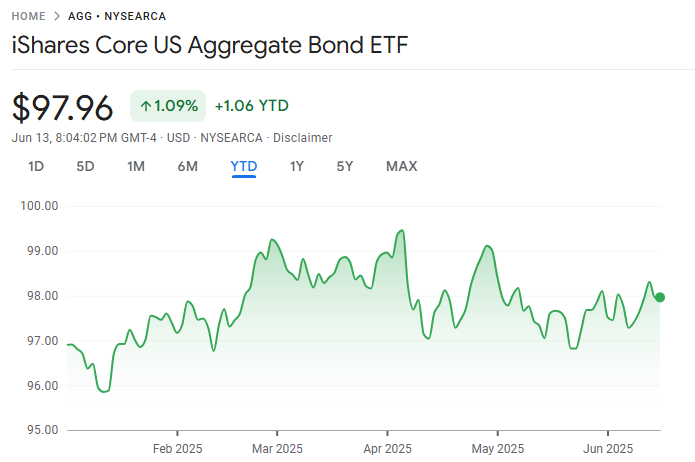
AGG refers to the iShares Core US Aggregate Bond ETF, one of the most widely recognised and traded bond ETFs in the market. It serves as a comprehensive benchmark for the US investment-grade bond market, tracking the Bloomberg US Aggregate Bond Index.
Investors interested in fixed income often consider AGG because it offers broad exposure to government, corporate, and mortgage-backed bonds. The fund provides an efficient way to gain diversified bond market exposure without purchasing individual bonds.
Because bonds can be complex and time-consuming to select, AGG simplifies the process by holding a basket of thousands of bonds, replicating the overall US bond market's performance. This makes AGG particularly appealing for investors seeking steady income and risk mitigation in their portfolios.
Why Should You Consider Investing in AGG ETF?
AGG is popular because it offers several benefits that can enhance an investment portfolio. Firstly, it provides instant diversification across various types of bonds, sectors, and maturities. This diversification reduces the risk of heavy losses if any single bond or sector underperforms.
Secondly, AGG offers liquidity. As one of the largest bond ETFs, it trades actively on major exchanges, allowing investors to buy or sell shares quickly and at transparent prices. This liquidity is crucial for those who want flexibility in managing their bond holdings without the hassle of dealing directly in the bond market.
Additionally, AGG is known for its low expense ratio. Keeping costs low is vital for long-term investors, as fees can significantly erode returns over time. The cost-efficiency of AGG makes it a cost-effective way to access the broad bond market.
How AGG Fits Into a Balanced Portfolio
AGG often plays a core role in a diversified investment strategy. Bonds typically provide stability and income, offsetting the volatility often seen in equity markets. By including AGG in a portfolio, investors can reduce overall risk while maintaining steady returns.
Investors who want to balance growth-oriented assets like stocks with safer, income-generating investments often turn to AGG. It acts as a ballast during market downturns, as bonds usually move inversely or less correlated to equities. This feature helps smooth portfolio returns and protect capital in uncertain times.
Moreover, AGG can be used for strategic asset allocation or tactical shifts. For example, some investors increase their exposure to AGG when anticipating stock market volatility or economic slowdowns. Others maintain a consistent allocation to AGG as part of their long-term investment plan.
What Are the Risks Associated with AGG?
While AGG provides many benefits, it is important to understand the risks involved. As a bond ETF, AGG is subject to interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, bond prices generally fall, which can lead to a decrease in AGG's value. Conversely, when rates fall, bond prices tend to increase, potentially boosting AGG's performance.
Credit risk is another factor. Although AGG invests primarily in investment-grade bonds, there is always some risk that bond issuers could default. This risk is mitigated through diversification but cannot be entirely eliminated.
Inflation risk is also relevant. If inflation rises faster than the income generated by bonds in AGG, investors may experience a decline in purchasing power. Therefore, some investors combine AGG with other assets or inflation-protected securities to hedge against this possibility.
How to Buy and Manage AGG ETF
Purchasing shares of AGG is straightforward for most investors. It can be bought through most brokerage accounts like EBC just like stocks. This accessibility, combined with its liquidity, makes AGG a convenient option for both individual and institutional investors.
Managing an investment in AGG requires understanding your overall financial goals and risk tolerance. Since AGG is a core bond holding, it is essential to determine the appropriate allocation within your portfolio. Rebalancing periodically ensures your portfolio maintains its intended risk-return profile.
Investors should also monitor interest rate environments and economic conditions, as these factors influence AGG's performance. Staying informed helps investors make decisions about when to adjust their holdings or diversify further.
Conclusion
AGG is a versatile and popular bond ETF that provides broad exposure to the US bond market. Its diversification, liquidity, and low costs make it an attractive choice for many investors seeking stability and income. While it carries risks related to interest rates and credit quality, these can be managed through thoughtful portfolio construction.
Whether you are a beginner looking to add bonds to your portfolio or an experienced investor seeking a core fixed income holding, AGG is worth considering. It offers a simple and effective way to participate in the bond market with the convenience of an ETF.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.