Since the Bank of Japan announced its interest rate hike, the global economic situation has been significantly affected by it, focusing investors' attention on Japan. With the volatility of the global economy and the frequent adjustments of monetary policies in various countries, the market is looking forward to the upcoming meeting of the Bank of Japan, which is expected to trigger the attention and reaction of the global market once again. In this regard, let's take a closer look at the Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution and its implications.

What is the BOJ?
Its official name is the Bank of Japan (Bank of Japan, BOJ), Japanese for "Bank of Japan" (にっぽんぎんこう), referred to as "Bank of Japan" (にちぎん). It was founded in 1882 and is headquartered in Tokyo. As the central bank of Japan, it is responsible for implementing monetary policy, maintaining financial stability, and promoting economic growth.
The Bank of Japan's leadership structure is headed by a president and two vice presidents, who together are responsible for the bank's operations and decision-making. The Bank's highest decision-making body is the Policy Board, which consists of the president, vice presidents, and other experts well-versed in economics and finance.
The Policy Board is responsible for formulating and implementing monetary policy to ensure the stability of the Japanese economy and the safe operation of the financial system. Members of the Board jointly participate in discussions and decision-making on the economic situation and policy options based on their expertise and experience to support the Bank of Japan's efforts in realizing its mission and objectives.
The Bank of Japan is the only institution in Japan authorized to issue yen bills and coins and is responsible for managing and supervising the nation's money supply. Its responsibilities include formulating and implementing monetary policy and regulating the money supply with the aim of maintaining economic stability and price stability.
By adjusting interest rates and other monetary policy instruments, the Bank of Japan is committed to the goals of achieving price stability and promoting economic growth. Therefore, the monetary policy set and implemented by the Bank of Japan not only affects the stability of the domestic economic environment but also has a direct impact on the operation of the financial system and the development of the market.
The Bank of Japan ensures the stable operation of the financial system and actively prevents and responds to possible financial crises by supervising and regulating banks and other financial institutions. This includes formulating supervisory policies, reviewing the capital adequacy and risk management practices of financial institutions, and overseeing the operation of financial markets. The Bank of Japan is committed to maintaining the health and stability of the financial system to support the sustainable development of the national economy.
In addition, the Bank of Japan manages and maintains domestic payment and settlement systems to ensure the safety and efficiency of financial flows. By supervising and regulating the operation of the payment system, the Bank of Japan ensures the smoothness and security of the payment and settlement process and facilitates economic activities.
The Bank of Japan also actively participates in the stabilization and development of international financial markets, cooperates with the central banks of other countries and international financial institutions to address global financial challenges, and promotes the safe and efficient operation of international payment and settlement systems. These initiatives not only enhance the reliability of the payment system but also contribute to the efficiency and stability of overall economic operations.
The Bank of Japan utilizes a variety of policy tools to achieve its monetary policy objectives, with interest rate policy being one of the most prominent tools. By adjusting the benchmark interest rate, the central bank directly influences market interest rates, thereby regulating the borrowing behavior of consumers and businesses. Raising interest rates helps to curb inflation, while lowering them stimulates economic growth, which is especially important in times of economic downturn.
In addition, central banks use an asset purchase policy known as Quantitative Easing (QE) to increase market liquidity by purchasing Treasury bonds and other financial assets. Such a policy not only reduces long-term borrowing rates and promotes consumption and investment activities, but also provides support during economic downturns or financial market stress and improves liquidity conditions in financial markets.
The Bank of Japan also communicates to the market the future direction of its monetary policy and its decision-making criteria through forward guidance to manage market expectations and promote economic stability. In recent years, in the face of the challenges of low inflation and slow economic growth, the Bank of Japan has implemented a very accommodative monetary policy, including keeping interest rates at very low levels and large-scale purchases of financial assets, to boost economic activity and the level of inflation while facing the risks of asset price bubbles and the negative impact of long-term interest rates.
In short, the Bank of Japan plays a key role in the Japanese economy, maintaining price stability, promoting economic growth, and ensuring the health and stability of the financial system through a variety of policy instruments. As the only institution authorized to issue yen bills and coins in Japan, the Bank of Japan is responsible for managing the money supply and influencing market activity through measures such as adjustments in interest rate policy, asset purchases, and forward guidance. These policies are designed to address the challenges of prolonged low inflation and slow economic growth by stimulating consumption and investment, raising inflation, and supporting the health of the economy.
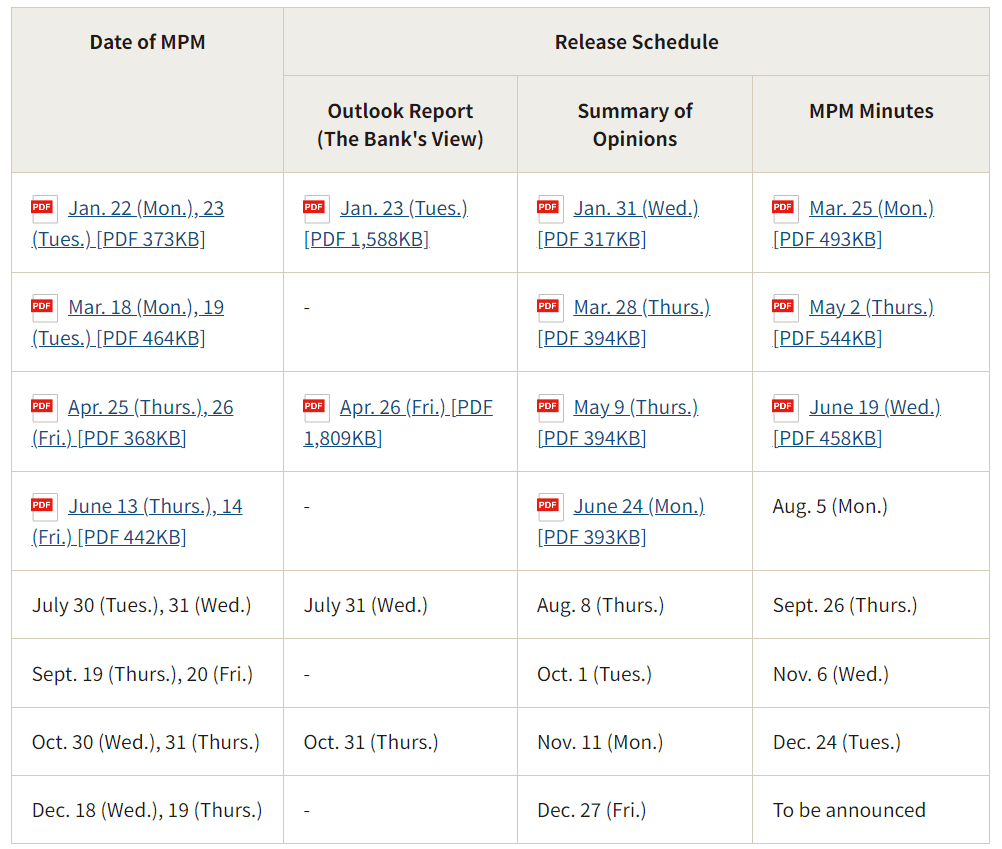
Bank of Japan Interest Rate Resolution
The Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution is one of the most important parts of its Monetary Policy Meeting (MPM). These meetings are usually held eight times a year and are announced in advance by the Bank of Japan. Usually on the second (i.e., last) day of the meeting, the Bank of Japan releases the interest rate resolution and the related policy statement. The exact time is usually around noon (Japan time) on the same day, and the 2024 interest rate resolution schedule is shown above.
The Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution, which determines whether to expand or scale back its asset purchase programs, including government bonds, corporate bonds, and other assets, is an important consideration for the Bank of Japan in the conduct of its monetary policy. These asset purchase programs are designed to increase market liquidity, lower long-term interest rates, and promote the goals of economic growth and inflation. By adjusting the size of purchases and the types of purchases, the Bank of Japan has the flexibility to respond to economic conditions and inflation expectations in order to achieve the objectives of monetary policy.
When deciding on interest rates and asset purchase programs, the Bank of Japan bases its assessment on the latest economic data and inflation forecasts. Its interest rate decisions take into account the overall growth trend of the Japanese economy and the level of inflation, as well as factors affecting the global economy and financial markets. The context for policy adjustments includes the strength of the current economic environment and domestic and foreign policy objectives aimed at promoting economic growth and ensuring price stability.
Policy guidance is an important tool for the Bank of Japan to communicate the future direction of monetary policy to the market, guiding the market's expectations for future interest rates and policy measures through the issuance of economic forecasts and strategy statements. Such guidance helps investors and economic participants predict economic trends and promotes market stability and economic growth.
The content of the interest rate resolution, which has attracted the most market attention in recent years, is the Bank of Japan's decision on whether to adjust its main policy rates, such as short-term and long-term interest rates. The Bank of Japan has maintained negative interest rates for seventeen consecutive years by adopting an accommodative monetary policy aimed at stimulating economic activity and boosting inflation. The objective of such policy measures is to encourage consumption and investment by lowering the cost of borrowing in order to promote economic growth and address the challenge of low inflation in the long term.
Effective March 19. 2024. the Bank of Japan announced an increase in interest rates to 1%. This decision triggered widespread market reaction and concern. As the economic and inflationary situation develops further, the market and investors are anticipating and watching the BOJ's future interest rate resolutions. Whether or not the rate hike will continue to be the focus of close attention from the public and investors, as it will have far-reaching impacts on the Japanese economy, financial markets, and the global economy,.
It is important to realize that the Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution has a significant impact on the financial market, especially in terms of the exchange rate. When the Bank of Japan raises interest rates, it may lead to the appreciation of the yen because high interest rates attract more capital inflows; conversely, lower interest rates may lead to the depreciation of the yen because of the decline in investment attractiveness. Such exchange rate changes directly affect Japan's international trade and investment competitiveness.
Meanwhile, the Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution has a broad impact on the stock market, not only involving the Japanese stock market but also affecting the global stock market. Its monetary policy initiatives, such as adjusting key interest rates or expanding its asset purchase program, directly affect the stock market investment environment and market sentiment. Low interest rates and increased asset purchases usually boost the stock market, as lower investment costs may prompt investors to increase equity investments and push up Stock Prices. On the contrary, tighter monetary policy may lead to a decline in the stock market as higher funding costs and reduced supply may dampen investors' purchasing power.
Moreover, the Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution has an important impact on the bond market, directly affecting the yields of Japanese government bonds and other bonds. Lowering interest rates or expanding asset purchases may lead to a decline in bond yields, while the opposite may lead to their rise, affecting investors' bond strategies and market performance.
In addition, the Bank of Japan's monetary policy decisions, in particular adjustments to interest rates and the asset purchase program, have a direct impact on the market's perception of future economic trends. Favorable economic expectations can boost the growth of economic activity by increasing the confidence of businesses and consumers, encouraging investment expansion, and increasing consumer spending. On the contrary, pessimistic market expectations may lead businesses and consumers to adopt conservative strategies and dampen the growth of economic activity. Therefore, the Bank of Japan's economic expectations and policy guidance are crucial in shaping market confidence and economic performance.
In short, the Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution and policy stance have important implications for investors, economists, and policymakers. This not only affects the performance of the capital and stock markets but also directly influences global economic expectations. As a result, the market pays a great deal of attention to the Bank of Japan's decision-making, and its policy direction could trigger widespread market volatility and investment strategy adjustments.
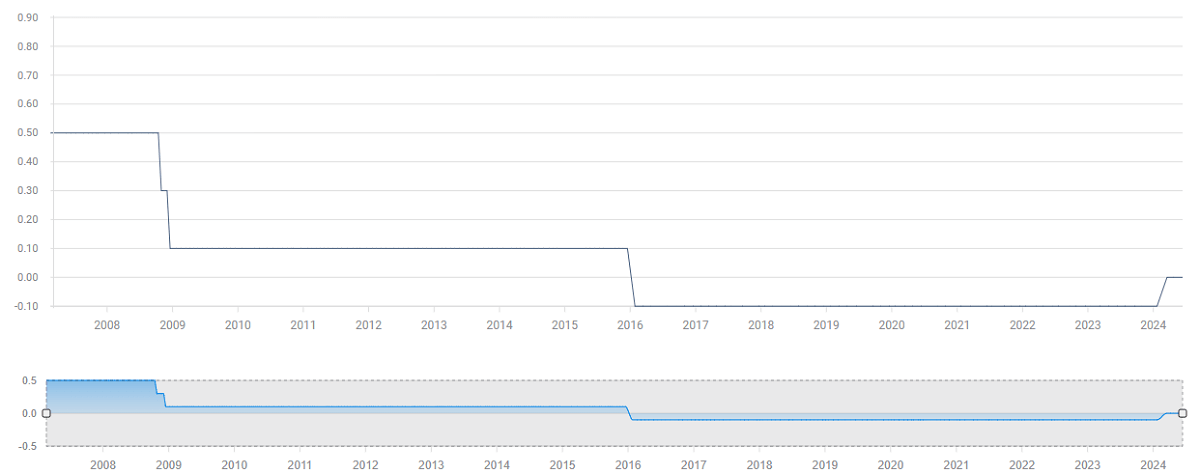 The Bank of Japan's Interest Rate Hike and Its Impact
The Bank of Japan's Interest Rate Hike and Its Impact
Since the bursting of the bubble economy in the 1990s, the Bank of Japan has experienced a prolonged period of low inflation and a low economic growth environment, and thus its monetary policy has been mainly accommodative. In recent years, as major economies around the world have been gradually raising interest rates to cope with inflationary pressures, whether or not the Bank of Japan will raise interest rates has become the focus of market attention.
The Bank of Japan has implemented a zero-interest rate policy since 1999. with the main objective of stimulating economic growth and raising the level of inflation by lowering market interest rates. This policy aims to promote consumption and investment while reducing borrowing costs to meet the challenges of prolonged low inflation and slow economic growth.
Since 2001. the Bank of Japan has taken steps to increase market liquidity by purchasing government bonds and other assets, a policy known as quantitative easing. These initiatives were aimed at lowering long-term interest rates and stimulating borrowing and investment activity in order to boost economic growth and counter deflationary pressures. Quantitative easing is also seen as an important tool to support the stability of financial markets and maintain the healthy functioning of the financial system by increasing market liquidity.
In January 2016. the Bank of Japan lowered its policy interest rate to minus 0.1%, a move aimed at further stimulating economic activity and boosting the level of inflation. By adopting a negative interest rate policy, the Bank of Japan seeks to boost bank lending and investment in order to boost economic growth and address the long-standing challenges of low inflation and sluggish economic growth.
It is important to realize that the original purpose of Japan's negative interest rate policy was to deal with long-term deflationary pressure. By setting negative interest rates, bank borrowing activities are encouraged to promote economic growth and inflation. For example, if the interest rate is negative 1%, depositors who deposit $100 next year will only get back $99. Borrowers will enjoy lower loan costs, stimulating consumption and investment.
It wasn't until July 2024 that the Bank of Japan announced that it was raising its benchmark interest rate from minus 0.1% to between 0%, ending a 17-year policy of negative interest rates. This decision marked Japan's first step towards a transition to a tighter monetary policy and triggered widespread interest and reaction from global markets.
The main motivation behind Japan's rate hike was the pickup in inflation in the Japanese economy. While the BOJ began observing inflationary pressures several years ago, they needed to ensure that the inflationary trend was sustained and confirm that inflation was firmly entrenched through data such as wage increases.20 The results of the wage negotiations in the spring of 24 showed that Japan's large companies increased employee pay by 5.28%, the highest increase in 33 years, which was seen as a key signal for the interest rate hike.
As a result, markets were expecting the Bank of Japan to raise rates at a later date, but the timing and strength of the hike exceeded some analysts' expectations. Because the Bank of Japan opted for a smaller rate hike and did not clarify the exact path of further tightening, this led to an expectation gap in the market. In this case, the yen did not appreciate as expected but instead fell below the 150 mark against the dollar again, reflecting the market's uncertainty and caution about the central bank's policy attitude.
It is important to note that Japan's interest rate hike policy may have multiple impacts. First, the return on investment in Japanese assets may improve, attracting more foreign capital inflows, especially from the U.S. and Europe. Second, the rate hike may raise the Japanese government's borrowing costs, limiting the space for its fiscal stimulus measures and even triggering sharp volatility in the Treasury bond market.
In addition, for global markets, the Bank of Japan's decision to raise interest rates may become an important reference for the policy paths of other central banks. In particular, among the economies that are still implementing accommodative monetary policies, such as the United States, Europe, and Australia, Japan's move to raise interest rates may provide a guide and reference for them, especially in assessing inflationary pressures, economic recovery, and asset market performance.
The impact is not limited to the timing and speed of policy adjustments but could also have far-reaching implications for global interest rate movements, capital flows, and exchange rate stability. Its move to raise interest rates may trigger risk appetite adjustments in global markets, affecting investors' allocation decisions across different asset classes. Investors may reassess their expectations of the direction of monetary policy and adjust their risk management strategies in response to changes in the global economy and financial markets.
In conclusion, the BOJ's decision to raise interest rates is not just a monetary policy adjustment but also an important signal for economic recovery and inflation management. Despite divergent market reactions, the future direction of the Japanese economy and the performance of the global markets will closely follow this historic policy shift.
The Bank of Japan's interest rate resolution and its impact
| Interest rate resolution |
Possible effects |
| Interest Rate Increase |
Tightening monetary policy to curb inflation and possibly slow economic growth. |
| Interest Rate Cut |
Looser policy to boost the economy, consumption, and investment. |
| Interest rates are stable. |
Maintain policy stability; markets watch the central bank's comments on the economy. |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.





 The Bank of Japan's Interest Rate Hike and Its Impact
The Bank of Japan's Interest Rate Hike and Its Impact