Currency fluctuations can significantly affect the profitability of international investments and trading positions. For traders and investors exposed to multiple currencies, currency hedging is essential in managing risk. But what exactly is currency hedging, how does it work, and why is it important in trading?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the meaning of currency hedging, its strategies, benefits, risks, and how you can use it effectively in your trading or investment portfolio.
The Fundamentals of Currency Hedging
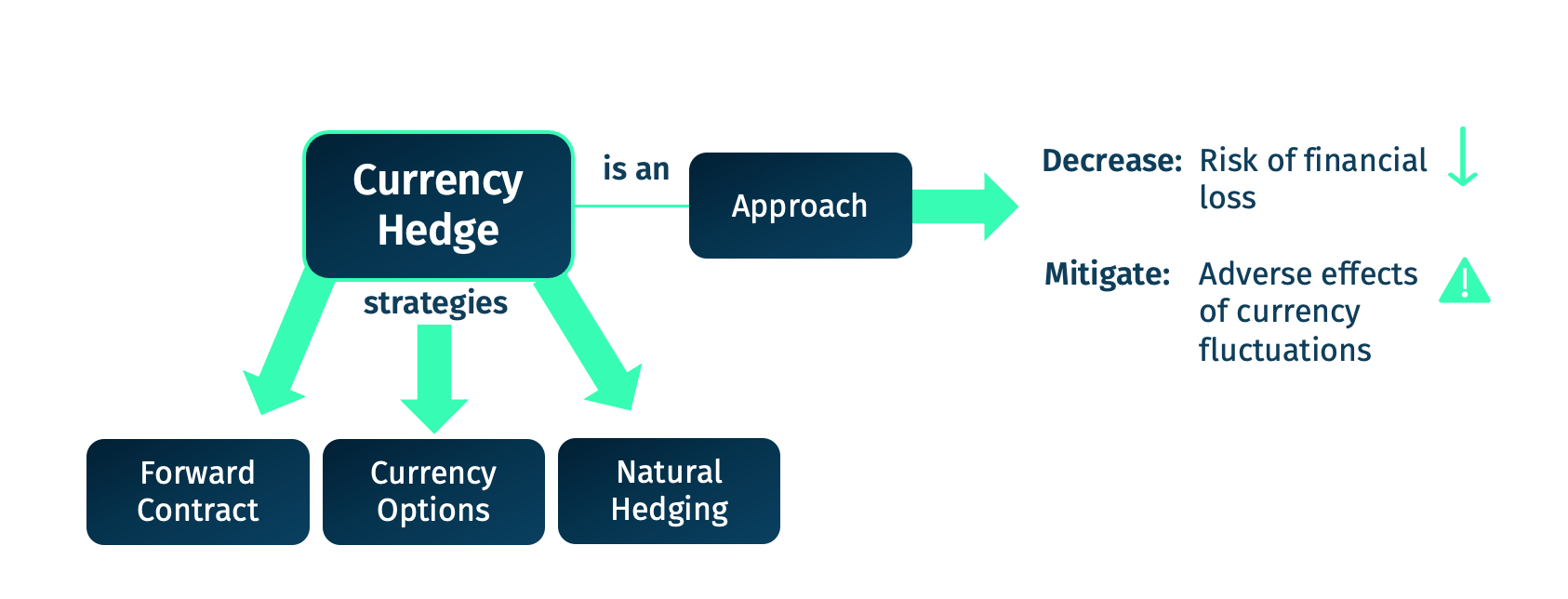
Currency hedging involves using financial instruments—like futures, options, forwards, and swaps—to offset the risk of adverse currency movements. The goal is not to make a profit from the hedge itself but to protect an existing investment or position from unfavourable exchange rate changes.
For instance, if a U.S. investor holds shares in a European company, the returns will be influenced by the euro's performance against the U.S. dollar. If the euro weakens, the investor's returns in USD terms could drop—even if the stock performs well in its home market. Currency hedging can help offset that potential loss.
Pros
Reduces risk of losses due to currency fluctuations
Increase predictability of cash flows and returns.
Helps achieve financial goals and budgeting accuracy
Useful in high-volatility environments
Cons
Can reduce potential gains if the market moves in your favour
Costly, especially with options and swap arrangements
Requires expertise to implement and manage effectively
Over-hedging can lead to missed opportunities.
Types of Currency Hedging Instruments
1) Forward Contracts
A forward contract allows two parties to agree on an exchange rate today for a future transaction. This is a private, over-the-counter (OTC) agreement between a buyer and a seller, which locks in the rate regardless of market movements.
2) Futures Contracts
Currency futures are standardised contracts traded on exchanges. They function like forward contracts but offer greater liquidity and counterparty protection due to the presence of clearinghouses.
3) Currency Options
An option gives the buyer the right—but not the obligation—to exchange currency at a pre-agreed rate before a specified date. This provides flexibility and downside protection but comes at a cost (a premium).
4) Currency Swaps
In a swap, two parties exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies. These are commonly used by multinational corporations and financial institutions with ongoing foreign exchange exposure.
Why Currency Hedging Matters
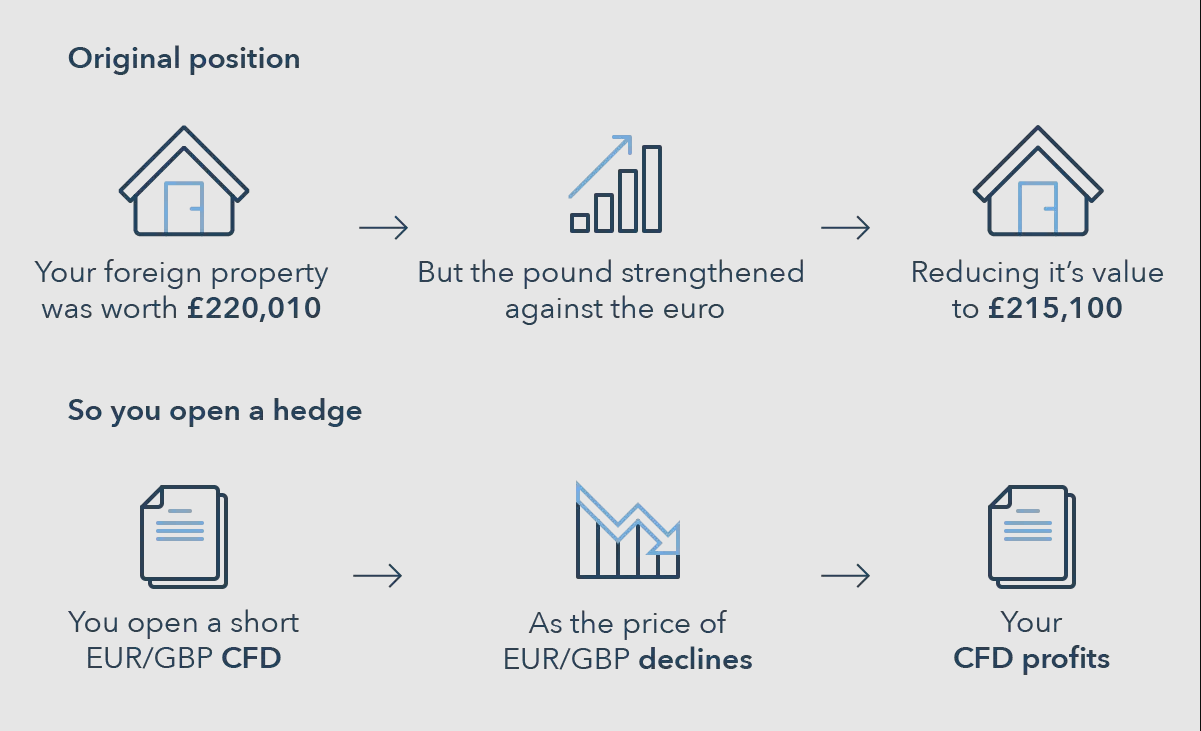
Risk Management: Currency markets are highly volatile. Hedging mitigates the risk of sharp fluctuations that could negatively impact profits.
Stability for International Business: Companies involved in exports and imports hedge to stabilise their revenues and manage costs.
Portfolio Protection: Investors hedge to safeguard global investments during currency uncertainty.
Compliance and Forecasting: Governments and multinational corporations rely on currency hedging to meet reporting standards and financial forecasts without surprises due to FX swings.
Real-World Examples
One real-world example is the use of hedging by U.S.-based multinational companies. Suppose a company like Coca-Cola sells products in Europe and receives payments in euros. If the euro weakens significantly against the dollar, the company's revenue could suffer when converted back into USD. Coca-Cola may use currency forwards or options to lock in a favourable EUR/USD rate, ensuring predictable income.
Another example is a UK-based fund investing in U.S. equities. If the U.S. dollar depreciates relative to the British pound, the fund's returns in GBP would decline. Hedging currency risk allows the fund to maintain steady returns independent from exchange rate swings.
Currency Hedging in 2025
As of 2025, hedging strategies have evolved due to the advancement of AI-driven platforms, real-time analytics, and fintech retail access to hedging tools. Companies are increasingly integrating dynamic hedging solutions that automatically adjust market signals.
The rise in geopolitical conflicts, supply chain shifts, and inflationary pressures worldwide has pushed more investors to take currency hedging seriously. Moreover, interest rate differentials between major central banks—such as the U.S. Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of Japan—have kept currency markets volatile, reinforcing the need for robust hedging mechanisms.
Best Practices
To implement effective hedging strategies:
Assess your exposure: Understand which currencies impact your portfolio or operations.
Choose the right tool: Pick the most suitable hedging instrument based on your risk profile.
Diversify: Spread exposure across multiple currencies and regions when possible.
Use expert guidance: Engage currency experts or use automated platforms for execution and monitoring.
Monitor market trends: Stay informed about geopolitical risks, central bank policies, and macroeconomic indicators.
Conclusion
In conclusion, currency hedging is no longer a tool used solely by large corporations or hedge funds. With global investment opportunities growing and exchange rates becoming more volatile, it's a key strategy for protecting wealth and ensuring consistent returns.
In 2025, as global economies continue to shift and interest rate policies diverge, the importance of currency hedging will only grow. Whether you're a retail trader or an institutional investor, understanding how to manage currency risk through effective hedging can make the difference between consistent performance and unexpected losses.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.