Gains with OCO orders can be maximised by strategically setting linked take-profit and stop-loss levels.
This automated approach ensures disciplined execution, even in volatile conditions, without the need for constant oversight.
In this article, we will explore how OCO orders work, their practical applications, step-by-step setup, key advantages and limitations, and answer common questions to help you trade more effectively.
What is an OCO Order and How Does it Work?
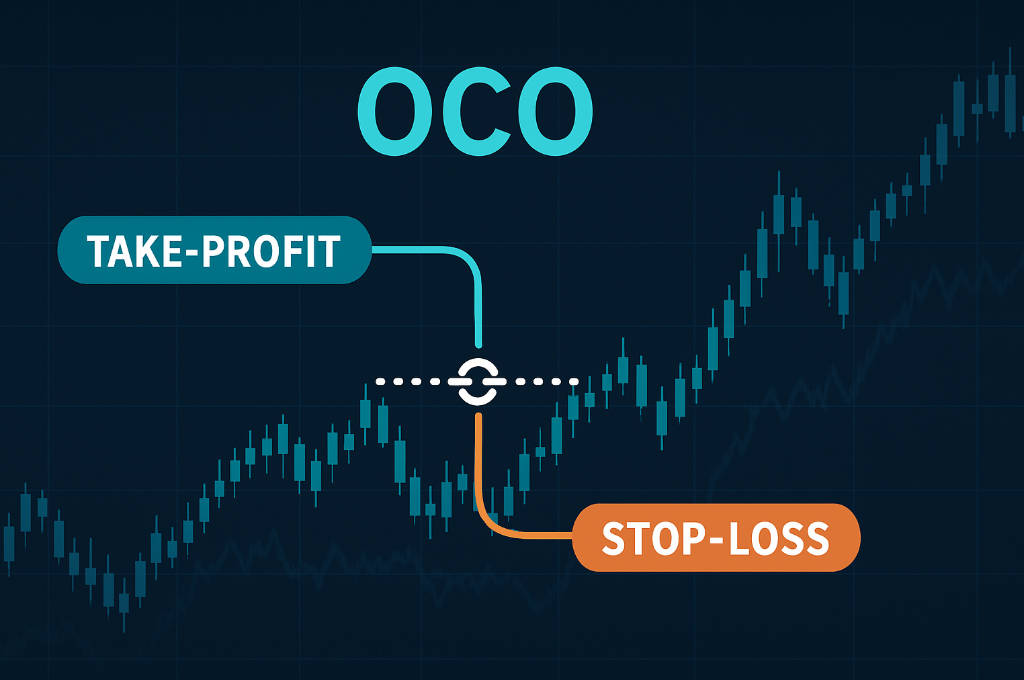
What is an OCO Order
An OCO (One-Cancels-the-Other) order is a type of conditional trading order that combines two separate orders into a single instruction. Typically, these orders include a stop order and a limit order, where the execution of one automatically cancels the other.
OCO orders are primarily used to automate trade management, allowing traders to set predefined levels for profit-taking and loss prevention simultaneously.
The primary purpose of an OCO order is to provide greater control over trades and reduce the need for constant market monitoring.
By combining two linked orders, traders can capture favourable market movements while protecting against adverse price shifts.
How OCO Orders Operate
The mechanics of an OCO order involve the simultaneous placement of two linked orders: a stop order and a limit order.
Stop Order: This is usually a stop-loss order, placed to limit potential losses if the market moves against the trade.
Limit Order: This is a target order, placed to secure profits when the market reaches a favourable price point.
Once an OCO order is active, the execution of one order automatically cancels the other. For instance, if the market reaches the stop price, the stop order is executed, and the limit order is cancelled.
Conversely, if the market reaches the limit price first, the limit order is executed, and the stop order is cancelled. This ensures that only one of the two outcomes occurs, preventing conflicts and overexposure.
Practical Applications of OCO Orders
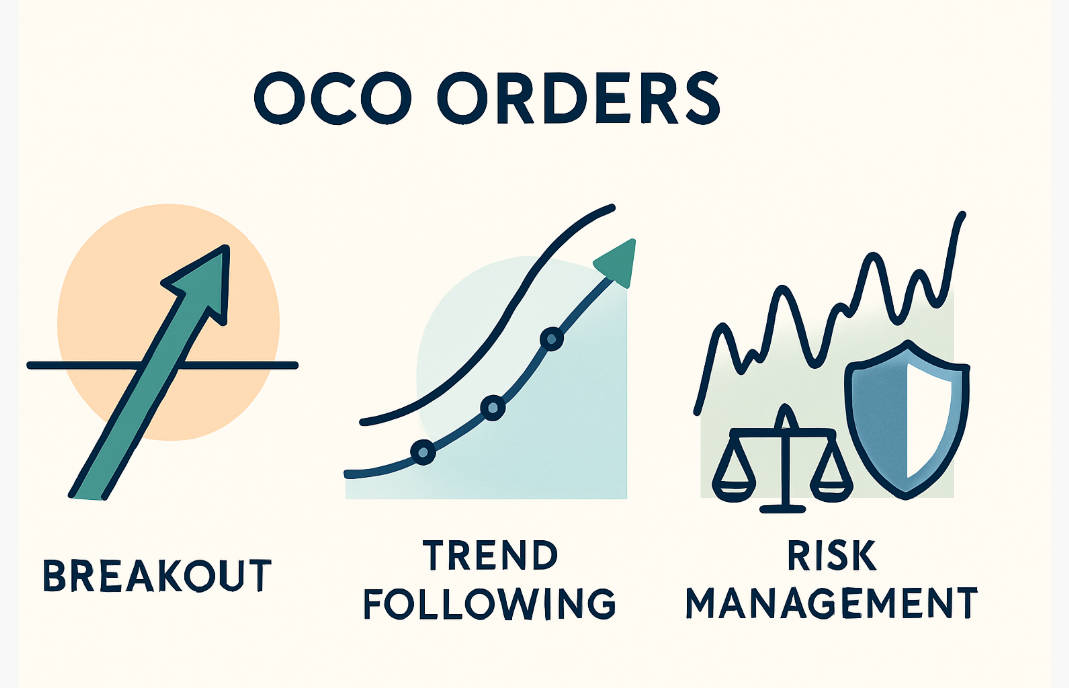
OCO orders are versatile tools in trading and can be applied across multiple strategies and market conditions.
Breakout Strategies
Traders often use OCO orders to capitalise on breakout opportunities. In such cases, the stop order is placed below a support level, while the limit order is set above a resistance level.
If the price breaks out of the established range, the relevant order executes, allowing traders to enter a position at the optimal point while limiting downside risk.
Trend Following
OCO orders can also be used to follow market trends. Traders set a limit order at a desired profit target and a stop order to protect against reversals. This strategy ensures that gains are captured while losses are controlled, particularly in trending markets.
Risk Management
Risk management is one of the most critical applications of OCO orders. By linking a stop-loss and a take-profit order, traders ensure that only one order is executed, avoiding scenarios where both profit and loss positions could be inadvertently triggered.
This automation reduces emotional decision-making and promotes disciplined trading.
Strategies to Optimise the Use of OCO Orders
While OCO orders provide automated risk management, their effectiveness largely depends on how they are implemented within a broader trading strategy. Traders can enhance their outcomes by adopting the following approaches:
1. Align Orders with Market Analysis
Before placing an OCO order, conduct thorough technical or fundamental analysis to determine key support and resistance levels. Placing stop-loss and limit orders at strategically chosen price points increases the likelihood of executing trades at optimal levels.
2. Adjust Orders Based on Volatility
Markets with high volatility may require wider stop-loss and take-profit margins to avoid premature execution.
Conversely, in stable markets, tighter levels can protect gains without risking unnecessary slippage.
3. Combine OCO Orders with Other Trading Tools
Using OCO orders alongside indicators such as moving averages, RSI, or Fibonacci retracements can enhance decision-making.
For example, a limit order aligned with a resistance level confirmed by multiple indicators can improve the probability of a successful trade.
4. Regularly Review and Update Orders
OCO orders are not "set and forget" tools. Traders should monitor market conditions and adjust their orders to reflect new trends, news events, or shifts in volatility.
This dynamic management ensures that OCO orders remain aligned with evolving market conditions.
5. Use OCO Orders to Manage Multiple Positions
Traders can deploy OCO orders across multiple positions in a portfolio to manage overall risk exposure.
By systematically linking stop-loss and take-profit levels, traders can maintain disciplined execution while managing diverse assets efficiently.
By applying these strategies, OCO orders can move beyond simple automation to become a sophisticated tool that enhances both profitability and risk management in trading.
Setting Up an OCO Order: Step-by-Step

Placing an OCO order requires careful planning and precise execution. The following steps outline the process:
1) Select the Asset
Identify the financial instrument you wish to trade, whether it is a stock, commodity, forex pair, or cryptocurrency.
2) Determine Price Levels
3) Place the OCO Order
Enter both the stop and limit orders simultaneously on your trading platform and ensure they are linked as an OCO pair.
4) Monitor Market Conditions
Although OCO orders automate execution, traders should remain aware of market developments that could influence order performance, such as volatility spikes or unexpected news events.
Advantages and Limitations of OCO Orders
Advantages
1) Automated Risk Management:
Traders can set predefined parameters for both profit-taking and loss-limiting, reducing the need for constant monitoring.
2) Flexibility Across Markets:
OCO orders can be used in a variety of trading environments, including equities, forex, and cryptocurrencies.
3) Operational Efficiency:
By ensuring that only one of the linked orders is executed, OCO orders prevent conflicting positions and streamline trade management.
Limitations
1) Platform Availability:
Not all trading platforms support OCO orders, so traders must verify availability before planning their strategy.
2) Impact of Market Conditions:
In highly volatile markets, slippage can occur, potentially affecting the execution price.
3) Complexity for Beginners:
OCO orders may be difficult for novice traders to set up and manage effectively without prior experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can an OCO order be used for both buying and selling?
Yes, OCO orders can be applied to both buying and selling positions. Traders can use them to automate entry or exit points depending on their strategy.
2. What happens if the market reaches both the stop and limit prices simultaneously?
Only one of the two linked orders will be executed. The system automatically cancels the other order, ensuring that traders are not left with conflicting positions.
3. Are OCO orders available on all trading platforms?
While many trading platforms provide OCO functionality, availability can differ. Traders should confirm with their platform provider whether OCO orders are supported.
4. Can an OCO order be modified after placement?
In most cases, OCO orders can be adjusted after they are placed. However, traders should exercise caution, as modifying one order may impact the linked order and the overall strategy.
Conclusion
OCO orders are a powerful tool for traders seeking to automate their trading strategy, manage risk effectively, and capture profits in a controlled manner.
By linking a stop order with a limit order, traders can maintain a disciplined approach to both entering and exiting trades, while mitigating potential losses.
Understanding how OCO orders function, when to use them, and their limitations is essential for both novice and experienced traders seeking to enhance their trading efficiency.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.




























