In the fast-paced world of trading, timing is everything. Traders are always looking for tools that can provide faster and more reliable signals to make informed decisions. One such tool is the DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average), an indicator designed to give quicker and smoother trend signals than traditional moving averages.
The DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) was introduced by Patrick Mulloy in 1994 to address the inherent lag in simple and exponential moving averages.
While the exponential moving average (EMA) reduces some of this lag compared to a simple moving average (SMA), it can still be slow to react to sudden market changes. The DEMA seeks to improve on this by combining two EMAs in a specific way, effectively reducing lag and providing more timely information about price movements.
Understanding the Mechanics of DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average)
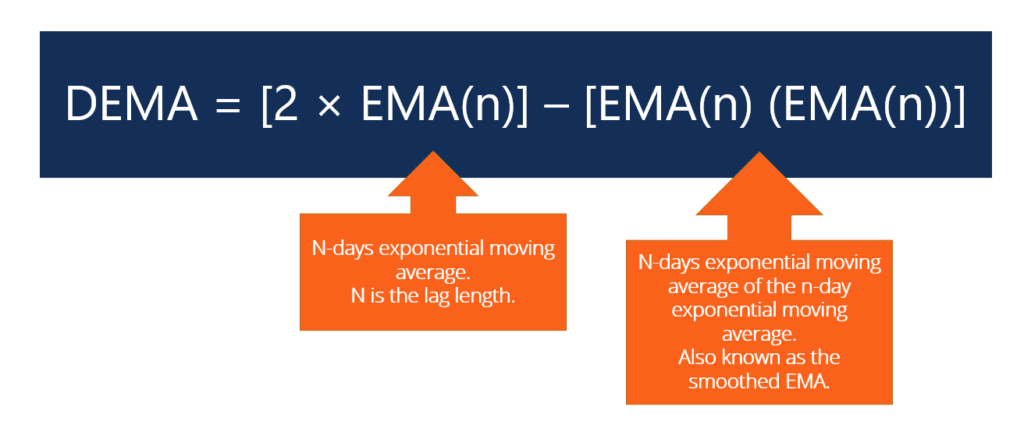
To truly appreciate what makes the DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) different, it is important to understand how it is calculated. The formula for DEMA involves calculating an EMA of the EMA itself, and then applying a correction factor:
DEMA = (2 × EMA) − EMA of EMA
This calculation results in a smoother curve that closely follows price action without the delays that commonly affect other moving averages. Traders benefit from this because they get earlier signals to enter or exit trades, which can be critical when market conditions change rapidly.
Unlike the SMA, which gives equal weight to all prices in the calculation period, the DEMA gives more importance to recent prices. This weighting combined with the double smoothing mechanism results in a moving average that is more responsive yet stable.
Why DEMA Matters for Traders
The purpose of the DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) is to help traders identify trends earlier and with greater confidence. For example, in trending markets, a DEMA will react faster to price changes than traditional averages, allowing traders to capture more of the move before the trend reverses.
Speed and responsiveness are particularly valuable in markets such as forex, where price changes can be swift and volatility high. By reducing lag, the DEMA provides signals that are closer to real-time price movements, giving traders an edge over those using slower indicators.
Moreover, DEMA can also help filter out market noise, making it easier for traders to distinguish between genuine trend changes and minor price fluctuations. This means fewer false signals and better timing for trade execution.
Using Double Exponential Moving Average in Trading Strategies
Traders apply the DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) in various ways depending on their trading style and objectives. A common approach is to use DEMA as a trend-following tool, where the direction of the DEMA line helps determine market bias. For instance, if prices are above the DEMA and the line slopes upwards, this is generally considered a bullish signal. Conversely, prices below a downward-sloping DEMA indicate bearish conditions.
Another popular technique involves combining multiple DEMAs with different time periods. A shorter-period DEMA crossing above a longer-period DEMA can signal a buy opportunity, while the opposite crossover might indicate it is time to sell or exit. This crossover strategy is similar to methods used with simple and exponential moving averages but benefits from the improved responsiveness of DEMA.
Traders may also use the DEMA to identify support and resistance levels in trending markets. The moving average often acts as a dynamic level where prices may bounce during pullbacks, offering potential entry points aligned with the trend.
Despite its strengths, the DEMA should not be used in isolation. Because markets can enter periods of consolidation or sideways movement, relying only on DEMA may lead to false signals. Combining DEMA with other technical indicators such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), or volume indicators can enhance decision-making by confirming trends and momentum.
Comparing DEMA with Other Moving Averages
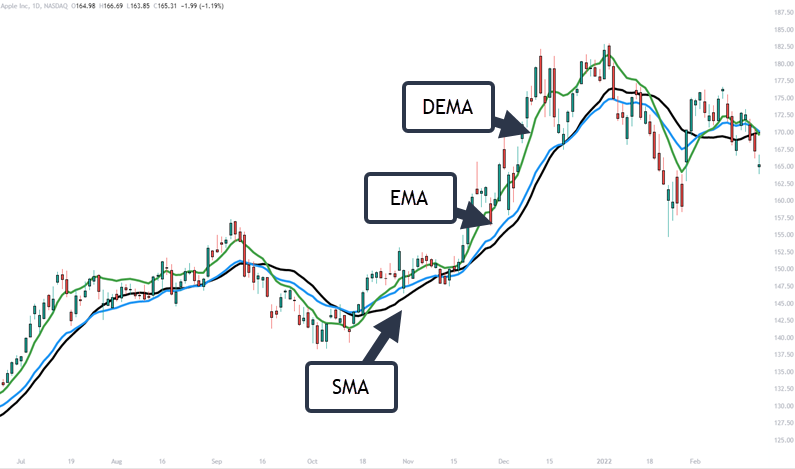
To understand the value of DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average), it helps to compare it with other commonly used moving averages like SMA and EMA.
The SMA calculates the average price over a specific period giving equal weight to all data points. While simple to use, the SMA tends to lag more significantly behind current price action, which can delay signals for trend changes.
The EMA improves on this by assigning more weight to recent prices, reducing lag and reacting faster to changes. However, the EMA can still produce lag and sometimes generate false signals in volatile or sideways markets.
DEMA goes a step further by doubling the smoothing effect, which means it responds even faster to price movements while maintaining a smoother line. This combination offers traders the benefit of early signals without too much noise or whipsaw action. For this reason, DEMA is often preferred by traders who require more timely signals without sacrificing stability.
Practical Considerations and Limitations of DEMA
While the DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) offers clear advantages, traders should be aware of its limitations. In choppy or non-trending markets, DEMA's sensitivity can sometimes lead to misleading signals. Rapid price fluctuations can cause the DEMA to give false breakouts or trend reversals, which can result in premature trades.
To mitigate these risks, traders often complement DEMA with other analysis tools and always apply proper risk management strategies, including stop-loss orders and appropriate position sizing.
Additionally, choosing the right time period for DEMA calculations is important. Shorter periods make DEMA more reactive but increase the chance of false signals, while longer periods provide smoother signals but with increased lag. Traders typically test and adjust settings based on the specific asset and market conditions they are trading.
Final Thoughts
The DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) is a valuable technical indicator that offers a faster and smoother alternative to traditional moving averages. Its ability to reduce lag helps traders identify trends earlier and make better-informed trading decisions. When used alongside other technical tools and solid risk management, DEMA can be an effective component of a comprehensive trading strategy. It is especially useful in volatile and fast-moving markets where timing can make the difference between profit and loss.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of DEMA is essential. While it is a powerful tool for trend detection, traders should avoid relying on it alone and always use a balanced approach to analysis. By integrating DEMA (Double Exponential Moving Average) into their trading toolkit, traders can gain a clearer view of market momentum and position themselves for improved trading outcomes.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.