India, the world's most populous country and fifth-largest economy, plays a massive role in global finance, trade, and investment. At the heart of its economic identity is the Indian Rupee (INR), the official currency that fuels transactions across markets, businesses, and households.
In 2025, the strength of the Indian Rupee remains a key focus for traders, investors, and policymakers alike.
This guide explains the indian currency, including its origins, current role, and projected valuation in 2025. It also examines its performance in global markets and the factors that impact its strength.
What Is the Currency in India?
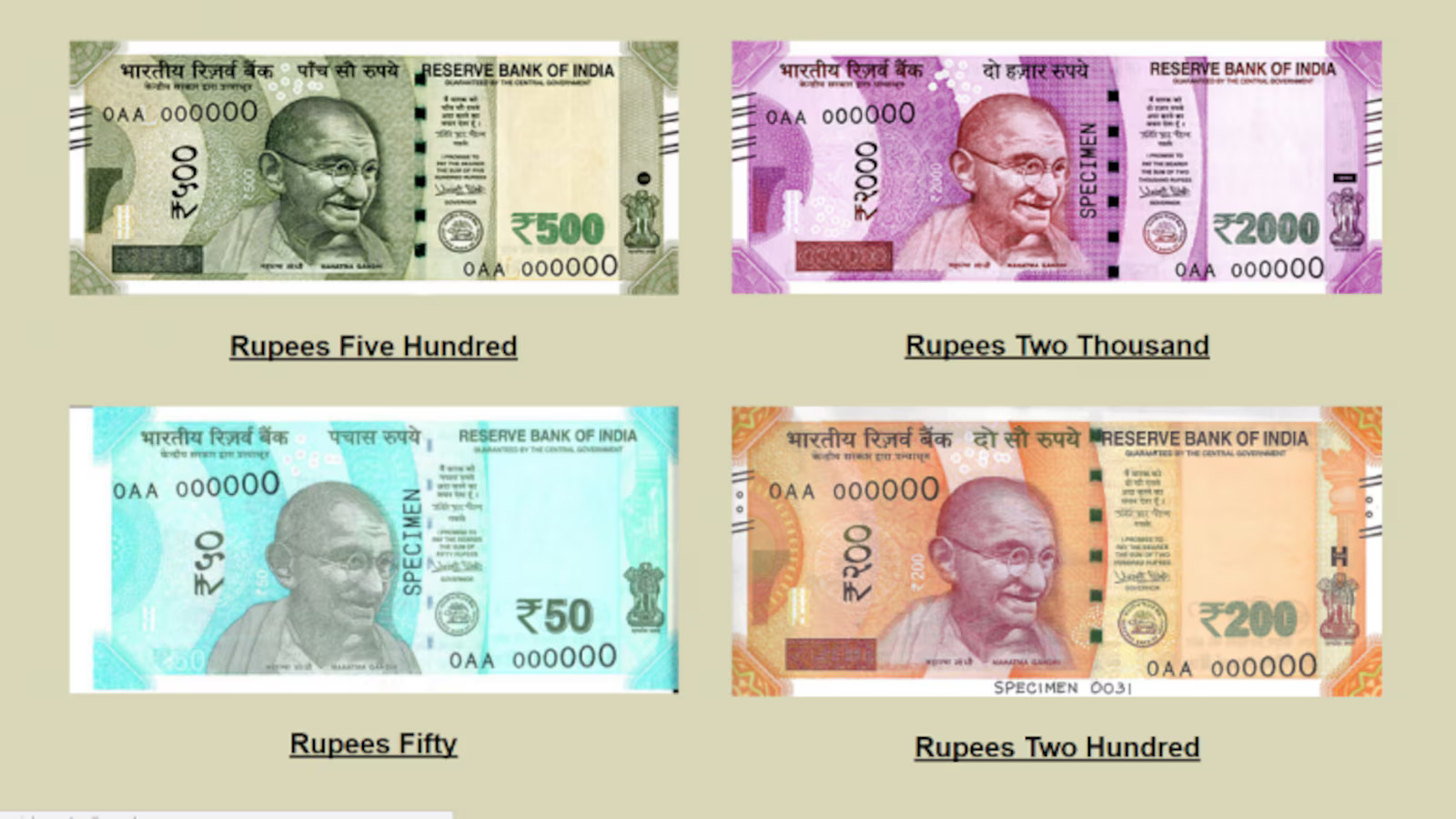

The Indian Rupee is the official currency of India, issued and managed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Its currency code is INR, and its symbol is ₹. One rupee is subdivided into 100 paise, although smaller denominations are increasingly rare in circulation.
The rupee is a fiat currency, meaning it is not backed by a physical commodity such as gold but by the economic stability and credibility of the Indian government and central bank.
A Brief History of the Indian Currency
The Indian Rupee has evolved through centuries of economic and political shifts:
The name "rupee" is derived from the Sanskrit word rupyakam, meaning "silver coin".
During the Mughal Empire and British colonial rule, silver-based coins were standard.
After gaining independence in 1947, India introduced its own currency, which was distinct from the British.
In 1991, India liberalised its economy and adopted a more market-driven currency valuation model.
In 2016, a significant monetary reform took place through demonetisation, which impacted currency circulation and promoted digital payments.
Over time, the rupee has transformed from a silver coin to a digital medium of exchange, reflecting India's economic journey.
What Is the Value of the Indian Rupee in 2025?
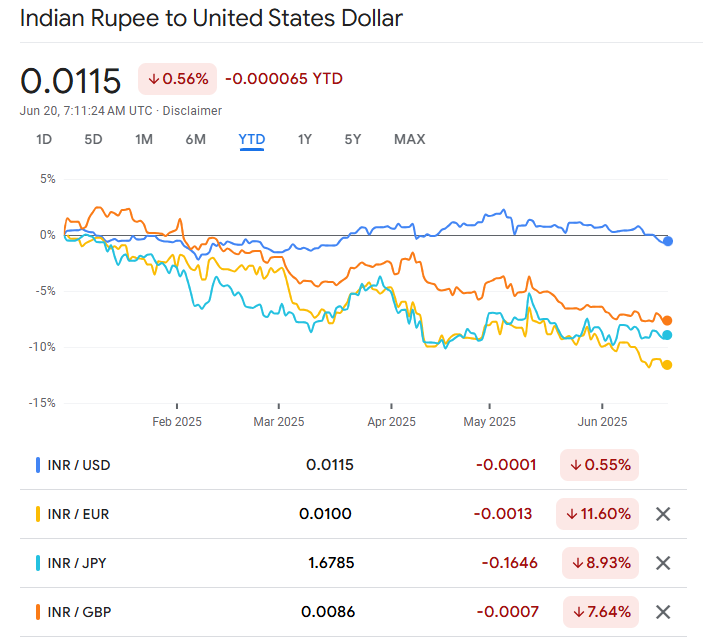
As of mid-2025, the Indian Rupee trades in a range of ₹82 to ₹84 per US dollar, reflecting a relatively stable trend compared to previous years. While the rupee has faced historical depreciation against the dollar, recent monetary tightening by the RBI and steady economic growth have helped stabilise the currency.
Against other major currencies:
₹1 equals approximately 0.0119 USD
₹1 equals approximately 0.0110 EUR
₹1 equals approximately 1.75 JPY
₹1 equals approximately 0.0093 GBP
Despite moderate fluctuations, the rupee remains broadly stable in 2025, thanks to India's increasing foreign exchange reserves, low current account deficit, and resilient services exports.
Is the Indian Rupee Strong or Weak in 2025?
To assess the strength of a currency, economists consider both its external value (other currencies) and internal purchasing power (domestic inflation and real income).
In 2025, the Indian Rupee is relatively moderately valued:
It is not as strong as currencies like the US Dollar, British Pound, or Swiss Franc in forex terms.
However, it is not excessively weak either, given India's improving fiscal health, trade competitiveness, and foreign investor confidence.
Inflation in India has moderated to around 4.5%, maintaining the rupee's internal strength.
The RBI has held policy rates steady while defending the rupee through market interventions when necessary.
In summary, while the rupee is not among the strongest global currencies, it is not in crisis. It remains regionally strong and stable enough to support trade and investment in South Asia.
Factors That Affect the Indian Currency's Strength
1) Monetary Policy
The RBI's decisions on interest rates and liquidity impact the rupee. Higher interest rates attract foreign capital inflows, supporting the currency. Conversely, rate cuts can weaken the rupee.
In 2025, the RBI has maintained a balanced stance, neither overtly hawkish nor dovish, which has helped avoid extreme volatility.
2) Foreign Investment
India continues to receive significant foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment. Sectors such as technology, manufacturing, and green energy attract foreign capital, increasing INR's demand.
Large inflows from institutional investors (FIIs) also support the rupee, especially during equity market rallies.
3) Trade Balance
India's trade balance—the difference between imports and exports—affects its demand. A widening trade deficit can pressure the currency, while strong exports (like IT services or pharmaceuticals) provide support.
In 2025, India's services exports remain robust, offsetting a slight rise in oil import costs.
4) crude oil prices
India is a major oil importer. When global crude oil prices surge, the demand for dollars increases, leading to rupee depreciation. In 2025, relatively stable oil prices near $80 per barrel have reduced pressure on the rupee.
5) Geopolitical Events
Global uncertainties such as wars, sanctions, or financial tightening can lead to safe-haven flows towards the USD, negatively impacting the rupee.
However, India's diplomatic balancing and internal reforms have helped insulate it against such shocks in recent years.
INR in the Forex Market

The Indian Rupee is actively traded in the foreign exchange (forex) market, primarily through these pairs:
USD/INR (US Dollar to Indian Rupee)
EUR/INR (Euro to Indian Rupee)
GBP/INR (British Pound to Indian Rupee)
JPY/INR (Japanese Yen to Indian Rupee)
Among them, USD/INR is the most liquid and widely tracked pair, used by businesses, traders, and the RBI to gauge currency trends.
Forex trading in INR is growing due to:
India's expanding role in global trade
More retail participation in online trading
Hedging needs by exporters and importers
RBI's gradual liberalisation of currency futures and options
In 2025, India's currency markets have matured and received better regulation, with NSE and BSE offering INR-based forex derivatives for hedging and speculation.
Is the Indian Rupee a Good Currency for Traders?
For forex traders, the rupee offers both opportunities and challenges:
High volatility during news events makes it attractive for short-term traders.
Interest rate differentials between INR and USD can create carry trade setups.
Liquidity is strong in USD to INR, but other INR pairs may have wider spreads.
Geopolitical headlines and RBI intervention can lead to unpredictable price swings.
Beginner traders should grasp the fundamentals of INR, pay attention to central bank actions, and implement risk management strategies when trading INR pairs.
Future Outlook: What's Ahead
Looking ahead, the Indian Rupee is expected to:
Trade in a controlled range, thanks to active RBI management
Benefit from India's GDP growth, forecast at around 6.5%
Strengthen if India's export markets continue to expand
Face challenges from global tightening cycles or oil price spikes
Some analysts project INR to appreciate modestly against the dollar if inflation remains under control and fiscal discipline continues.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the Indian Rupee may not rival the US dollar in terms of global dominance, it has carved out a growing and respected role in international trade and emerging market portfolios. In 2025, the Indian economy has demonstrated resilience by effectively managing domestic inflation, global pressures, and the growth of its digital ecosystem.
For investors, forex traders, and global businesses, understanding the movements of the Indian Rupee (INR) provides valuable insights into one of the world's fastest-growing economies. As India continues to expand its economic influence, the INR is expected to gain greater significance both regionally and globally.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.




























