Foreign currency trading, also known as Forex (FX) trading, is the global marketplace where currencies are exchanged against one another. With over $7.5 trillion traded daily, it is the largest and most liquid financial market globally.
If you've ever exchanged your local currency for another while travelling abroad, you've participated in a basic form of foreign currency exchange. However, in Forex trading, individuals and institutions trade currencies to make a profit.
So, what exactly is foreign currency trading? In simple terms, it's buying one currency while selling another at the same time, hoping that the exchange rate will move in your favour. In this guide, you'll learn the meaning of foreign currency trading, how it works, its importance, risks, strategies, and tips to get started.
What Is Foreign Currency Trading?

Foreign currency trading is the act of exchanging one currency for another to make a profit from changes in exchange rates. Currencies are always traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro vs US Dollar) or GBP/JPY (British Pound vs Japanese Yen).
For example:
If you believe the Euro will strengthen against the Dollar, you buy EUR/USD.
If you believe the Euro will weaken against the Dollar, you sell EUR/USD.
Understanding foreign currency trading is crucial for anyone who wants to explore financial markets. Unlike stocks or commodities, currencies are influenced by global factors such as:
Economic data (inflation, GDP, unemployment rates)
Central bank policies (interest rates, monetary policy)
Political stability
Geopolitical events
For traders in India and South Africa, Forex trading offers the opportunity to engage in worldwide markets without significant capital investments.
How Does Foreign Currency Trading Work?
Trading foreign currencies works through a decentralised global market where participants exchange currencies electronically over-the-counter (OTC). There is no central exchange, unlike stock markets.
Here's how it works step by step:
1) Currency Pairs: Every trade involves two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency.
2) Bid and Ask Price:
3) Leverage and Margin:
Traders can control large positions with small amounts of money thanks to leverage (e.g., 1:100).
4) Profit and Loss:
The difference in exchange rates determines whether a trader makes a profit or loss.
Example of Forex Trading
Suppose you believe the Euro will strengthen against the Dollar:
You buy 1 lot of EUR/USD at 1.1000.
After a few hours, the price rises to 1.1050.
Profit = 50 pips. With a standard lot size, that equals $500 profit.
But if the price falls to 1.0950 instead, you would face a $500 loss.
Types of Foreign Currency Pairs
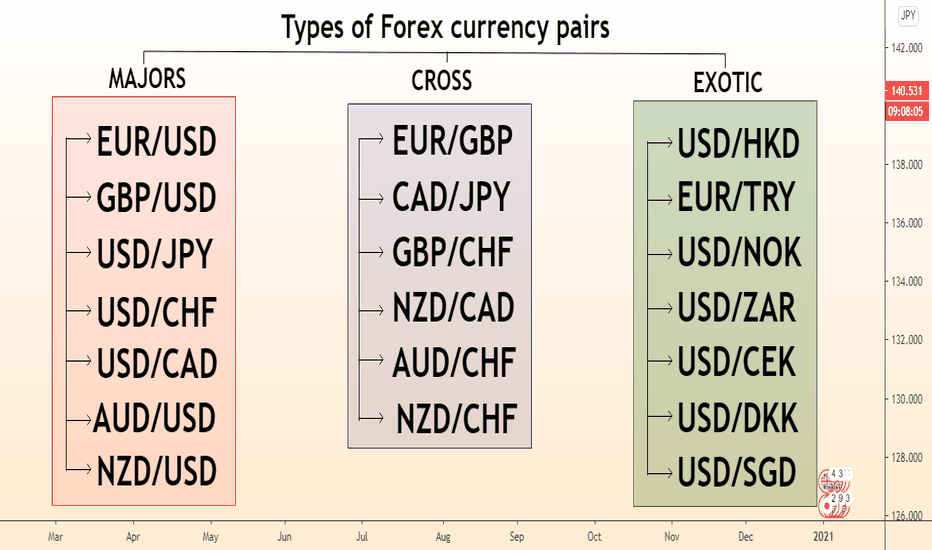
Currency pairs are classified into three main types:
1. Major Pairs
These consist of the most commonly exchanged currencies globally, always paired with the US Dollar (USD).
Examples: EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY, USD/CHF.
Why trade them? They offer high liquidity and lower spreads.
2. Minor Pairs
These pairs do not include the USD but involve other major currencies.
Examples: EUR/GBP, AUD/JPY, GBP/CHF.
Why trade them? They provide diversification opportunities.
3. Exotic Pairs
These pair a major currency with a currency from a developing economy.
Examples: USD/INR, USD/TRY, EUR/SEK.
Why trade them? Potential for higher returns, though riskier.
What Are the 4 Forex Market Sessions?
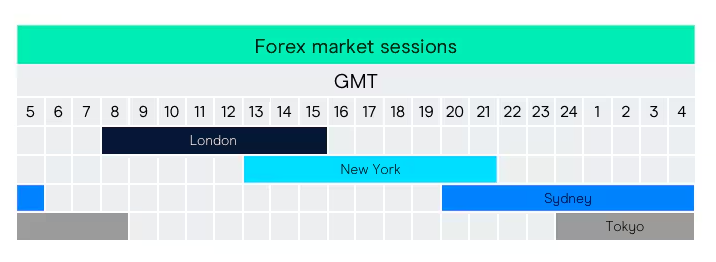
The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, thanks to overlapping global sessions:
Sydney Session: Opens the market (Asian trading).
Tokyo Session: Major Asian market hours.
London Session: Largest and most liquid session.
New York Session: The second-largest market, overlapping with London.
For traders, the London and New York overlaps are usually the most profitable times to trade due to higher volatility.
Why Is Forex Trading Important?
Foreign currency trading is vital for global economic activity. Without it, international trade and investments would not be possible.
For instance, when an Indian company imports goods from the United States, it must convert rupees into dollars. Similarly, when tourists travel abroad, they need to exchange their local currency.
For traders and investors, Forex offers:
High liquidity: Easy to enter and exit trades.
24/5 market access: Unlike stock markets, Forex is open almost all week.
Low barriers to entry: Many brokers allow small deposits to start trading.
How to Start Foreign Currency Trading

If you're new to Forex trading, here are the steps to get started:
Learn the Basics: Understand how pairs, pips, and leverage work.
Choose a Reputable Broker: Brokers such as EBC Financial Group are a great starting point, as they are regulated by authorities and licensed in their local jurisdictions.
Open a Demo Account: Practice trading without risking real money.
Develop a Trading Plan: Define risk tolerance, strategy, and goals.
Start Small: Begin with small amounts before scaling up.
Stay Updated: Follow economic news and market events.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Advantages and Risks of Foreign Currency Trading
| Advantages |
Risks |
| Accessible with small capital |
High leverage may lead to large losses |
| 24/5 trading availability |
Market volatility can cause sudden moves |
| High liquidity for easy entry/exit |
Scams and unregulated brokers pose risks |
| Profit opportunities in up and down markets |
Requires strong discipline and learning curve |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can Beginners Trade Forex With Small Capital?
Yes, many brokers, such as EBC, allow beginners to start trading Forex with small deposits, sometimes as low as $10–$100.
2. How Much Profit Can I Make From Foreign Currency Trading?
Profits in Forex depend on your capital, strategy, leverage, and risk management. While some traders achieve regular profits, many encounter losses, so it's not guaranteed income but a high-risk investment.
3. What Are the Best Times to Trade Forex?
The best times to trade are during high-liquidity sessions such as the London-New York Session, especially when they overlap.
4. What Tools Do I Need to Succeed in Forex Trading?
Traders often utilise a trading platform (MT4 or MT5), technical indicators (RSI or Moving Averages), and an economic calendar to monitor GDP, CPI, and central bank actions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, foreign currency trading is the largest and most exciting financial market, offering countless opportunities for traders worldwide. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced trader, learning the basics of Forex from currency pairs to strategies is the first step toward success.
By mastering risk management and staying informed about global events, you can navigate this dynamic market and use Forex trading as a tool to grow wealth in 2025 and beyond.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.