If you have ever researched brokers or explored global markets, you have likely seen the term ASIC, but few new traders truly understand what it means or why it matters.
Understanding ASIC begins with examining how it supports transparent, efficient, and trustworthy financial markets in Australia, a subject that remains relevant among investors, analysts, and new traders searching for reliable financial knowledge.
What Is ASIC Australia?

ASIC is the Australian Securities and Investments Commission, a national authority that regulates companies, financial markets, financial services, credit providers, auditors, and corporate disclosures within Australia.
Traders and investors across the world reference ASIC when assessing broker licensing, market transparency, regulatory compliance, and consumer protection.
ASIC was established to improve market fairness, strengthen investor confidence, support business integrity, and maintain an open financial ecosystem that attracts both domestic and global capital.
Its responsibilities continue to expand as markets evolve toward digital trading, sustainable finance, and cross-border investment.
Core Functions of ASIC
The commission performs multiple interconnected roles that influence how markets and companies operate. These functions directly affect traders, analysts, and investors who rely on accurate information, fair market conduct, and protective frameworks.
1. Market Supervision
ASIC supervises Australia’s authorized financial markets, including securities exchanges, derivatives markets, futures markets, and settlement facilities.
Market supervision from ASIC helps ensure:
Trading platforms follow fair rules
Issuers disclose accurate information
Market participants avoid manipulative practices
Investors access timely, truthful market data
2. Oversight of Financial Services
ASIC licenses and monitors financial advisers, brokers, investment firms, insurers, and credit providers. This role is increasingly significant with the rise of online trading, high-growth retail investing, and digital finance technologies.
ASIC’s oversight ensures providers deliver financial products honestly, transparently, and with competence, reducing risks for retail investors who trade stocks, derivatives, forex pairs, ETFs, or alternative investment products.
3. Company Regulation and Corporate Reporting
ASIC maintains the national register of companies and monitors annual financial reports, director details, audit quality, and corporate governance practices.
Trending topics include:
For traders using fundamental analysis, ASIC’s corporate filings database allows deeper insight into company performance, risk exposure, and leadership quality.
4. Consumer Protection
ASIC enforces rules that shield consumers from misleading financial advertising, unfair lending practices, product misrepresentation, and harmful investment schemes.
This includes oversight of:
Consumer protection remains one of ASIC’s highest-priority mandates, especially during periods of economic stress and rising cost of living.
5. Compliance, Business Education and Enforcement
ASIC supports businesses through guidance documents, compliance tools, and educational materials. However, it also maintains strong enforcement powers that include:
Investigations
Court actions
Civil penalties
License suspensions
Director bans
Compensation orders
This balanced approach encourages ethical business behavior and long-term market stability.
ASIC Australia in 2025: Key Developments and Market Trends
2025 has been a defining year for ASIC, characterized by a visible shift toward stronger enforcement, deeper market supervision, and an expansion of responsibilities aligned with global financial trends.
Below are the most important developments as of 2 December 2025.
1. Stronger Enforcement and Litigation Activity
ASIC has increased actions against:
Misleading sustainability claims
Unlicensed investment offerings
Audit independence breaches
Aggressive property investment schemes
High-risk credit models
Breaches of financial advice obligations
Market manipulation and insider trading cases
The rise of retail trading has pushed ASIC to address online misrepresentation, social media investment scams, and algorithmic trading misconduct.
2. Audit Quality Crackdown
Audit quality has been one of the most trending financial regulation topics of 2025. ASIC significantly expanded audit inspections, focusing on:
Revenue recognition accuracy
Asset valuation methods
Sustainability and climate disclosures
Independence between firms and audit clients
High-risk reporting environments
Some of Australia’s largest audit firms faced penalties for failing independence tests, creating a strong signal for accountability across the profession.
3. Regulatory Simplification for Businesses
ASIC is working to simplify complex regulatory documents across:
This initiative aims to reduce the compliance burden on small businesses and fast-growing startups, supporting the country’s competitiveness in global capital markets.
4. Technology and Cyber Resilience Focus
Through 2025, ASIC emphasised:
This shift reflects the increasing dependence on automated trading systems, online brokers, and digital onboarding platforms.
5. Sustainable Finance and Green Disclosure
ESG investing continues to trend globally. ASIC is enforcing stricter rules on:
This aligns Australia with global markets seeking greater accountability in environmental disclosures.
ASIC’s Approach to AI, Automated Trading, and Algorithmic Risk
AI-driven trading, algorithmic execution models, robo-advisers, and automated investment platforms are rapidly transforming Australian markets.
ASIC has responded by strengthening expectations around operational resilience, model risk, AI transparency, and system governance.
ASIC’s 2025 Focus Areas
Model governance: Firms must ensure AI models behave predictably, avoid bias, and operate within risk boundaries.
System testing and validation: Automated trading systems must undergo stress testing, backtesting, and scenario analysis.
Operational resilience: Firms must demonstrate they can recover from outages, cyberattacks, or model failures that could cause market disruption.
Transparent client communication: Firms must disclose how AI tools influence trading decisions, pricing, or recommendations.
Real-time monitoring: High-frequency and algorithmic traders are expected to maintain continuous oversight to detect anomalies or harmful trading patterns.
Why ASIC Matters to Traders and Investors

ASIC is a crucial reference point for anyone trading or analyzing financial markets.
1. Broker Research and Licensing
Traders rely on ASIC licensing when assessing broker legitimacy. Licensing indicates oversight, internal controls, segregation of client funds, and ongoing financial supervision.
2. Market Integrity for Trading Strategies
Whether using technical analysis or fundamental strategies, traders benefit from confidence that markets operate fairly and corporate disclosures are accurate.
3. Global Investment Comparisons
Understanding ASIC helps investors compare regulatory standards across regions. Investors often evaluate regulators to understand risk levels, compliance expectations, and market reliability.
4. Corporate Transparency for Equity Analysis
When analyzing ASX-listed companies, traders depend on accurate data from ASIC registers, audit reports, and enforcement news to guide long-term investment decisions.
ASIC Licensing Requirements for Brokers and Financial Firms
ASIC requires most financial firms operating in Australia to hold an Australian Financial Services Licence (AFSL).
This licensing framework is a core component of financial system stability because it ensures that brokers, advisers, and investment platforms meet strict operational and conduct standards before providing services to the public.
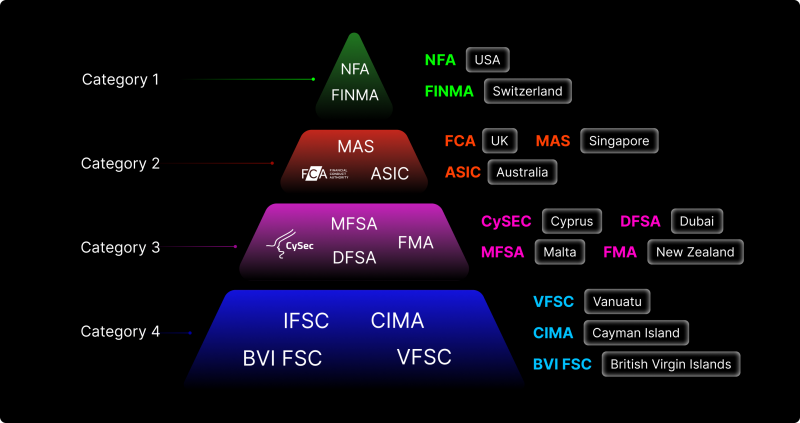
Core AFSL Requirements
Firms applying for an AFSL must demonstrate:
Organisational competence with trained, qualified responsible managers.
Adequate financial resources, including liquidity buffers that support client servicing and risk exposure.
Transparent disclosure practices for fees, risks, and product characteristics.
Robust internal governance, including conflict-of-interest controls and reporting systems.
Cybersecurity and operational resilience standards, which were elevated significantly in 2025 due to rising technology risks.
Membership in external dispute resolution schemes, ensuring retail clients have avenues for complaints.
Brokers with a valid AFSL must follow strict client-fund rules, reporting obligations, and conduct standards. This helps traders evaluate operational trustworthiness, fee transparency, and risk controls, especially when comparing Australian brokers with offshore entities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is ASIC Australia in simple terms?
ASIC is the national authority that regulates companies, financial markets, financial advisers, brokers, credit providers, and corporate reporting. It works to ensure fair and transparent financial activity.
2. What does ASIC supervise in the financial system?
ASIC supervises markets, listed companies, brokers, investment firms, consumer-credit providers, insurance practices, financial advisers, auditors, and business conduct.
3. Why do traders and investors care about ASIC?
Traders look at ASIC licensing to evaluate broker safety, market transparency, and information reliability. Analysts rely on ASIC filings when performing equity research or assessing company risk.
Summary
ASIC Australia plays a central role in maintaining the stability, reliability, and fairness of the country’s financial ecosystem. Its 2025 priorities focus on enforcement, audit quality, sustainable finance, cybersecurity, and simplified regulation.
For traders and investors, understanding ASIC offers a clearer view of market integrity, broker credibility, corporate accountability, and consumer protection.
Clear market rules and transparent disclosure standards ultimately support more informed trading decisions and enhanced financial literacy.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.
























