A stock split is a routine corporate action that changes how a company’s shares are structured and traded, but not what the company is worth.
In simple terms, a stock split occurs when a company increases or decreases the number of its outstanding shares, adjusting the share price proportionally without affecting its market capitalisation or the total value of an investor’s holdings.
Companies use stock splits to manage share price levels, support liquidity, and improve accessibility for a broader range of investors, while leaving the underlying business value unchanged.
How a Stock Split Works
A stock split works by adjusting the number of shares outstanding while keeping the total investment value unchanged. For example, if a company’s shares are trading at £200 and it announces a 2-for-1 stock split, each existing share is divided into two new shares priced at £100 each.
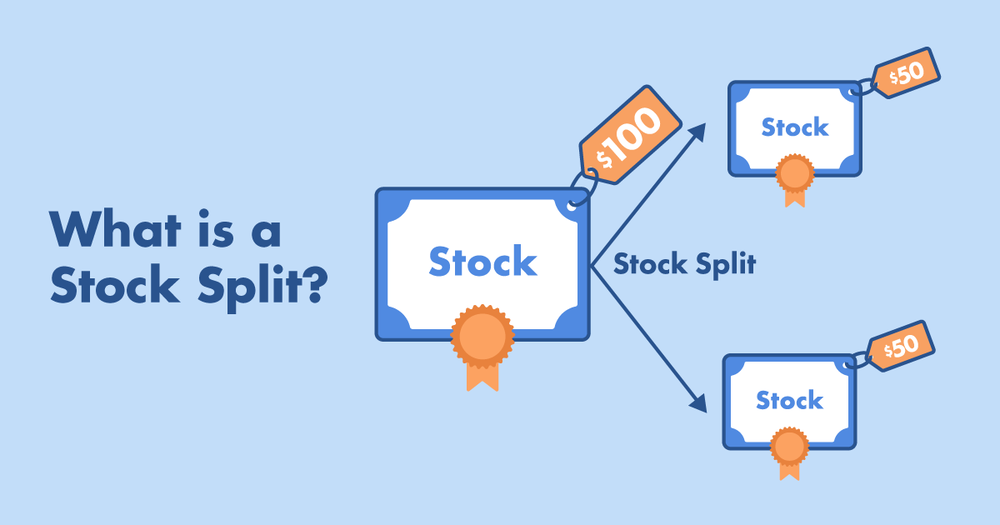
An investor who previously owned one £200 share would now hold two £100 shares, with the total value of the holding remaining the same.
This process does not affect the company’s market capitalisation or an investor’s percentage ownership. Instead, it changes the share count and per-share price to improve trading flexibility and make the stock more accessible to a wider range of market participants.
Why Companies Choose to Split Their Stock
Improve market liquidity: High share prices can limit participation from retail investors. A stock split lowers the price per share, making the stock easier to trade and often increasing daily trading volume.
Broaden investor access: By reducing the nominal share price, companies make their stock more accessible to a wider range of investors, helping expand the shareholder base without changing ownership value.
Signal management confidence: Stock splits are often announced during periods of strong performance. While they do not affect fundamentals, they can signal that management expects continued growth and stable demand for the shares.
Manage price perception: In industries where investors compare stocks based on price, a very high share price can appear expensive even when valuation metrics are similar. A split helps align the share price with industry norms and reduces the risk of misperceived overvaluation.
Types of Stock Splits and Their Purpose
Stock splits adjust the number of shares outstanding without changing a company’s total market value. In practice, they influence how a stock trades and how it is perceived by the market. The two types that matter most to investors are forward stock splits and reverse stock splits.
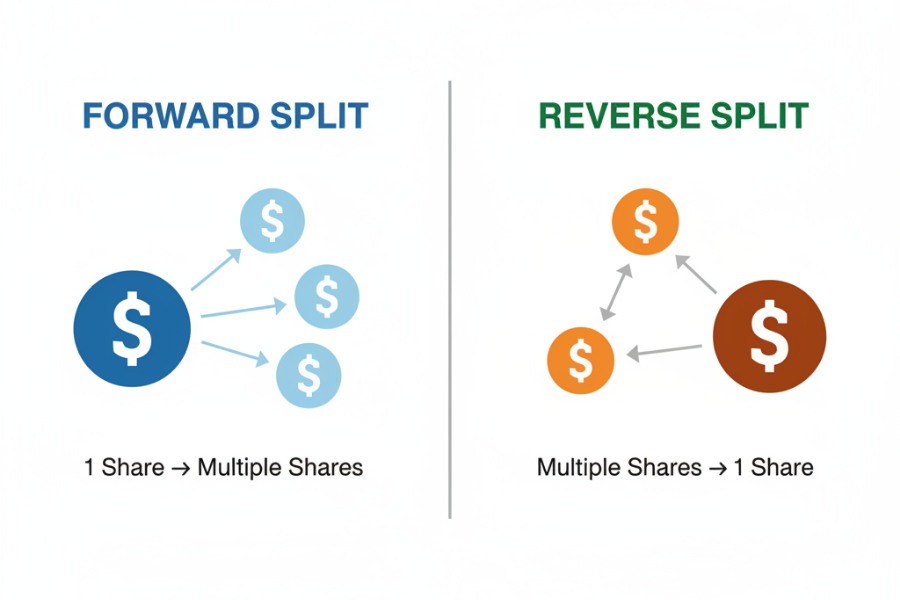
1. Forward Stock Split
A forward stock split increases the number of shares by dividing each existing share into multiple new shares, such as a 2-for-1 or 3-for-1 split. The share price declines proportionally, leaving market capitalisation unchanged.
Purpose:
Improve accessibility: A lower share price makes the stock easier for retail investors to buy.
Enhance liquidity: More shares outstanding often lead to higher trading volume and tighter bid-ask spreads.
Signal confidence: Forward splits are commonly associated with companies that expect sustained growth and strong demand for their shares.
What it means for investors:
The split itself does not create value, but it can support smoother trading and broaden the shareholder base.
2. Reverse Stock Split
A reverse stock split reduces the number of shares by combining multiple shares into one, such as a 1-for-10 split. The share price increases proportionally, while total market value remains unchanged.
Purpose:
Lift share price: Helps move the stock out of very low price ranges.
Meet listing requirements: Exchanges often require a minimum share price to remain listed.
Improve market perception: A higher nominal price may attract institutions that avoid penny stocks.
What it means for investors:
Reverse splits are mechanically neutral but are often viewed cautiously, as they may reflect underlying financial or performance challenges.
Impact Of Stock Split On Options and Derivatives
Stock splits do not only affect common shares; they also require adjustments to options and other equity derivatives linked to the underlying stock. These changes are handled mechanically to ensure that neither option holders nor issuers gain or lose value purely because of the split.
1. Contract size adjustment
Following a split, the number of shares represented by an options contract is adjusted proportionally. After a 2-for-1 split, for example, a contract that previously covered 100 shares would typically cover 200 shares.
2. Strike price recalibration
At the same time, the option’s strike price is adjusted in inverse proportion to the split ratio. A call option with a £200 strike price would become a £100 strike price following a 2-for-1 split.
3. Why option value remains neutral
Because both contract size and strike price change simultaneously, the option’s notional value remains unchanged immediately after the split. Subsequent gains or losses depend on price movement, volatility, and time decay, not the split itself.
4. Operational handling by exchanges
Exchanges and clearing organisations standardise these adjustments. Brokers automatically update positions, margin requirements, and contract specifications, meaning investors do not need to take action.
Impact of a Stock Split on Investors
A common question is whether a stock split changes the value of an investment. The short answer is no. From an investor’s perspective, a stock split is a structural adjustment, not a financial one.
If you hold £1,000 worth of shares before a split, you will still hold £1,000 worth afterward, despite changes in share count and price per share.
There can, however, be indirect effects. A lower share price may attract increased retail interest, potentially boosting short-term demand. Trading volume and investor behaviour may also shift around the announcement period.
For investors using platforms that support fractional shares, stock splits are handled automatically. Ownership percentage remains unchanged, and no action is required.
Real-World Examples of Stock Splits
Examining real-world cases helps clarify what a stock split is in practice. Apple has executed multiple stock splits over its history, most recently a 4-for-1 split in 2020.
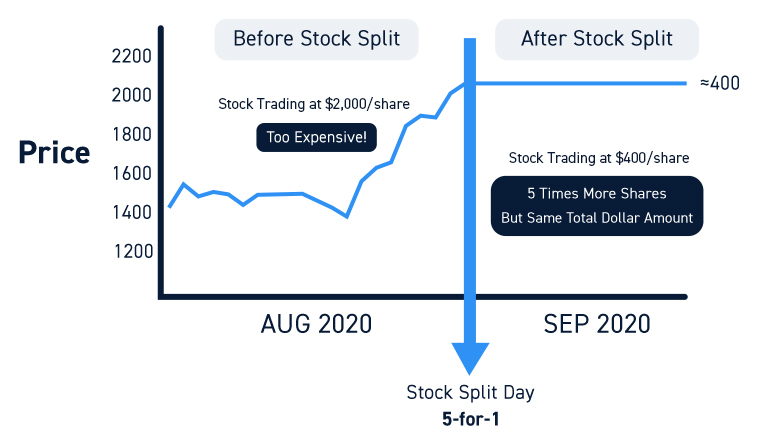
That split followed a period of strong earnings growth and a rapidly rising share price, with the aim of improving accessibility for everyday investors without changing the company’s underlying value.
Another notable example is Netflix’s announcement of a 10-for-1 forward split, intended to make its shares more affordable after a sustained increase in valuation.
Do Stock Splits Affect Valuation Metrics
From a valuation standpoint, stock splits are mechanically neutral. Metrics such as earnings per share, price-to-earnings ratios, and book value per share adjust proportionally to reflect the new share count. Market capitalisation remains unchanged at the time of the split.
That said, investor perception can shift. A lower share price may feel more approachable, even though the underlying economics are unchanged. This distinction between mathematical valuation and market psychology can influence short-term trading behaviour.
Common Misconceptions About Stock Splits
Stock splits create value for investors
Stock splits guarantee future price increases
Forward stock splits always signal strong fundamentals
Reverse stock splits are only used by failing companies
The type of stock split alone tells the full story
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Does a stock split make shares cheaper?
A stock split lowers the price per share, but it does not make the company cheaper in valuation terms. Market capitalisation and ownership value remain unchanged after the split.
2. Can a stock split increase a stock’s price over time?
A stock split itself does not cause price appreciation. Any post-split price movement depends on fundamentals, earnings growth, market conditions, and investor demand.
3. Do stock splits affect dividends?
Dividend amounts per share are adjusted proportionally after a split. The total dividend income an investor receives remains the same unless the company changes its dividend policy.
4. Are stock splits good for long-term investors?
Stock splits do not directly benefit long-term returns, but they can improve liquidity and accessibility. For long-term investors, company fundamentals matter far more than the split itself.
5. What happens to fractional shares after a stock split?
Fractional shares are automatically adjusted by brokers to reflect the new share structure. Investors retain the same proportional ownership without needing to take any action.
6. Should investors buy a stock just because it announced a split?
A split announcement alone is not a sufficient reason to invest. Investors should evaluate earnings, valuation, competitive position, and long-term growth prospects rather than relying on the split as a signal.
Conclusion
So, what is a stock split in simple terms? It is a corporate action that adjusts the number of shares in circulation and the price per share, without changing the total value of an investor’s holdings.
For companies, stock splits are tools to improve tradability, expand investor participation, meet exchange requirements, or position the share price within a preferred range.
For investors, a stock split represents a technical change in share structure,not a change in the company’s intrinsic value.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.