Managing downside risk is crucial in pursuing growth in a volatile and unpredictable market like 2025. One effective safeguarding tool for a portfolio is using inverse exchange-traded funds (ETFs).
These instruments are designed to increase in value when the underlying index or asset declines, making them ideal for hedging against market downturns.
This guide will explain how inverse ETFs work, why investors are turning to them in 2025, the different strategies to deploy them effectively, and the risks every investor should understand before diving in.
What Are Inverse ETFs?

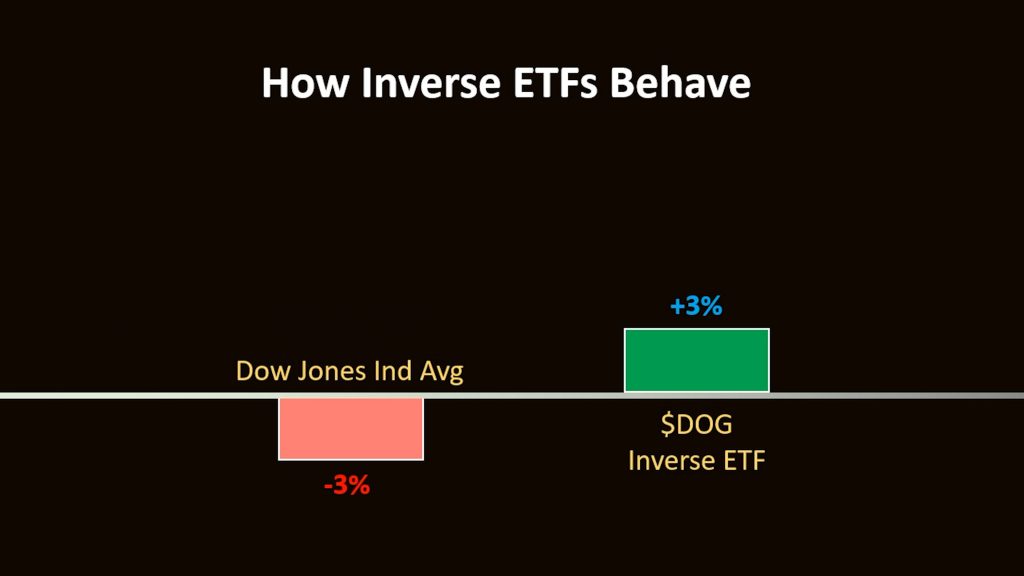
Inverse ETFs, also known as "short ETFs" or "bear ETFs," are designed to deliver the opposite performance of a specific benchmark or index. For example, if the S&P 500 falls by 1%, an inverse S&P 500 ETF is expected to rise by approximately 1% for that same day.
These funds achieve their performance using a combination of derivatives, including swaps, futures contracts, and other financial instruments. They reset daily, which means their inverse correlation only holds for single-day movements, making them ideal for short-term trading or tactical hedging rather than long-term investing.
How It Works: Mechanics and Daily Reset
As mentioned above, Inverse ETFs use complex instruments to replicate the inverse return of an index daily. They rebalance at the end of each trading day to reset their inverse exposure. This daily reset indicates that the effects of compounding can have a significant impact on returns over several days.
For example, if the S&P 500 drops 1% on Day 1 and rises 1% on Day 2, the net change is not zero due to the inverse ETF's compounding nature. Over time, this can lead to tracking errors if held longer than intended.
It is why inverse ETFs are recommended primarily for short-term hedging. Investors who hold them for multiple days or weeks should monitor performance closely, especially in volatile markets.
Outlook for Inverse ETFs in 2025
As volatility remains a massive theme in 2025 due to rate uncertainty, geopolitical unrest, and slower global growth, inverse ETFs will stay in high demand. Institutional use has increased significantly, especially among hedge funds and proprietary trading firms using them in arbitrage and volatility strategies.
Retail investors have also become more sophisticated. Educational platforms and brokerages now offer more tools to monitor and manage inverse ETF exposure in real-time. With AI-based portfolio management systems gaining ground, many robo-advisors even incorporate tactical hedging using inverse ETFs during market stress periods.
Types Available in 2025
As mentioned, the range of inverse ETFs available has expanded significantly. Investors can now find inverse ETFs tied to broad indexes, sectors, commodities, bonds, and even cryptocurrencies. Some of the most commonly used inverse ETFs include:
SPDN – Inverse S&P 500 ETF
SH – ProShares Short S&P 500
PSQ – Short Nasdaq-100
SDS – UltraShort S&P 500 (2x leverage)
DOG – Short Dow 30
SJB – Short High Yield Bonds
More niche inverse ETFs have also gained traction in 2025, covering sectors like tech, energy, and emerging markets. With the increasing popularity of artificial intelligence and biotech sectors, new inverse ETFs are also tracking those segments for tactical hedging.
Why Hedge with Inverse ETFs in 2025?
1) Volatile Economic Outlook
As of mid-2025, markets are experiencing increased uncertainty. Persistent inflation, high interest rates, and geopolitical tensions have generated volatility. While major indexes have recovered, sharp pullbacks continue to threaten equity-heavy portfolios.
2) Protection Without Selling Core Assets
Inverse ETFs allow investors to protect gains or offset losses without selling their long-term positions. This is especially useful in taxable accounts where selling would trigger capital gains taxes or disrupt asset allocations.
3) Rapid Reaction to Market Events
With inverse ETFs, traders can quickly respond to market news — earnings surprises, Fed announcements, or economic data — without engaging in complex short-selling or options trading strategies.
Popular Hedging Strategies Using Inverse ETFs
1. Portfolio Overlay Hedging
Investors can allocate a percentage of their total portfolio — say 10% to 20% — to an inverse ETF corresponding to their primary exposure. For instance, if most of your portfolio is aligned with the S&P 500, buying SPDN or SH can serve as a hedge.
2. Sector-Specific Protection
If you're heavily invested in technology, an inverse tech ETF like REW (ProShares UltraShort Technology) can help mitigate sector-specific downturns without liquidating your core positions.
3. Event-Driven Trading
Traders anticipating sharp market reactions to specific events, like Federal Reserve meetings or earnings seasons, can use inverse ETFs to capitalise on short-term declines without resorting to derivatives like puts or shorting.
4. Inverse ETF Pairs Trading
Some investors use inverse ETFs alongside leveraged long ETFs in a pairs trading strategy. For example, during high volatility, they might short a 2x leveraged ETF and go long its inverse equivalent to neutralise market risk while profiting from volatility decay.
Benefits and Risks
Inverse ETFs offer a range of advantages for both retail and institutional investors:
No Need to Short Securities: You gain bearish exposure without needing to borrow stocks or use a margin account.
Accessibility: Available via regular brokerage accounts; no special approvals or margin arrangements are required.
Transparency: Like other ETFs, inverse ETFs publish daily holdings and offer full visibility.
Liquidity: Most major inverse ETFs are highly liquid with tight bid-ask spreads.
Tax Efficiency: In taxable accounts, inverse ETFs allow hedging without triggering a taxable event from selling core positions.
Despite their appeal, inverse ETFs are not without risks. Investors must understand these drawbacks before using them as a hedging tool.
Daily Reset Risk: Due to daily rebalancing, long-term holders may experience significant tracking errors, especially in volatile markets.
Compounding Effect: Over multiple days, returns may deviate from expected performance due to compounding—this can magnify losses.
Not Suitable for Buy-and-Hold: Inverse ETFs are designed for tactical, short-term moves, not long-term hedging or investing.
Sector or Index Bias: Inverse ETFs focused on narrow sectors or volatile assets may experience amplified tracking errors.
Psychological Stress: Watching an inverse ETF fall while the market rallies can cause emotional trading decisions that impact long-term portfolio health.
When Should You Use?

1) During Anticipated Short-Term Market Declines
If you expect a short-term correction due to economic data releases, geopolitical tensions, or central bank decisions, inverse ETFs can help you hedge quickly and efficiently.
2) As a Tactical Hedge
Some investors use inverse ETFs to hedge a portion of their portfolio — typically the beta-heavy assets — while maintaining core positions in stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
3) In a Downtrend Confirmation
Technical traders often look for confirmation of bearish momentum before adding inverse ETFs. Tools like moving averages, MACD, RSI, or candlestick patterns can help validate entry points for these trades.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Inverse ETFs can be powerful tools for hedging against market risk, protecting gains, or profiting from short-term corrections. However, they must be used with caution and an understanding of their mechanics. They are not ideal for long-term investing, but can provide meaningful protection when used tactically.
Regardless, in 2025's market environment—defined by uncertainty, elevated rates, and fragile sentiment—inverse ETFs give investors a flexible and accessible way to stay protected while investing.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.