The Turtle Soup trading strategy, developed by Linda Bradford Raschke and detailed in her book Street Smarts: High Probability Short-Term Trading Strategies, offers traders a contrarian approach to market movements. Unlike traditional trend-following strategies, Turtle Soup capitalises on false breakouts, aiming to profit from price reversals that occur when markets fail to sustain new highs or lows.
Introduction to Turtle Soup
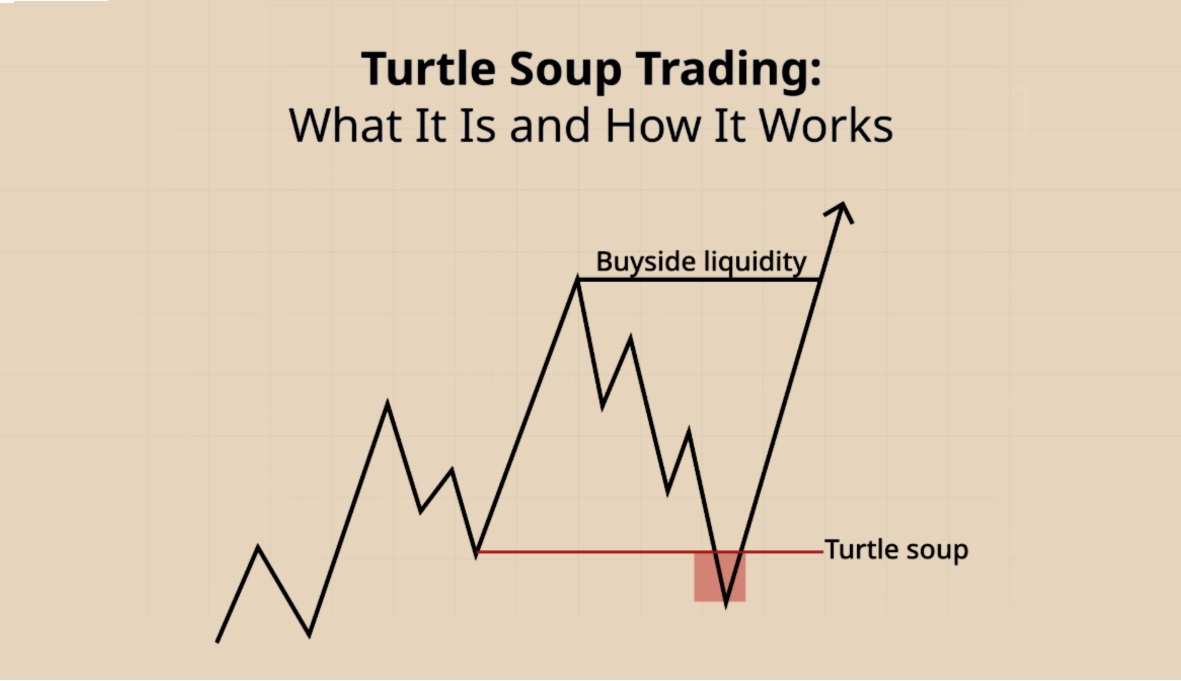
The Turtle Soup strategy is a reversal trading method that seeks to exploit failed breakouts. In contrast to trend-following strategies, which aim to profit from sustained price movements in one direction, Turtle Soup identifies situations where the market briefly moves beyond a key support or resistance level but then reverses direction. Traders enter positions in the opposite direction of the breakout, anticipating that the initial move was a false signal.
This approach is particularly effective in markets prone to false breakouts, where price action temporarily breaches significant levels only to retrace shortly after.
Key Concepts in Turtle Soup Trading
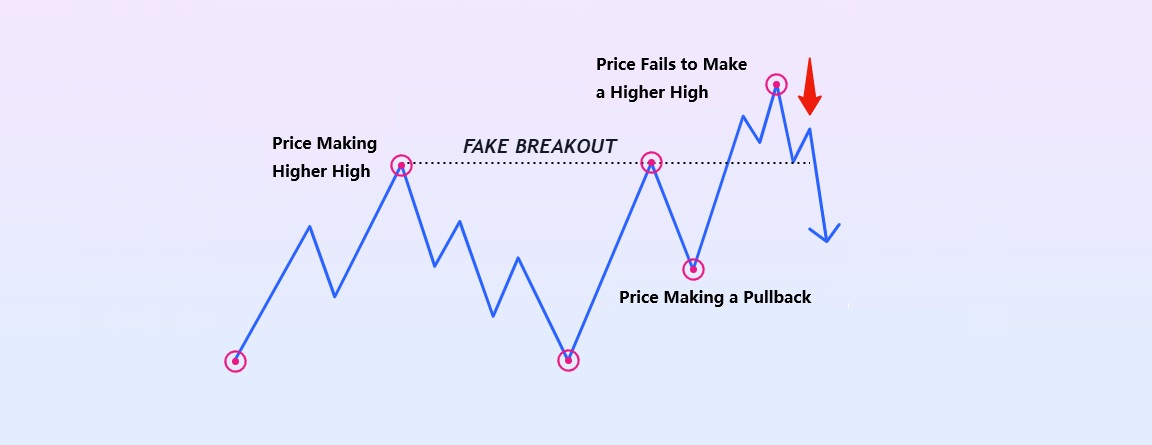
A false breakout occurs when the price moves beyond a key support or resistance level but fails to maintain momentum in that direction. These events often trap traders who enter positions based on the breakout, only for the price to reverse and move against them.
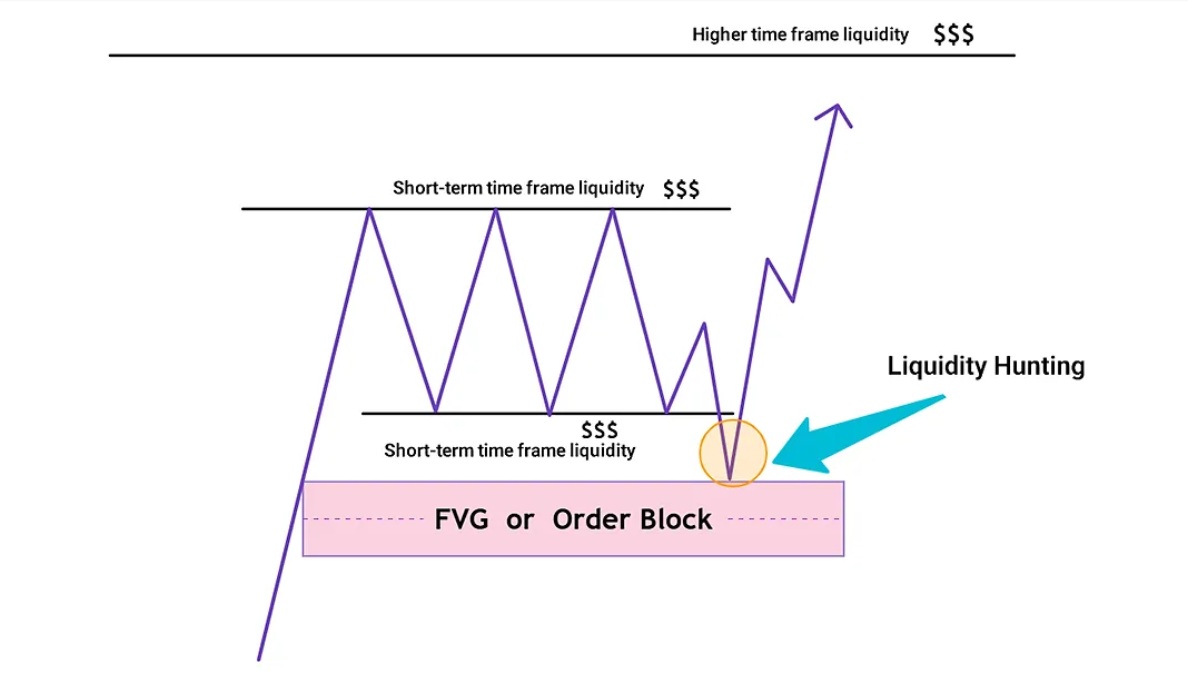
Market participants often place stop-loss orders just beyond significant support or resistance levels. When the price briefly breaches these levels, it can trigger a cascade of stop-loss executions, providing liquidity for institutional traders to enter positions at more favourable prices. Turtle Soup aims to capitalise on these liquidity traps by entering trades in the direction opposite to the false breakout.
Reversal entries involve taking positions that go against the prevailing market movement, anticipating a price reversal. In the context of Turtle Soup, traders enter trades opposite to the direction of a false breakout, expecting the price to revert to its previous range.
Setup Identification in Turtle Soup Trading
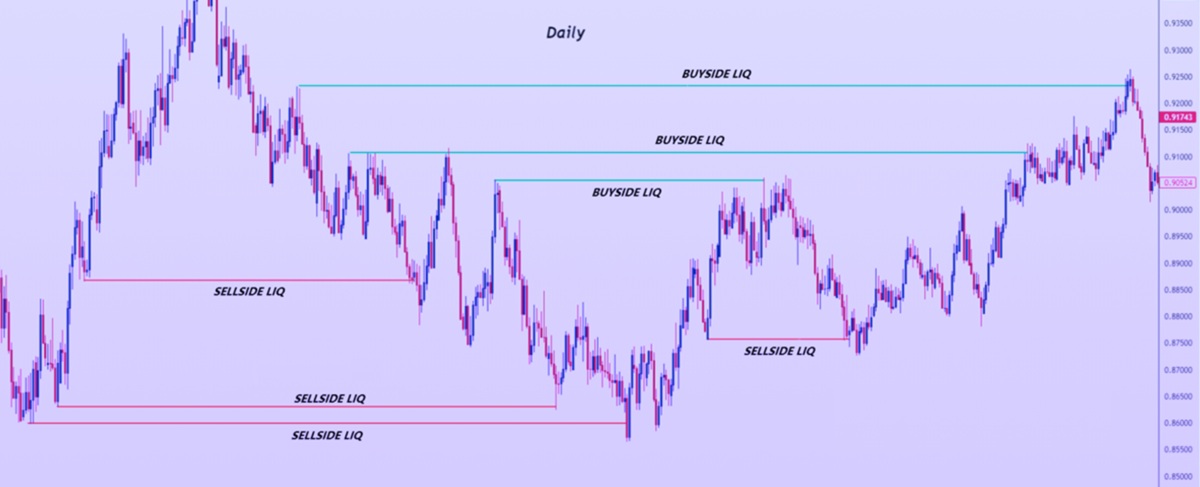
Identifying potential Turtle Soup setups involves recognising specific market conditions:
Break of Key Levels: The price moves beyond a significant support or resistance level, indicating a potential breakout.
Immediate Reversal: The price quickly retraces back into the previous range, suggesting the breakout was false.
Volume Confirmation: An increase in trading volume during the reversal can confirm the validity of the false breakout.
Traders should look for these conditions on higher timeframes, such as the 4-hour or daily charts, to ensure the significance of the levels being breached.
Entry Criteria in Turtle Soup Trading
The entry point for a Turtle Soup trade is crucial to maximise potential profits and minimise risks:
Entry Point: Enter the trade when the price closes back inside the previous range, indicating the failure of the breakout.
Stop-Loss Placement: Place a stop-loss order just beyond the breakout point to limit potential losses if the price continues in the breakout direction.
Position Sizing: Determine the position size based on the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss, ensuring that the risk per trade aligns with the trader's risk tolerance.
Utilising limit orders can help achieve optimal entry prices, reducing slippage and improving trade execution.
Exit Strategies in Turtle Soup Trading
Effective exit strategies are essential to lock in profits and manage risk:
Profit Targets: Set profit targets based on previous support or resistance levels, where the price is likely to encounter obstacles.
Trailing Stops: Implement trailing stops to protect profits as the price moves in favour of the trade, allowing for potential gains while safeguarding against reversals.
Time-Based Exits: Exit the trade after a predetermined period if the price has not reached the profit target or stop-loss, to avoid prolonged exposure to market risk.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting exit strategies can help adapt to changing market conditions and optimise trade outcomes.
Risk Management
Proper risk management is vital to ensure long-term profitability and protect capital:
Risk per Trade: Risk only a small percentage of the trading capital on each trade, typically between 1% and 2%, to prevent significant losses.
Position Sizing: Adjust position sizes based on the volatility of the asset being traded and the distance to the stop-loss, maintaining consistent risk levels.
Regular Review: Continuously monitor and assess the effectiveness of the trading strategy, making adjustments as necessary to adapt to market changes.
Implementing these risk management practices helps traders navigate the inherent uncertainties of the financial markets and maintain a disciplined approach to trading.
Conclusion
The Turtle Soup trading strategy offers a unique approach to capturing profits from market reversals following false breakouts. By focusing on failed breakouts and liquidity traps, traders can position themselves to benefit from price reversals that often occur when markets fail to sustain new highs or lows. However, like all trading strategies, Turtle Soup requires careful analysis, disciplined execution, and effective risk management to achieve consistent profitability.
For further exploration of the Turtle Soup strategy and its applications, consider reviewing Linda Bradford Raschke's book Street Smarts: High Probability Short-Term Trading Strategies, which provides in-depth insights and practical examples.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.























