The Bear Flag pattern remains one of the most trusted signals in technical analysis for identifying the continuation of a downtrend.
This formation captures a pause in selling pressure before the market resumes its downward move, giving traders a crucial edge in timing entries and managing risk.
In this guide, we’ll break down how the Bear Flag forms, what it reveals about market sentiment, and how traders can use it to anticipate further price declines and refine their short strategies.
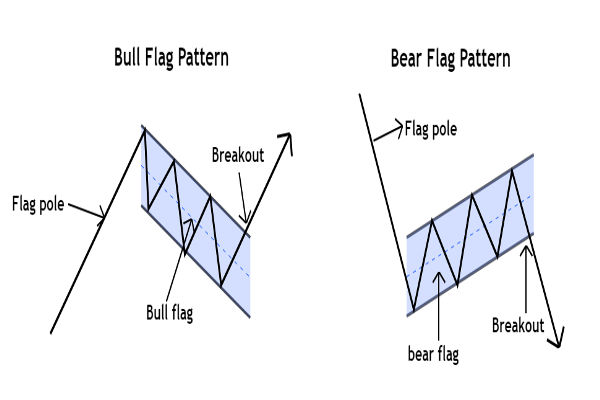
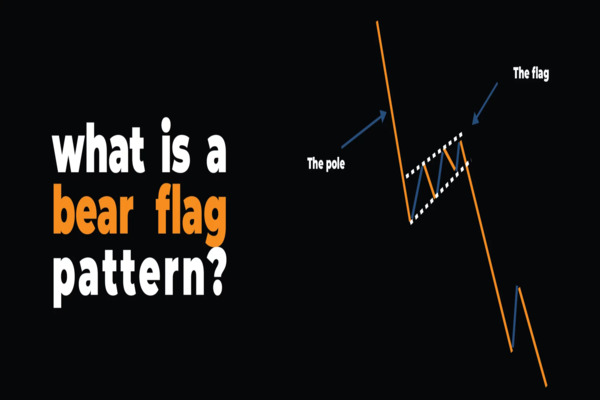
What Is a Bear Flag Pattern?
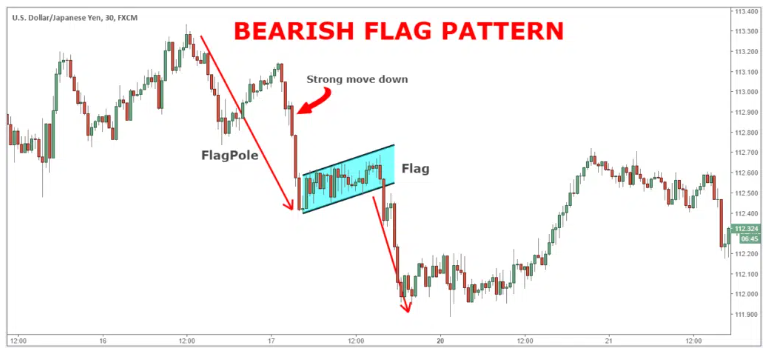
A Bear Flag pattern is a short-term continuation formation that appears during a downtrend. It signals a brief pause or consolidation before sellers regain control and drive prices lower.
The pattern reflects a temporary counter-move within broader bearish momentum, a moment when markets catch their breath before resuming the decline.
It consists of two distinct parts:
1. The Flagpole:
A steep, swift decline driven by strong selling pressure that sets the tone for the prevailing downtrend. This sharp move defines the pattern’s bearish foundation and signals aggressive momentum from sellers.
2. The Flag:
A brief consolidation phase where prices move within a tight, slightly upward or sideways channel. This pause reflects temporary buying or short-covering rather than a true reversal, often serving as the setup for the next leg lower.
When price breaks decisively below the lower boundary of the flag, the pattern is confirmed, and traders often interpret it as a signal for continued downside momentum.
Advantages and Disadvantages Of Bear Flag Pattern
Before you dive into using the Bear Flag pattern in your strategy, it’s important to understand that no chart formation is flawless.
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Provides clear continuation signals in established downtrends |
False signals can occur in volatile or range-bound markets |
| Offers defined entry and exit points based on breakout levels |
Requires confirmation through volume or other indicators |
| Useful for timing short-selling opportunities |
Misidentifying consolidation patterns may lead to premature entries |
| Works well across multiple timeframes (intraday to weekly charts) |
Pattern reliability decreases during low-liquidity periods |
| Helps traders align with broader market momentum |
Breakouts may fail if the overall trend weakens or reverses |
How to Spot a Bear Flag Pattern on Charts
The Bear Flag is one of those setups that looks deceptively simple but carries plenty of meaning for traders who understand market behavior.
It typically forms when a strong selloff pauses briefly before continuing lower, a pattern that reflects short-term exhaustion rather than a true shift in sentiment.
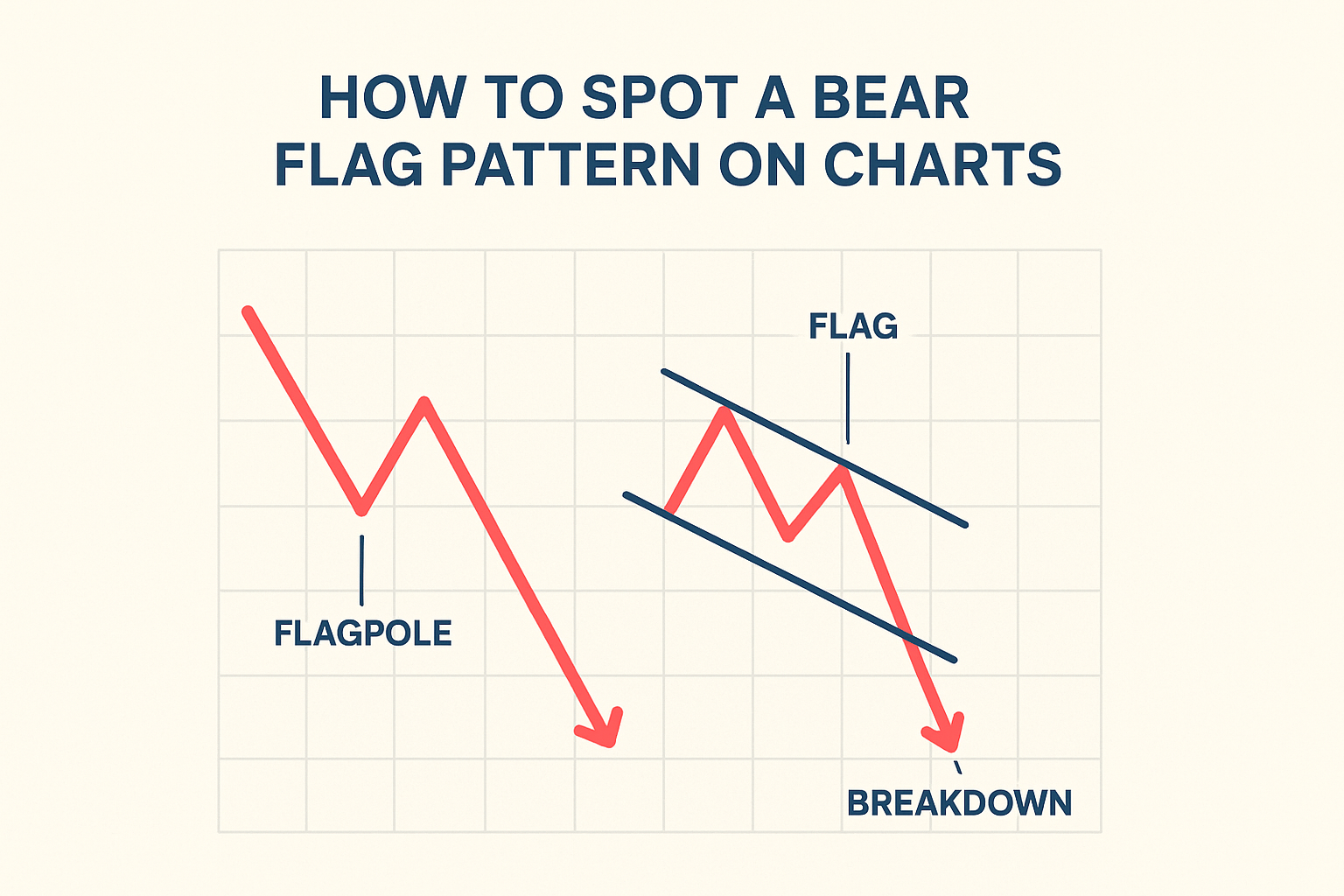 1. The Flagpole – The Sharp Drop:
1. The Flagpole – The Sharp Drop:
Every Bear Flag begins with a steep, almost vertical fall in price. This move shows that sellers are firmly in control and momentum is strong.
You’ll usually see heavier trading volume here, confirming that the market is in a decisive downtrend.
2. The Flag – The Pause Before the Next Move:
After that initial drop, prices start to move sideways or drift slightly higher in a narrow range. This short consolidation forms the “flag.” It represents a tug-of-war between bargain hunters and existing sellers, but typically lacks the strength to reverse the trend.
Volume often dips during this phase, hinting that the rally is running on low fuel.
3. The Breakdown – Continuation of the Trend:
The pattern completes when prices break below the lower boundary of the flag and selling pressure picks up again.
That’s the moment traders watch for: the potential resumption of the original downtrend. Many use the height of the flagpole to project how far the next leg lower might extend.
Bear Flag vs. Bear Pennant: Know The Difference
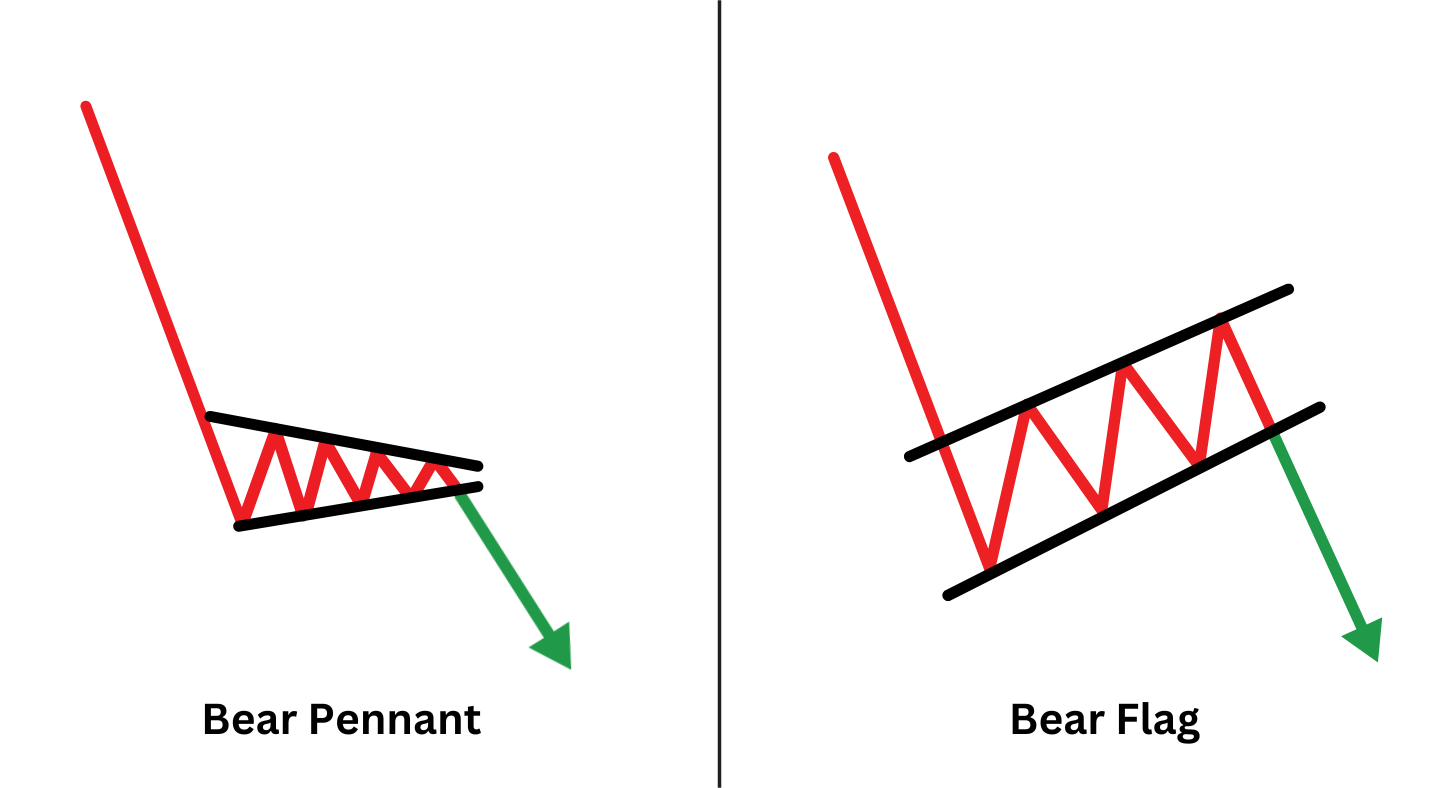
Many traders mix up the Bear Flag with the Bear Pennant because both show up during downtrends and often lead to another leg lower. The main difference is in how they look.
A Bear Flag forms when prices pause and move slightly upward or sideways in a rectangular shape after a sharp drop. In contrast, a Bear Pennant looks more like a small triangle, where prices tighten between two converging lines before breaking down again.
Common Beginner Mistakes
Many traders jump in too early, selling before the price breaks below the flag’s lower boundary with convincing volume. Others mistake a long consolidation for a Bear Flag when it’s really a reversal.
Volume is often ignored, even though fading volume during the pause and strong volume on the drop are key signals. Finally, poor risk control like over-leveraging or placing stops too tight can turn a good setup into a costly one.
Investor Trading Tips
Entry Point: Enter a short trade only after the price clearly breaks below the flag’s lower trendline, confirming bearish momentum.
Profit Target: Estimate your target by measuring the flagpole’s height and projecting that distance downward from the breakout point.
Stop Loss: Set a stop-loss slightly above the flag’s upper boundary to limit potential losses if the pattern fails.
Volume Confirmation: Look for rising volume on the breakout; stronger volume adds credibility to the move.
Combine with Indicators: Strengthen your setup by using confirmation tools such as moving averages, RSI, or MACD to gauge trend strength and momentum.
These steps help traders trade Bear Flags with greater precision, balancing opportunity with proper risk control.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1.Is the Bear Flag pattern accurate?
It’s reliable in downtrends but can give false signals in volatile or low-volume markets.
2: How do I trade with the Bear Flag pattern?
Short after a breakdown below the flag, set stop above the flag, target equals flagpole height.
3: Bear Flag vs Bear Pennant?
Flag: rectangular consolidation. Pennant: small triangle. Both continue downtrends.
Final Thoughts
The Bear Flag remains one of the most practical continuation patterns for traders navigating bearish markets. When identified correctly, it can offer a clear roadmap for timing short entries and managing downside exposure.
The key lies in confirmation to watch for volume expansion on breakdowns, maintain disciplined stop-loss levels, and align trades with the broader market trend.
In volatile conditions like those seen in 2025, precision and patience matter more than speed. The traders who treat the Bear Flag as part of a structured strategy, rather than a standalone signal, are often the ones who stay consistent when markets turn unpredictable.
Practice these strategies first in a forex demo account. These risk-free environments let you hone your bear flag recognition and test trade execution without putting real money on the line.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 1. The Flagpole – The Sharp Drop:
1. The Flagpole – The Sharp Drop: