commodities.
Often defined by exchanges (e.g., oil tick = $0.01).
While similar in concept, these terms apply to different markets and are not interchangeable.
7) Pip Calculators and Tools
Useful Tools:
Online pip calculators: Enter pair, lot size, and leverage.
Trading platforms (MT4, MT5): Show pip movements in real-time.
Risk calculators: Use pip distance to set stop-loss or take-profit levels based on account size.
These tools help automate pip value calculations and improve decision-making.
8) Tips for Managing Pip Risk
Managing pips effectively is critical for risk management in forex trading.
Best Practices:
Use a stop-loss: Always define your maximum pip loss per trade.
Adjust lot sizes: Trade smaller lots if you're a starter.
Track pip-to-dollar ratio: Know how many pips equal a meaningful loss or gain for you.
Avoid high-spread pairs: Pairs with high spreads require more pips to break even.
Use pip-based trading plans: Set consistent pip targets (e.g., 30 pips profit, 20 pips stop).
9) Pip-Based Trading Strategies for Beginners
Mastering how to use pips in actual trading strategies is the next step after learning what pips are. For beginners, pip-focused strategies help bring structure to trading decisions and keep risk under control. Here are several beginner-friendly strategies built around pip movement:
1. Fixed Pip Target Strategy
This is a simple and disciplined strategy where traders aim for a consistent number of pips per trade—regardless of the currency pair.
How it works:
Set a daily or trade-specific pip target (e.g., 20 pips per trade).
Use technical analysis to enter trades with favourable risk-reward ratios.
Close the trade when the profit target is reached or when the stop-loss (e.g., 10–15 pips) is hit.
Pros:
2. Scalping Small Pip Moves
Scalping involves entering and exiting trades quickly to capture small pip profits—usually 5 to 15 pips at a time.
Key requirements:
Low-spread currency pairs such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD.
Fast execution and a broker with minimal slippage.
Strong focus and discipline to exit trades quickly.
Best tools:
1-minute or 5-minute charts
Momentum indicators like RSI or Stochastic
Tight stop-loss (often 5–10 pips)
3. 50-Pip-a-Day Strategy
This is a popular beginner method that seeks to capture 50 pips in a single trade using price action or breakout setups.
Approach:
Use support/resistance or trendlines.
Enter trades around key levels during times of high volatility (e.g., London or new york session opening).
Stop-loss: 20–30 pips.
Take-profit: 50 pips or trailing stop.
Why it works:
4. Pip Range Trading Strategy
This strategy is effective in sideways markets, where prices bounce between defined support and resistance levels.
How to implement:
Identify a price range (e.g., 30 to 50 pips wide).
Buy near support, sell near resistance.
Set tight stop-losses (10–15 pips).
Take profit as the price approaches the other side of the range.
Ideal market conditions:
5. Breakout Pip Strategy
Designed to take advantage of strong price movements after consolidation.
Strategy steps:
Identify consolidation or flag/pennant patterns.
Place entry orders a few pips above resistance or below support.
Measure expected movement (e.g., 30–100 pips depending on time frame).
Set stop-loss just inside the consolidation zone.
Helpful tools:
Bollinger Bands
Moving Averages
Volume indicators
6. Risk-Based Pip Sizing Strategy
Before entering any trade, calculate your ideal position size based on how many pips you're willing to risk.
Example:
Account balance: $1,000
Risk: 2% ($20)
Stop-loss: 20 pips
Use a position sizing calculator to determine lot size that limits your loss to $20 if the price moves 20 pips against you. This method aligns pip losses consistent with your risk tolerance.
10) Why Are Pips Important?
Pips help traders measure price changes, risk, and potential profit or loss in a trade. They are a standardised unit of measurement across the forex market.
Use Cases:
Measuring price movement: EUR/USD rose by 50 pips.
Defining stop-loss or take-profit: A 20-pip stop-loss.
Calculating trade outcomes: A trade gained 100 pips.
Pips provide consistency, making it easier to compare different trades or currency pairs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding pips is essential for trading forex effectively. Pips are the foundation for calculating profits, measuring volatility, and managing risk. Whether you're day trading EUR/USD or swing trading GBP/JPY, pips are your guideposts for decision-making.
By mastering pips, you build confidence in your trade setups and risk management techniques. It's one of the most crucial steps toward becoming a successful forex trader.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.