From AI-fuelled gains and fintech optimism to real estate slumps and regulatory risks, China's market index highlights a mix of investor confidence and deep structural weaknesses.
For decades, China's stock market has been regarded as both an engine of economic growth and a barometer of shifting investor sentiment. From the retail-driven booms of the 2000s to the volatility of the mid-2010s, Chinese equities have often captured global headlines. Today, the focus is back on Beijing and Shanghai as mainland indices surge to decade highs. The Shanghai Composite Index and CSI 300 have staged a remarkable comeback in 2025. powered by technological optimism, policy support, and renewed participation from domestic investors.
Yet behind this surge lies a more complex story: fragmented exchanges, cautious long-term investors, and structural risks in the broader economy. Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone seeking to grasp not only the performance of China's market indices, but also their wider implications for global finance.
An Overview of China's Market Index
China's market index, primarily represented by the Shanghai Composite Index and the CSI 300. tracks the performance of companies listed on mainland exchanges. The Shanghai Composite covers all stocks listed on the Shanghai Stock Exchange, while the CSI 300 focuses on the largest and most liquid A-shares from both Shanghai and Shenzhen. Together, these indices serve as key barometers of the Chinese economy, reflecting shifts in policy, investor sentiment, and industrial growth.
Recent Performance Trends in China's Market Index
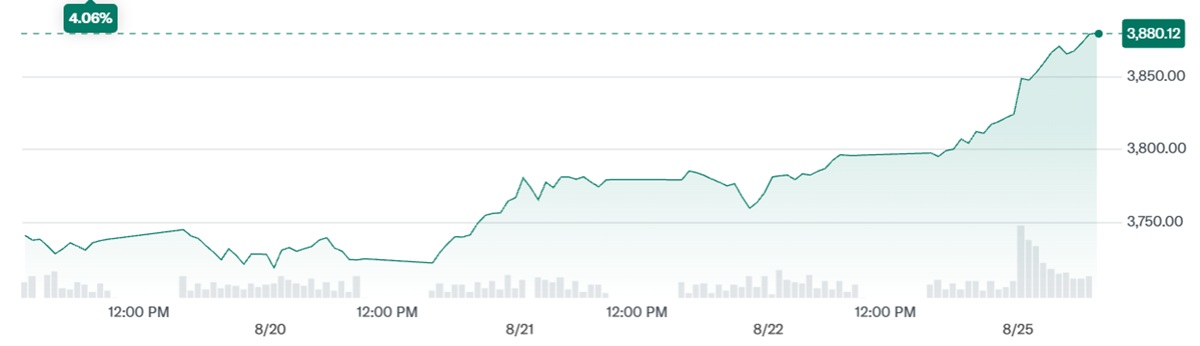
Mainland Chinese equities have surged to their highest level in nearly a decade. The Shanghai Composite Index closed at approximately 3 825.76. marking its strongest finish since August 2015 and reflecting a gain of around 14 % year-to-date. Other sources affirm a similar reading—around 3 771.10—indicating a significant rally propelled by enthusiasm across tech sectors, fintech, and stablecoin-related stocks. The CSI 300 index, which tracks 300 large-cap stocks across Shanghai and Shenzhen, also rose, buoyed by renewed investor optimism.
This upswing coincides with more measured trend improvement. For context, in mid-August, the Shanghai Composite hovered near 3 727. its highest level since August 2015. This rally, primarily driven by domestic investor activity and policy tailwinds, reflects both momentum and cautious optimism—that this phase could extend, unlike speculative bubbles of the past.
Key Drivers Behind China's Market Index Rally
Several factors have propelled the rise in China's market index:
Technology and AI: The rapid growth of AI-related companies and semiconductor firms has boosted investor appetite.
Policy Support: The government's stimulus efforts and pledges to improve liquidity have reassured markets.
Retail Investor Participation: Individual investors continue to play a dominant role in mainland exchanges, amplifying volatility during both rallies and downturns.
Global Trade Dynamics: Signs of stabilisation in trade relations have also contributed to renewed foreign investor interest in China's market index.
China's Market Index Structure: Multiple Exchanges & Fragmentation
China's capital markets remain highly fragmented—a patchwork comprising the Shanghai Stock Exchange, Shenzhen Exchange, STAR Market, ChiNext, and the relatively new Beijing Stock Exchange. Each platform caters to different types of companies, particularly innovation-focused small- and mid-cap issuers.
This multiplicity has created inefficiencies: boom-and-bust cycles often follow investor attention shifting between exchanges. For instance, the Beijing Stock Exchange, though younger, has seen more IPO applications in 2025 than STAR and ChiNext combined—indicative of speculative fervour and investor chasing of the latest buzzy platform.
Such structural segmentation may dampen the overall effectiveness of China's market system—despite an impressive combined market capitalisation (~US $18 trillion)—by impeding liquidity, undermining institutional trust, and making it difficult for companies to transition between platforms.
Challenges & Structural Risks for China's Market Index
Despite the euphoric market mood, structural vulnerabilities remain:
Real estate slump continues to erode broader economic confidence.
Retail sales and credit growth are disappointing, and in July 2025. fixed asset investment plunged 5.2 % year-on-year, marking the steepest decline in over two decades (excluding the pandemic period).
Consumer and factory gate prices remain flat or deflationary.
Regulatory enforcement remains a concern, particularly in light of recent insider-trading crackdowns—including investigations into former CSRC officials accused of profiteering from suspected IPO-related manipulations—highlighting ongoing issues with market integrity and oversight.
Outlook & Policy Implications
For this market rally to translate into a sustainable rebound rather than a bubble, structural reform is essential. Ideas include consolidating exchanges or at least harmonising their regulatory frameworks to reduce speculative shifting and boost transparency and liquidity.
Policy support is also critical. Continued discipline in industrial overcapacity, coupled with measures to stimulate domestic consumption and investment, could shore up economic fundamentals—though recovery likely will take time.
Concluding Thoughts
China's stock market is experiencing a notable rebound, with indices like the Shanghai Composite and CSI 300 touching decade highs. The rally is fuelled by optimism around technology sectors, renewed policy attentiveness, and a shift from bonds to equities.
Yet this price action occurs against a backdrop of structural complexity—multiple fragmented exchanges, shifting investor sentiment, and ongoing economic weakness. For China's market to mature into a resilient and reliable driver of capital formation, reforms centred on consolidation, transparency, and investor protection are essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the Shanghai Composite Index?
It is the main benchmark of the Shanghai Stock Exchange, covering both A-shares (domestic) and B-shares (foreign-accessible). It reflects the overall performance of China's largest and most liquid stock market.
2. Why are Chinese markets rallying in 2025?
The rally is being driven by optimism in technology sectors such as artificial intelligence and semiconductors, policy efforts to address industrial overcapacity, and growing enthusiasm around fintech and stablecoin-related stocks.
3. What risks still threaten the market's stability?
Structural fragmentation across exchanges, the lingering property sector slump, weak consumer dmand, and concerns about regulatory transparency all continue to challenge the long-term sustainability of the rally.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



























