Day trading is a form of trading where positions in financial instruments are opened and closed within the same trading day. It involves high-stakes decisions and requires a disciplined approach, making it suitable for individuals who thrive in fast-paced environments.
In this article, we will cover everything you need to know about day trading, from the basic concepts and tools to advanced strategies and risk management practices.
Introduction to Day Trading: Understanding the Essentials
1. What is Day Trading? A Comprehensive Overview
Day trading refers to the practice of buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. The aim is to take advantage of short-term price movements to generate profits. Unlike long-term investors who hold positions for months or years, day traders close their trades before the market closes to avoid overnight risks.
Key Differences Between Day Trading and Long-Term Investing:
Day Trading:
Short-term focus (same day trades)
Involves frequent buying and selling
Capital is tied up for shorter periods
Relies heavily on technical analysis
Long-Term Investing:
Long-term focus (months or years)
Less frequent trades
Investments are held through market cycles
Emphasises fundamental analysis
2. Why Choose Day Trading? Potential Advantages and Drawbacks
Advantages:
Profit Potential: Day traders can make significant profits from small price movements by using leverage.
Flexibility: As a day trader, you can work from anywhere with an internet connection.
No Overnight Risk: Positions are closed before the market closes, reducing exposure to overnight market movements.
Drawbacks:
High Risk: The fast-paced nature of day trading can lead to significant losses if not managed carefully.
Emotional Stress: Day trading can be mentally and emotionally taxing, requiring strong discipline and control.
Time Commitment: To succeed, day traders must dedicate significant time to research, analysis, and monitoring the market.
The Core Concepts of Day Trading: Essential Knowledge for Beginners
1. Types of Markets in Day Trading: Stocks, Forex, and Cryptocurrencies
Day traders can operate across different markets, each with its unique characteristics.
Stock Market: The most popular market for day traders, involving the buying and selling of shares in publicly traded companies.
Forex Market: Involves trading currencies in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD), offering high liquidity and 24-hour access.
Cryptocurrency Market: Highly volatile and operating around the clock, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are attractive to day traders seeking substantial price swings.
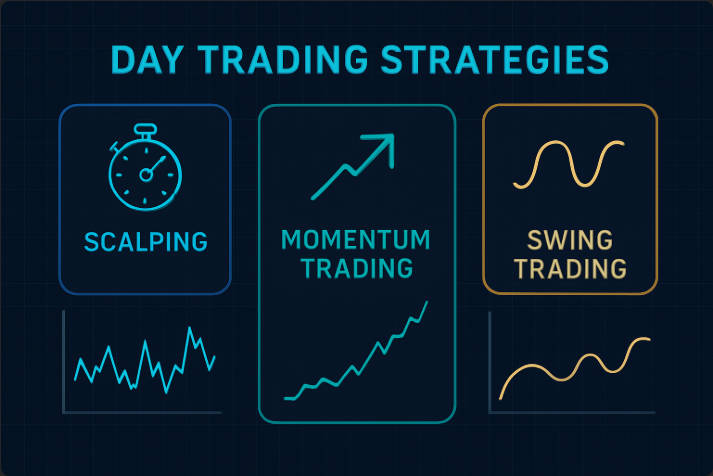
2. Day Trading Strategies: Common Approaches and Techniques
Day trading strategies vary, but some are more commonly used. Below are the main strategies employed by successful day traders:
Scalping: A strategy that involves making numerous small trades throughout the day, aiming to profit from small price movements. Scalpers typically use high leverage and require a fast internet connection.
Momentum Trading: Involves identifying and trading on the momentum of stocks or assets that are moving significantly in one direction. This strategy focuses on identifying trends early and riding them until the momentum slows.
Swing Trading (Within a Day): Traders look for stocks or assets that will experience short-term movements, holding them for a few hours or less.
3. Fundamentals of Day Trading: Key Terms and Concepts Explained
Understanding key terms is essential for navigating the world of day trading.
Pips: A unit of measurement for currency pairs in Forex trading. A pip is the smallest price move a currency can make.
Leverage: Allows day traders to control a larger position than their account balance would typically allow, magnifying both potential profits and losses.
Spread: The difference between the buy and sell price of an asset. A narrower spread is preferred for day trading, as it reduces transaction costs.
Margin: The amount of money a trader needs to deposit with their broker to open a leveraged position.
Tools of the Trade: Essential Technology for Effective Day Trading
1. Choosing a Day Trading Platform: Key Features and Considerations
A reliable trading platform is the backbone of day trading. The following features should be considered when selecting a platform:
Execution Speed: Fast execution of trades is essential for day trading to avoid slippage.
Charting Tools: Platforms should provide advanced charting capabilities for technical analysis.
Low Fees and Commissions: Minimise transaction costs, as frequent trading can eat into profits.
Customer Support: Reliable support is essential to resolve technical issues swiftly.
Popular Trading Platforms:
MetaTrader 4/5: A widely-used platform offering advanced charting tools and customisable features.
ThinkorSwim: A platform from TD Ameritrade known for its powerful charting tools and educational resources.
Interactive Brokers: Offers a range of advanced trading tools with a low fee structure.
2. Trading Software and Charting Tools for Day Traders
Effective charting software is crucial for analysing price patterns and identifying entry and exit points. Popular options include:
TradingView: A cloud-based charting tool known for its social trading features and detailed technical analysis.
MetaTrader 4/5: Provides comprehensive charting tools with a wide range of indicators, ideal for Forex and CFD trading.
Technical Indicators:
Moving Averages (MA): Helps to identify trends by smoothing out price data.
Relative Strength Index (RSI): Measures the speed and change of price movements, helping traders identify overbought or oversold conditions.
MACD: A trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price.
3. Leveraging Real-Time News and Data Feeds in Day Trading
Real-time news is crucial for making informed decisions in day trading. Financial news platforms like Bloomberg and Reuters provide up-to-the-minute reports on market-moving events. Additionally, economic calendars track key events like earnings reports and central bank meetings.
Creating a Day Trading Plan: Structured Approach to Consistent Profits
1. Setting Clear Goals in Day Trading: Defining Profit and Loss Parameters
A well-thought-out trading plan helps day traders stay disciplined and avoid emotional decision-making. Key components of a trading plan include:
Profit Goals: Setting realistic targets for daily, weekly, or monthly profits.
Loss Limits: Determining the maximum acceptable loss per day or trade to avoid significant capital erosion.
2. Selecting Your Trading Style: Active vs. Passive Day Trading
Day traders can choose between different levels of trading activity:
Active Day Trading: Involves making frequent trades throughout the day, aiming to profit from minor price movements.
Passive Day Trading: Fewer trades are made, with positions held for longer durations within the day. This strategy requires less time but still relies on good market analysis.
3. Time Commitment for Day Trading: Scheduling Your Trading Sessions
Day traders typically need to be active during market hours, often around key market open times. A day trader’s schedule will depend on the market they trade in:
Stock Market: Active from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM (Eastern Time)
Forex Market: Open 24 hours, five days a week
Cryptocurrency Market: Open 24/7
Managing Risk in Day Trading: Protecting Your Capital

1. Risk Management in Day Trading: Setting Appropriate Capital Allocation
Managing risk is essential to day trading success. One key aspect is determining the percentage of capital to risk on each trade. Most day traders risk no more than 1-2% of their account balance per trade.
2. Developing a Risk-to-Reward Strategy: Maximising Profits while Minimising Losses
Traders should aim for a positive risk-to-reward ratio. For example, a ratio of 2:1 means you are targeting profits that are twice the size of your potential loss.
3. Using Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Essential Tools for Risk Control
Stop-loss orders automatically close a trade if the price moves against the trader by a set amount, limiting losses. Similarly, take-profit orders lock in profits when a trade reaches a predetermined level.
Psychological Aspects of Day Trading: Mastering the Mental Game
1. Controlling Emotions: How to Stay Calm Under Pressure in Day Trading
The fast-paced nature of day trading can trigger strong emotions. Successful traders must maintain emotional control, avoid impulsive decisions, and stick to their trading plan.
2. Handling Losses: Developing Resilience and Staying Disciplined
Losses are an inevitable part of day trading. Developing resilience and learning from mistakes is key to long-term success. A disciplined approach helps traders stay focused and avoid revenge trading.
Legal Considerations for Day Traders: Complying with Regulations
1. Tax Implications of Day Trading: Reporting and Paying Taxes
Day traders must report their profits as income on their tax returns. In the US, short-term capital gains are taxed at ordinary income tax rates. Traders should keep detailed records of all trades for tax purposes.
2. Regulatory Requirements in Day Trading: Staying Compliant
Day traders must comply with market regulations. In the US, for example, the Pattern Day Trader Rule requires traders with less than $25,000 in their accounts to limit their day trading activity to three trades per week.
Advanced Tips for Day Trading Success: Continuing Your Journey

Continuous Learning: Staying Updated on Market Trends and Trading Strategies
Successful day traders never stop learning. Regularly reading trading books, attending webinars, and participating in online trading communities can help refine strategies and stay updated on new techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is day trading?
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. Traders aim to profit from short-term price movements, closing all positions before the market closes to avoid overnight risk.
2. How much capital do I need to start day trading?
The minimum capital required varies by market and broker. Generally, a starting balance of $2.000-$5.000 is recommended for stock trading. For Forex or cryptocurrency, smaller amounts may suffice due to lower margin requirements.
3. What are the best markets for day trading?
The most popular markets for day trading are stocks, forex, and cryptocurrencies. Each offers different benefits, with stocks providing stability, forex offering liquidity, and cryptocurrencies delivering high volatility and potential for quick profits.
4. What is leverage in day trading?
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. While it can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. A proper risk management strategy is essential when using leverage.
5. What is the difference between scalping and momentum trading?
Scalping involves making many small trades to profit from minor price movements. Momentum trading focuses on identifying assets with strong trends and capitalising on the sustained price direction until it weakens.
Conclusion
Day trading offers the potential for significant profits but comes with high risks that require careful management and a disciplined approach. Success in this fast-paced field relies on a strong trading plan, effective risk management, and the ability to stay emotionally grounded.
By mastering the necessary tools, strategies, and psychological aspects, aspiring day traders can build a foundation for long-term success. Continuous learning and practice are key to navigating the complexities of day trading and achieving consistent profitability.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.