In the world of fixed income, investors are often faced with a choice between short-term security and long-term potential. The BIL ETF, formally known as the SPDR Bloomberg 1-3 Month T-Bill ETF, has grown in popularity as a low-risk, ultra-short-term option. Meanwhile, longer-term bonds remain a traditional avenue for those seeking yield and capital appreciation over time.
When comparing the bil etf with longer-term bonds, the decision largely depends on your investment horizon, risk tolerance and expectations for interest rates. While both belong to the fixed-income family, their behaviours under different market conditions are distinctly different.
What Is the BIL ETF?
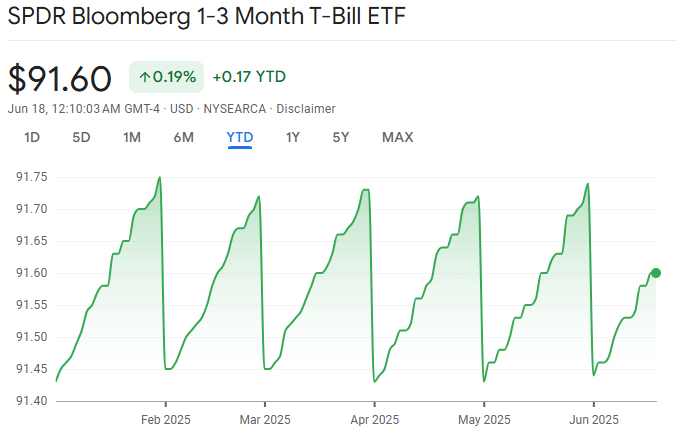
The bil etf is designed to track the performance of US Treasury bills with maturities between one and three months. These are considered among the safest assets in the financial world, backed by the full faith and credit of the US government. As a result, the bil etf is frequently used by investors looking for liquidity and minimal volatility.
One of the defining features of the bil etf is its low duration. Duration refers to how sensitive a bond’s price is to changes in interest rates. Because the bil etf holds ultra-short-term securities, its duration is very low, which means it is highly resistant to interest rate movements. This makes it a popular place to park cash during periods of uncertainty.
The Role of Longer-Term Bonds
Longer-term bonds, on the other hand, typically refer to government or corporate debt instruments with maturities of 10 years or more. These bonds usually offer higher yields to compensate for the greater risks associated with long-term lending, such as inflation and interest rate changes.
While the bil etf offers capital preservation, longer-term bonds provide more potential for total return. However, they also come with more volatility. A rise in interest rates, for example, can significantly reduce the market value of a long-term bond. Conversely, falling rates can cause bond prices to rise, creating opportunities for capital gains.
Income Potential: Bil ETF vs Longer-Term Bonds
One of the clearest distinctions between the bil etf and longer-term bonds is income generation. In general, longer-term bonds offer higher yields. Investors looking for steady income might favour these instruments when rates are stable or falling.
However, when interest rates are rising, short-term instruments like the bil etf can offer competitive yields without the price risk. This is particularly relevant in environments where central banks are tightening monetary policy. As yields on short-term Treasury bills increase, so too does the yield on the bil etf, often adjusting more quickly than long-term bonds.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
The bil etf has an extremely low sensitivity to interest rate movements. This makes it appealing during periods of rate hikes, as it maintains its value while still offering modest returns. Investors do not face significant capital losses with the bil etf even if interest rates surge.
In contrast, longer-term bonds are highly sensitive to rate changes. Their prices move inversely to interest rates, meaning a significant hike can erode their value quickly. Investors holding these bonds to maturity may still receive their full principal and interest, but those needing to sell early could face losses.
Liquidity and Flexibility
Liquidity is another major consideration when comparing the bil etf to longer-term bonds. The bil etf is highly liquid, trading actively on major exchanges and allowing investors to move in and out quickly. Its short maturity profile also makes it ideal for tactical shifts in asset allocation.
Longer-term bonds are less liquid, particularly in volatile market conditions. Some may trade on secondary markets, but with wider spreads and potential pricing inefficiencies. For investors seeking flexibility, the bil etf is usually the more convenient and accessible option.
Inflation Considerations
Inflation plays a critical role in fixed income investing. Longer-term bonds are more vulnerable to inflation, as rising prices erode the real value of their fixed payments. Over a decade or more, this can have a substantial impact on real returns.
The bil etf, while also exposed to inflation, adjusts more quickly as it constantly rolls over into new short-term securities. In a rising inflation environment, yields on Treasury bills tend to move higher, helping the bil etf to keep pace better than fixed long-term bonds.
Strategic Allocation
Many investors do not choose one over the other but instead use both. The bil etf is often used for short-term liquidity needs, emergency funds or as a place to park capital temporarily. It is also favoured during periods of uncertainty or when the yield curve is inverted.
Longer-term bonds are typically used for liability matching, income generation or to add duration to a portfolio. They are more suitable for investors with long time horizons and a tolerance for interim volatility. The two serve different purposes, and understanding these roles is key to constructing a balanced fixed income strategy.
Which Is Better?
There is no universal answer to whether the bil etf or longer-term bonds are better. The right choice depends entirely on your goals. If you are looking for stability, capital preservation and minimal sensitivity to rates, the bil etf is likely the more suitable choice. It performs particularly well in volatile or rising rate environments.
If, on the other hand, you seek higher income, potential capital gains and can tolerate more risk, longer-term bonds may offer better long-term performance. They reward investors willing to endure the ups and downs of interest rate cycles.
Conclusion
The decision between the bil etf and longer-term bonds is ultimately one of risk, time horizon and market outlook. The bil etf offers unmatched safety and liquidity, ideal for conservative or tactical investors. Longer-term bonds, while riskier, provide opportunities for higher returns and diversification.
A well-structured portfolio may contain both, using the bil etf for cash management and flexibility, while reserving long-term bonds for income and growth. By understanding the distinct advantages and drawbacks of each, investors can position themselves more effectively in changing market environments.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



























