The IWM ETF (iShares russell 2000 etf) is one of the most widely traded exchange-traded funds in the United States. It provides broad exposure to small-cap American companies, making it a popular choice for investors seeking growth opportunities beyond large-cap stocks. Whether you're building a diversified portfolio or exploring tactical strategies, understanding the fundamentals of IWM is essential.
What Is IWM?

Launched by BlackRock under its iShares brand, the iShares Russell 2000 ETF (ticker: IWM) tracks the Russell 2000 Index—a benchmark comprising approximately 2.000 of the smallest publicly traded companies in the U.S. equity market. These are companies that typically fall just outside the S&P 500 in terms of market capitalisation.
IWM was introduced in May 2000 and has grown to become a key vehicle for accessing the small-cap segment of the U.S. market. The fund offers passive index exposure, meaning it seeks to replicate the performance of the Russell 2000 rather than outperform it.
This ETF is commonly used by institutional and retail investors alike, whether for hedging, short-term trading, or long-term investment. Its high trading volume also makes it a favourite among options traders and day traders.
Fund Size, Liquidity & Expense Ratio
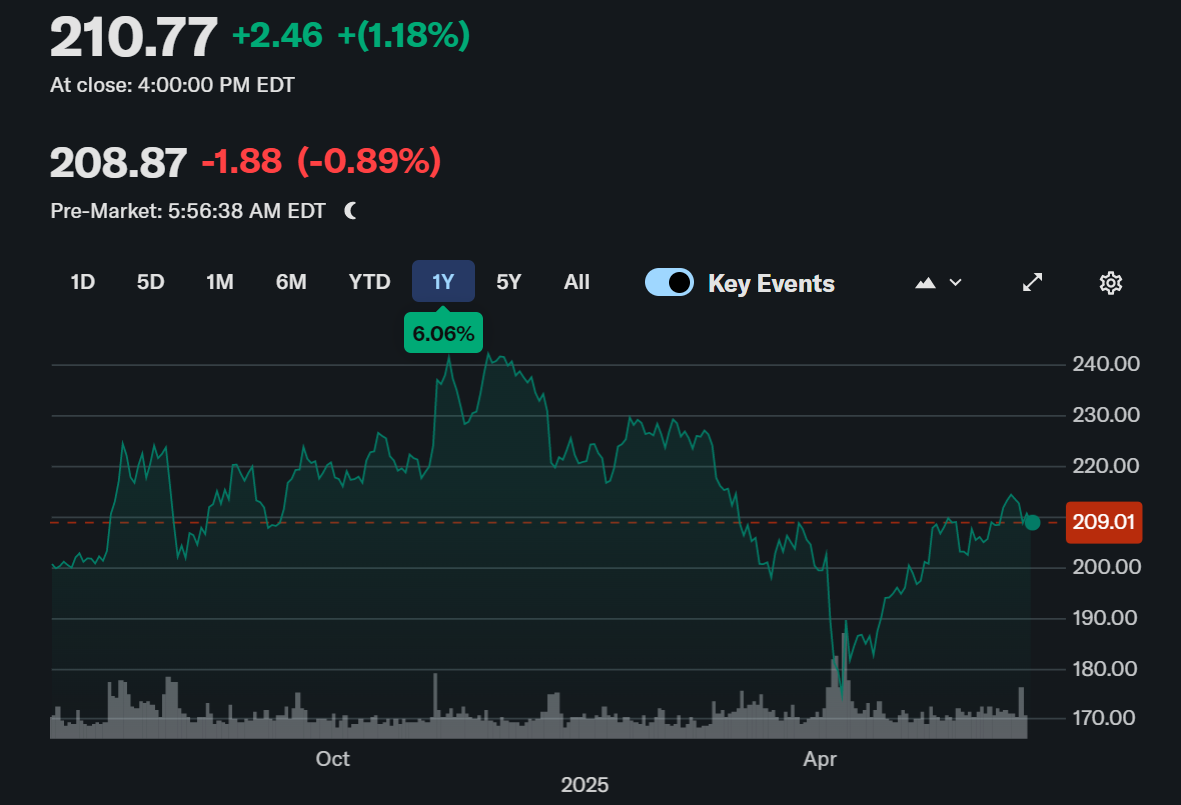 As of mid-2025. IWM manages over $65 billion in assets under management (AUM), placing it among the largest small-cap ETFs globally. The fund's daily trading volume regularly exceeds 25 million shares, reflecting its deep liquidity and tight bid-ask spreads.
As of mid-2025. IWM manages over $65 billion in assets under management (AUM), placing it among the largest small-cap ETFs globally. The fund's daily trading volume regularly exceeds 25 million shares, reflecting its deep liquidity and tight bid-ask spreads.
From a cost perspective, IWM charges an expense ratio of 0.19%, which is relatively standard for ETFs tracking niche or volatile market segments. While this is slightly higher than ultra-low-cost large-cap ETFs such as VOO or SPY, the cost is justified by the more complex and broader composition of the underlying index.
Importantly, the high liquidity of IWM makes it ideal for active traders and institutional players, as it allows for swift entries and exits with minimal slippage. This is a key advantage over some smaller, less liquid small-cap ETFs.
Portfolio Composition & Top Holdings
The IWM ETF tracks around 1.940 companies across a diverse mix of sectors, although the fund is more heavily weighted toward industrials, healthcare, financials, and consumer discretionary stocks.
Since it's a capitalisation-weighted index, no single company has a significant impact on the fund's overall performance. This is in contrast to large-cap ETFs where companies like Apple or Microsoft can dominate the index.
Top holdings typically account for less than 0.5% each and change regularly due to the fluid nature of small-cap companies. As of the latest data, IWM's largest holdings might include firms such as:
Super Micro Computer, Inc.
Axon Enterprise, Inc.
First Citizens BancShares, Inc.
However, the list of top names changes frequently due to market capitalisation rebalancing and volatility in the small-cap space.
Performance Metrics & Risk Profile
The historical performance of IWM is notably different from large-cap indices like the S&P 500. Over the past two decades, small-cap stocks have experienced higher volatility but have also delivered strong performance in certain economic cycles, particularly during early recoveries and periods of aggressive growth.
Here's a quick look at IWM's average total return (as of 2025. annualised):
1-year: +6.2%
3-year: +4.8%
5-year: +7.1%
10-year: +8.5%
The fund's beta is around 1.3. indicating higher volatility relative to the S&P 500. Investors should also consider the standard deviation of returns, which reflects increased risk and price fluctuation.
IWM tends to underperform during market downturns or periods of rising interest rates, as small-cap companies often have weaker balance sheets and less pricing power than their large-cap peers. However, it may outperform during economic expansions, making it a suitable choice for investors with a higher risk tolerance.
Ideal Investor & Suitability
IWM is best suited for investors looking to gain diversified exposure to U.S. small-cap equities, either as a core satellite holding or as a short-term trading instrument. It can play a valuable role in:
Diversified portfolios seeking broader U.S. equity exposure
Tactical allocations when small caps are expected to outperform
Hedging strategies due to its options liquidity and high turnover
However, it may not be ideal for risk-averse investors or those seeking consistent dividends, as small-cap companies are typically less established and more volatile. The ETF also has limited international exposure, which may be a concern for those wanting global diversification.
Additionally, IWM does not employ ESG screening, so investors with environmental or ethical preferences may wish to explore alternative funds in the small-cap space.
Final Thoughts
The iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM) offers an efficient and liquid way to access nearly 2.000 U.S. small-cap stocks in a single investment. It plays a vital role for both long-term investors seeking growth and traders looking to capitalise on market volatility.
While it comes with higher risk and greater price swings than its large-cap counterparts, IWM is an essential tool in the toolkit of investors who understand the dynamics of small-cap investing. With its robust liquidity, well-diversified holdings, and strong historical performance in economic upswings, IWM remains a compelling choice in 2025 for those willing to embrace the volatility that comes with opportunity.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



























