What Is Dollar-Cost Averaging?
Dollar-cost averaging (often shortened to DCA) is a simple yet effective investment strategy where you put a fixed amount of money into a particular asset or fund at regular intervals—regardless of whether the price is high or low. The aim is to spread your investment over time rather than committing all your money in one go.
It's especially popular among those who don't want to—or simply can't—predict the perfect time to invest. Instead of trying to time the market (which even professionals struggle to do consistently), DCA takes a more methodical and disciplined approach. It helps traders ease into the market while potentially reducing the risks tied to sudden price swings.
In short, DCA is more about consistency than clever timing. And for many, that can make all the difference.
How DCA Works in Practice
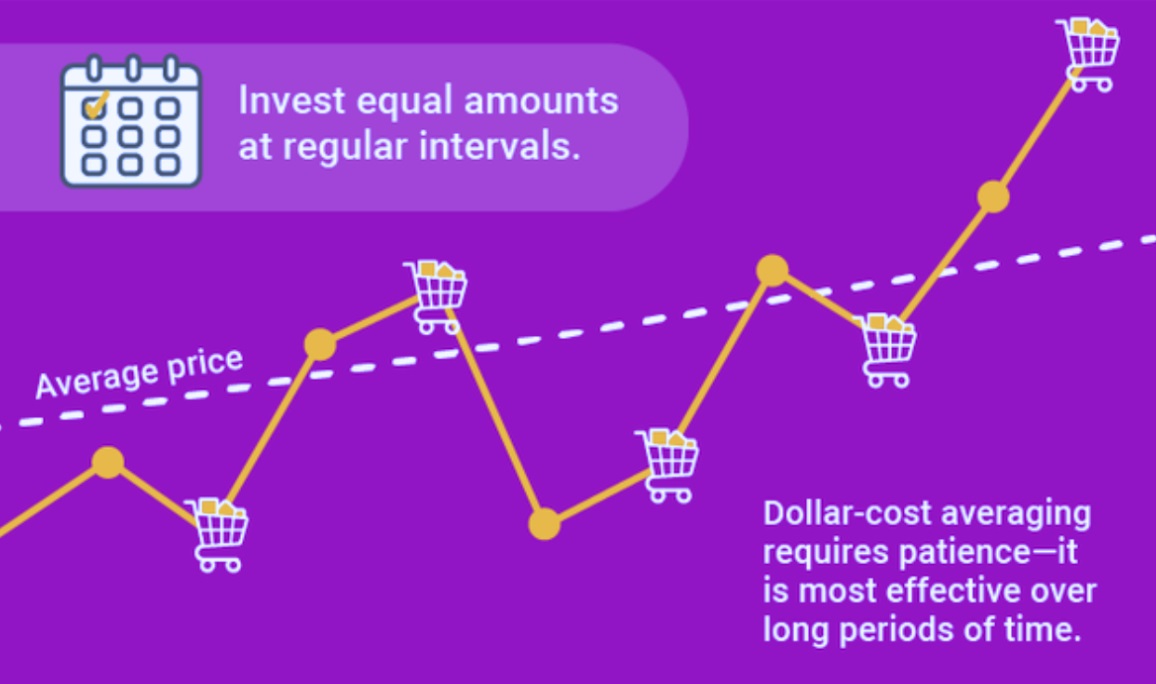
Imagine you want to invest £2.000 in a particular stock or index fund. Rather than investing the full amount at once, you might decide to invest £200 every month for 10 months. If the price goes down, your £200 buys more shares; if it goes up, it buys fewer. Over time, you'll have purchased shares at a variety of prices—some high, some low—which helps to average out your cost per unit.
This strategy is most often used in long-term investing, especially when people are contributing to pensions or building wealth gradually through savings plans. It's also well suited for beginners who may not feel confident trying to "read" the market or who simply don't have a large lump sum to invest all at once.
Automated investing tools, such as those offered by digital platforms and robo-advisers, often make it easy to set up and maintain a DCA approach. Once the plan is in place, it typically runs on autopilot—investing the same amount, on the same day, every month.
Benefits of Regular Investing
One of the main benefits of DCA is that it helps reduce the emotional pressure that often comes with investing. When markets fall, many traders panic and sell. When prices surge, others rush in out of fear of missing out. DCA helps sidestep these highs and lows by sticking to a consistent plan. You're not making decisions based on headlines or gut feelings—just routine.
It also removes the guesswork. Since you're investing the same amount regularly, you don't have to worry about finding the "right" moment to invest, which frankly, is often impossible to determine in real time.
DCA can also help traders avoid the risk of putting all their money into the market just before a downturn. By spacing out your investments, you reduce the chance of suffering large losses from poor timing.
Finally, it's a great way to build healthy financial habits. Making investing a monthly routine—just like paying a bill or saving for a holiday—encourages discipline and long-term thinking.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Although DCA is straightforward, it's not entirely foolproof. One of the most common mistakes is stopping the plan too soon—especially during market downturns. DCA works best over the long term, so pulling out early defeats the purpose of smoothing out the ups and downs.
Another mistake is being too hands-off. While it's good to avoid constant tinkering, it's also important to review your strategy occasionally. Make sure the assets you're investing in still align with your goals and risk tolerance.
People also sometimes forget that DCA doesn't protect you from losses if the overall market declines over time. It helps with volatility, not poor performance. Choosing quality investments remains essential.
Lastly, some traders expect DCA to deliver better returns than lump-sum investing. The truth is, if markets are rising steadily, lump-sum investing often performs better. DCA is more about managing risk and emotional behaviour than squeezing out the highest return.
Is DCA Right for You?
Dollar-cost averaging isn't a silver bullet, but it can be a very practical and reassuring strategy—especially for new traders or those with a regular income and a long-term outlook. It works particularly well if you prefer a steady, low-stress approach to building your portfolio.
If you find market volatility unnerving, or if you want to build wealth gradually without trying to predict price movements, DCA is likely a good fit. It also suits those who value structure and want to form consistent saving habits.
That said, it's not always the most efficient route if you already have a lump sum ready to go and are investing for the long term. In those cases, it may be worth speaking to a financial adviser about what makes most sense based on your specific goals and risk appetite.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.