Previously, we learnt how to place trades in MT4. However, in real trading, executing an order is not as simple as clicking a button. Because market conditions change constantly, traders must adjust their execution methods to align with their objectives.
MT4 offers two primary types of order execution: market execution and pending orders.
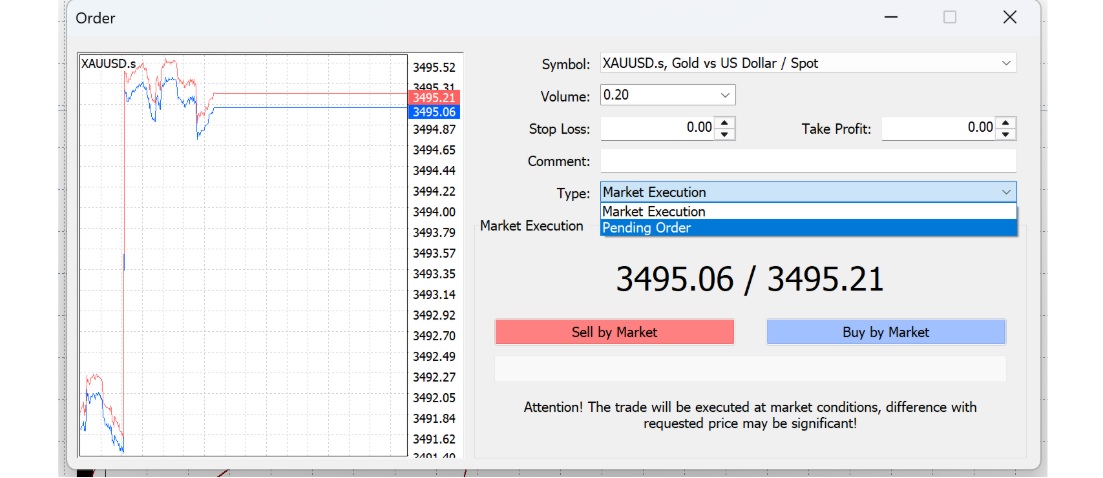
Market Execution
As the name suggests, a market execution is executed immediately at the current market price. For example, if gold is trading at USD 3.470.20. placing a market buy order will execute at that price.
Market execution is particularly useful in strong trending conditions, where traders wish to follow the momentum by buying into an uptrend or selling into a downtrend.
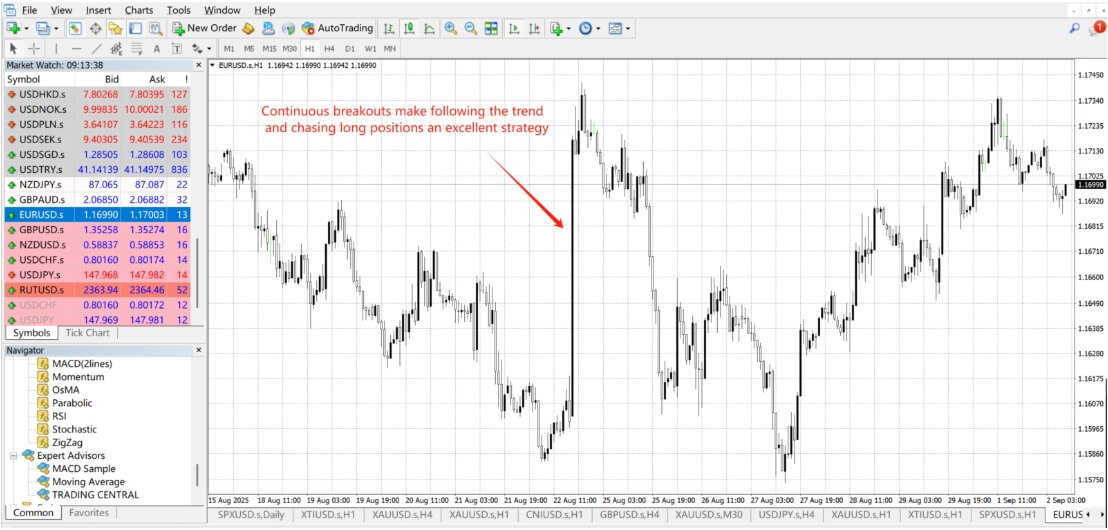
However, market orders are subject to liquidity. Poor liquidity may result in slippage, where the actual execution price differs from the quoted price. For instance, if you place a buy order at USD 3.470.20 but it executes at USD 3.470.50. you pay an additional USD 0.30 due to slippage.
Pending Orders
A pending order is only triggered when the market reaches a pre-set price. For example, if you set a sell order at USD 3.500. the order will only be executed once the market touches that level; otherwise, it remains inactive.
Pending orders allow for more precise execution. A buy order will be executed exactly at the pre-set price, but a sell order is executed at the pre-set price minus the spread. This means that if you place a sell limit at USD 3.500 and the market just touches 3.500. widened spreads due to volatility may prevent the order from being filled.
Therefore, liquidity is critical for both market and pending orders.
In addition, compared with market orders, MT4 also provides four types of pending orders.
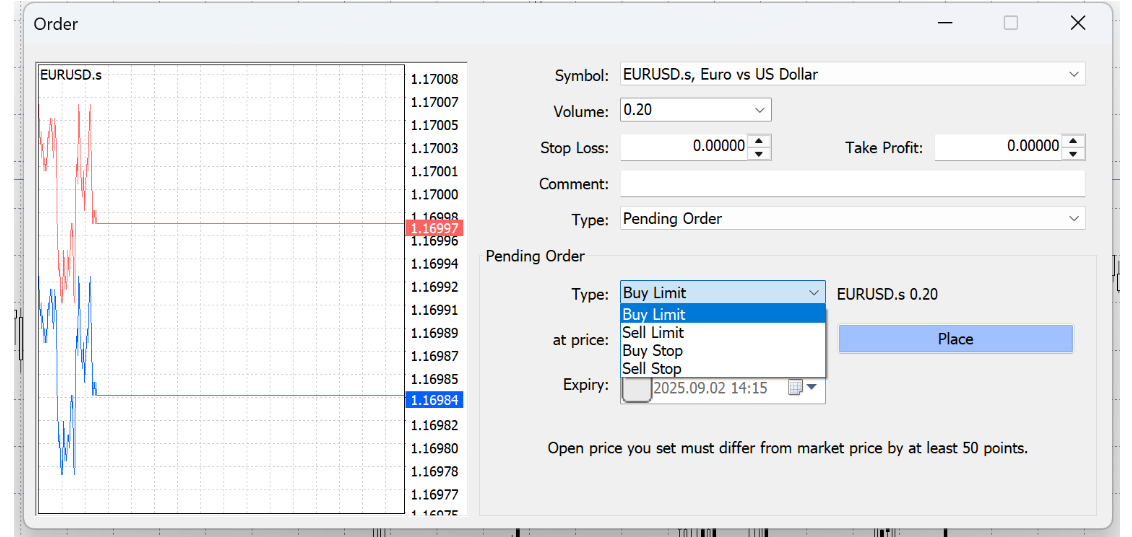
Pending orders are considered a more advanced method of trade execution, as they reflect a trader's anticipation of future price movements. Each of the four types corresponds to a distinct trading strategy, as outlined below.
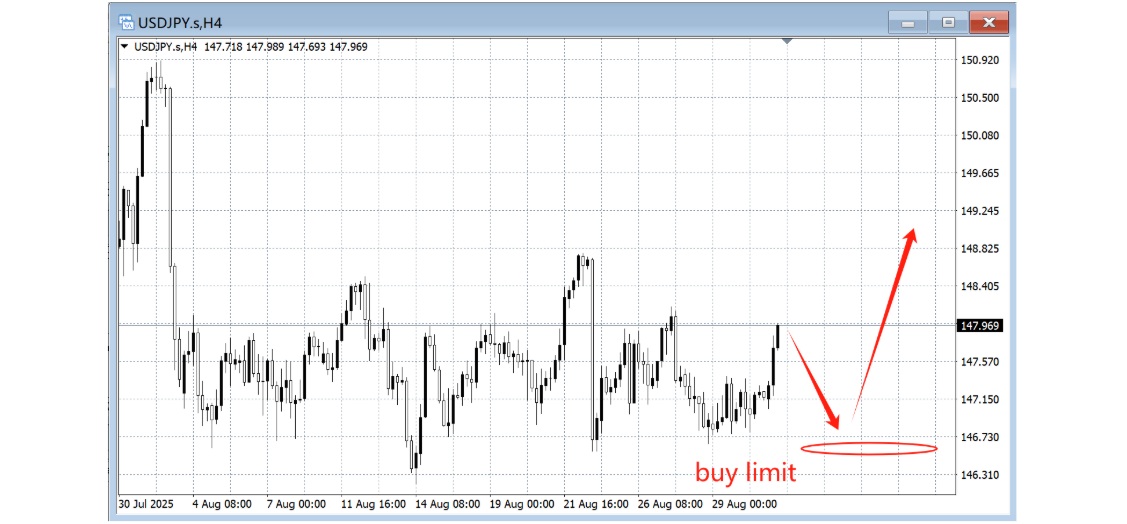
1. Buy Limit:
An order to buy below the current market price, typically used when you expect a temporary dip before the market resumes higher. It allows you to "buy the dip" at a more favourable level.
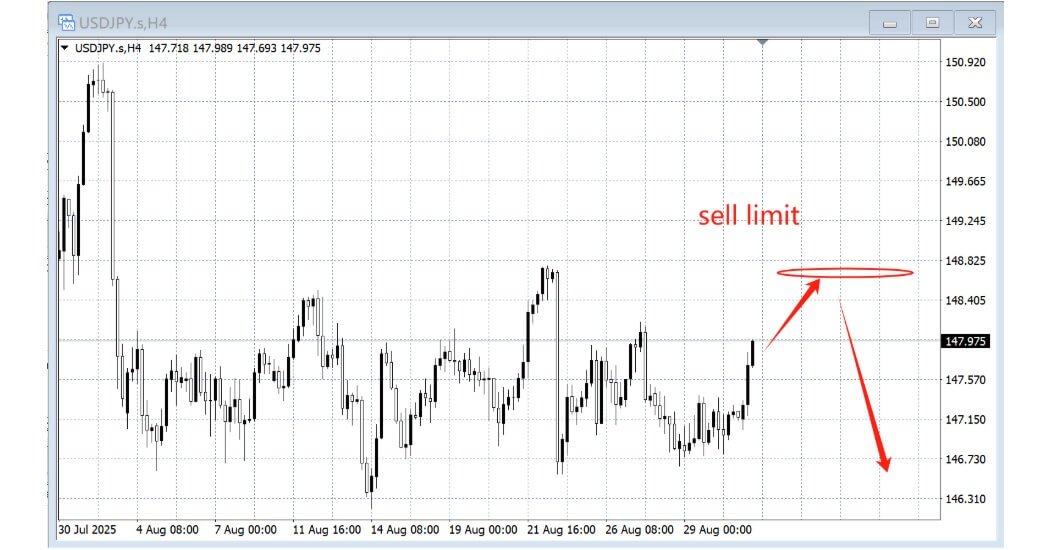
2. Sell Limit:
An order to sell above the current market price, often placed when you anticipate a short-term rally before the market turns lower. It's a way to "sell the rally" near resistance.
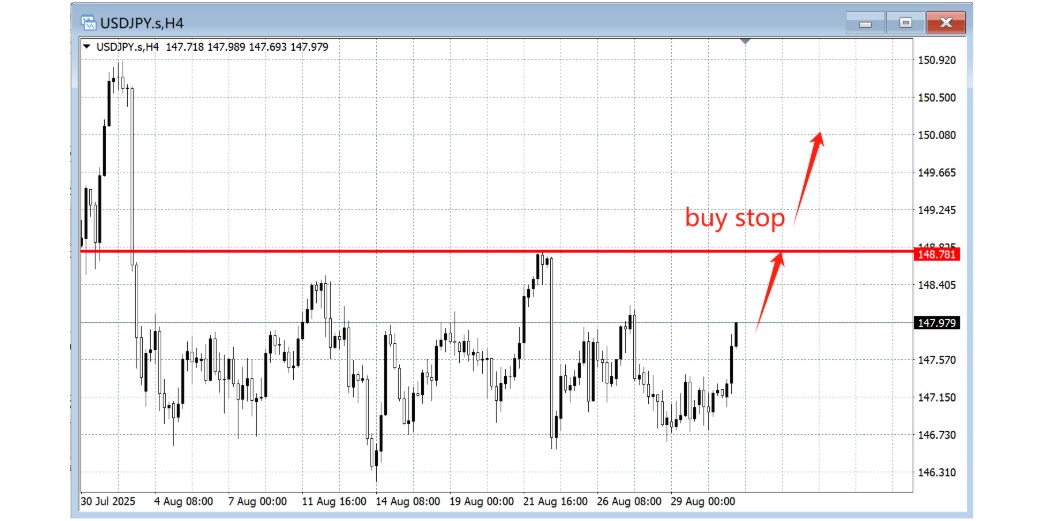
3. Buy Stop:
An order to buy above the current market price, designed to catch upward breakouts. If price pushes through resistance, the order triggers and joins the momentum.
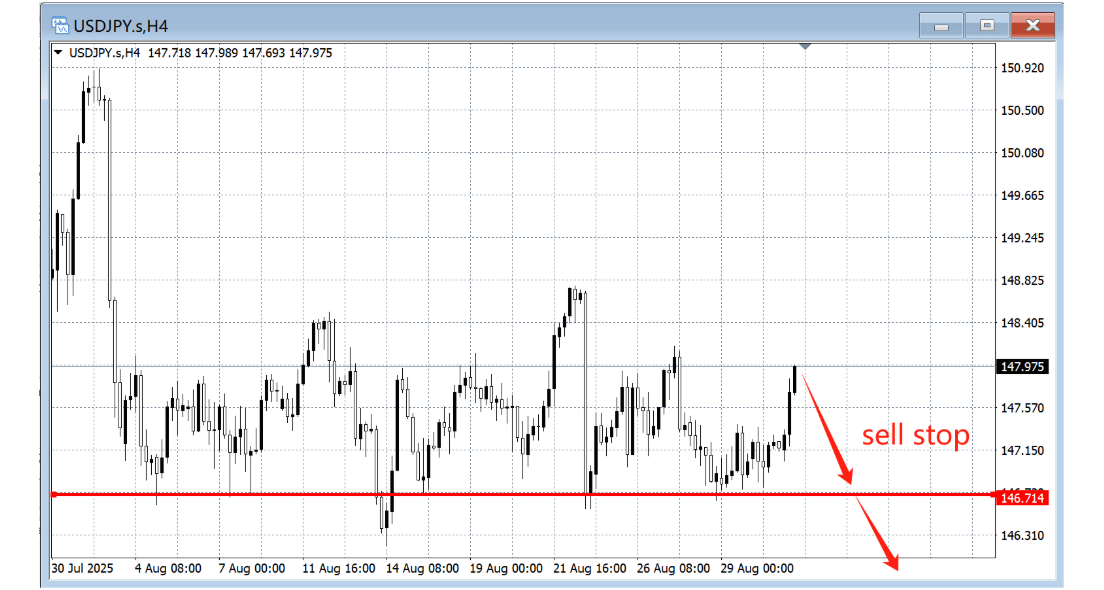
4. Sell Stop:
An order to sell below the current market price, used to enter on downside breakouts. When support gives way, the order activates and rides the move lower.
Traders need to match their order type to the market environment. Market orders work best when speed is critical, while pending orders are better suited for setting up strategic entries. The ability to switch between the two is what keeps traders adaptable in different market conditions.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.