Nvidia still sits at the center of the AI hardware story, but it no longer runs alone.
In data centers, Nvidia’s GPUs power most of today’s large language models. Analysts estimate the company still controls roughly 80 to 90 percent of the AI accelerator market, with its H100 and H200 chips forming the backbone of global AI training infrastructure.
At the same time, competitors are moving faster, big customers are looking for second suppliers, and custom chips from cloud platforms are starting to bite. That mix is now shaping both Nvidia’s growth path and the trading setup across the whole AI-chip complex.
This commentary is for information only and is not investment advice.
The AI Chip Race In 2025
The economics of AI are pulling huge capital into chips and data centers. Bloomberg Intelligence estimates generative AI could generate around 2 trillion dollars in revenue by 2032.
Global data center infrastructure spending tied to AI is tracking close to 290 to 300 billion dollars in 2024-2025, with Alphabet, Microsoft, Amazon and Meta responsible for almost 200 billion dollars of that.
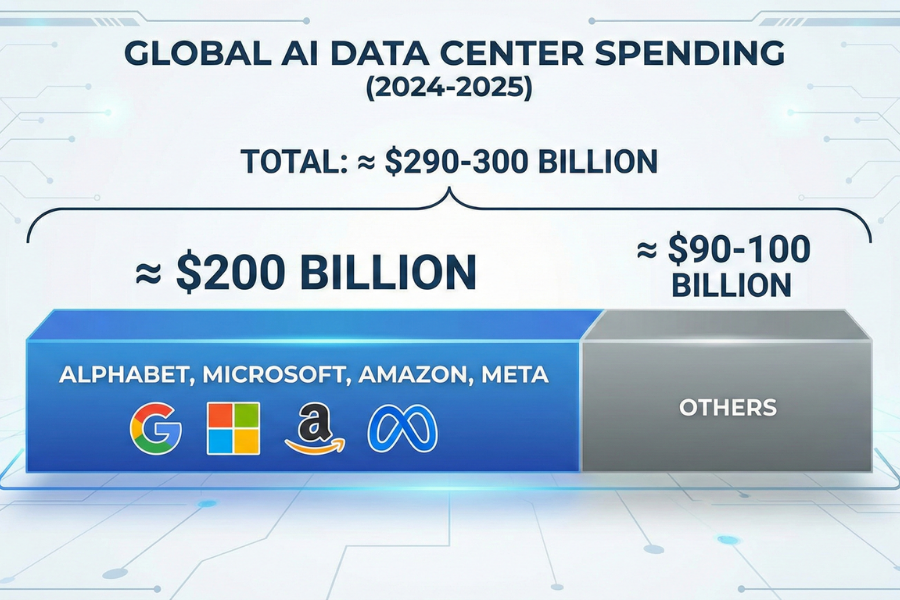
On the supply side, AMD projects the broader AI chip market, including accelerators, CPUs and networking, could reach about 1 trillion dollars by 2030.
That forecast assumes that Nvidia’s current near-monopoly in AI accelerators will gradually dilute as rivals ship more competitive hardware.
For traders, this matters in two ways:
The Main Nvidia Competitors in AI Hardware
Below are the key listed names whose technology and stock performance most directly influence how investors think about Nvidia.
1. AMD (AMD): Closest GPU Rival
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) is Nvidia’s most visible direct competitor in data center GPUs.
Its Instinct MI300 series is already shipping into major cloud providers, and management has guided to AI data center GPU revenue of roughly 4.5 billion dollars this year, with a long-term view of a 1 trillion dollar AI chip market.
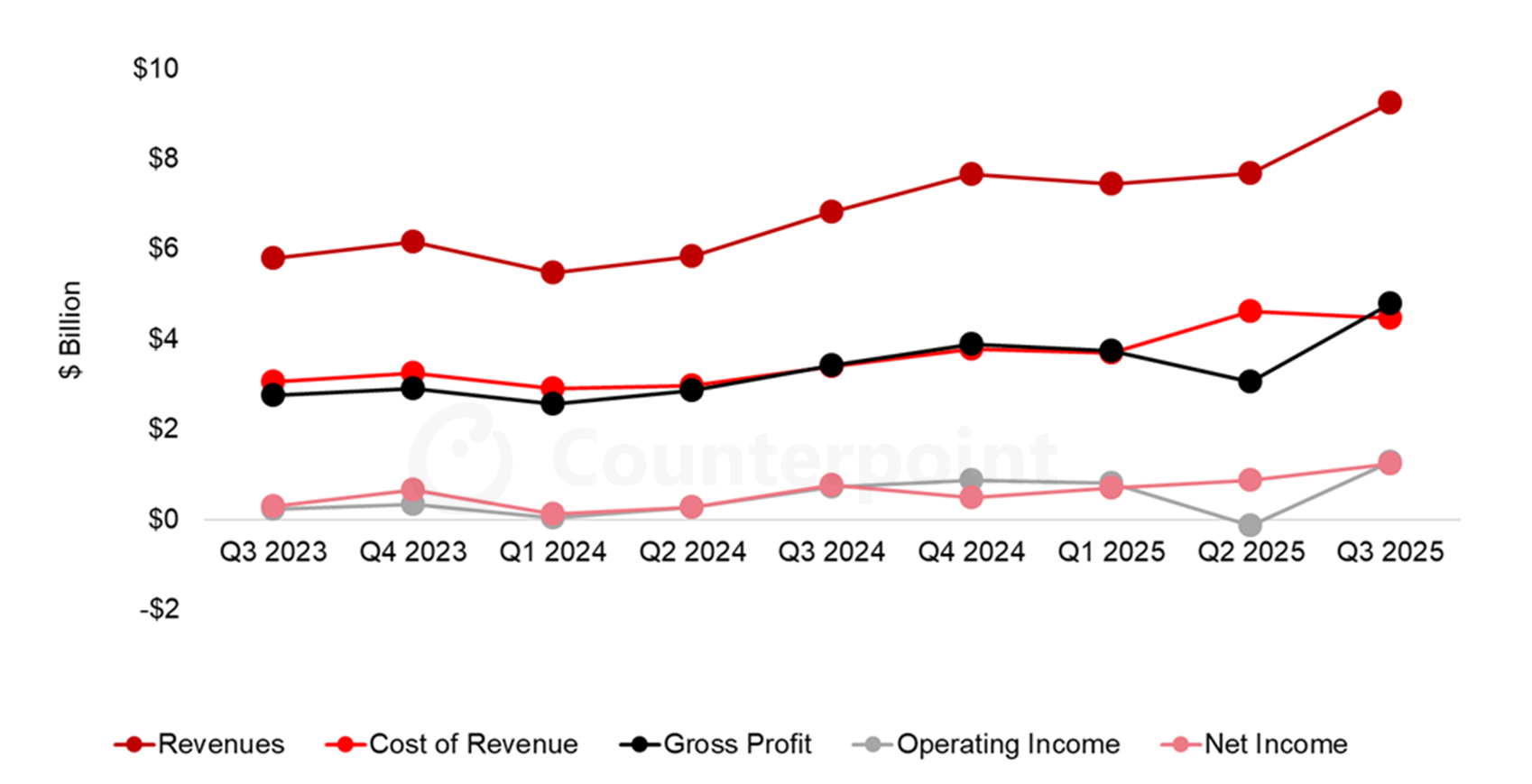
Q3 2025 revenue reached about 9.2 billion dollars, up 36 percent year on year, with EPS above expectations, and the company expects further growth in Q4 driven by AI products.
Impact on Nvidia:
Large customers such as Microsoft, Meta and OpenAI are keen to avoid dependence on a single supplier. Even partial adoption of AMD’s GPUs gives them pricing leverage when negotiating with Nvidia.
When headlines highlight AMD wins or strong AI guidance, investors often rotate between the two stocks rather than adding new money to the sector. This can cap Nvidia’s short-term upside, especially when tech valuations look stretched.
2. Intel (INTC): Gaudi AI accelerators and GPUs
Intel is trying to re-enter the high-performance compute race with its Gaudi line of AI accelerators and new Arc Pro GPUs for AI and workstation workloads.
At Computex 2025 the firm announced wider Gaudi 3 availability in rack-scale and PCIe formats, targeting cloud providers and enterprise AI.
While Intel’s AI revenue base is still small compared with Nvidia, every credible Gaudi deployment gives hyperscalers a second or third option for training and inference. Over time this chips away at Nvidia’s ability to charge premium prices per GPU.
3. Alphabet / Google (GOOGL): TPUs as a direct threat
Alphabet is now one of Nvidia’s most serious long-term competitors, even though most of its AI chips are used internally or sold through Google Cloud.
Google’s tensor processing units (TPUs) are custom AI accelerators that run its own models and customer workloads.
Cloud documentation suggests newer TPU v5e and v6e instances can offer several times better performance per dollar for certain inference tasks than comparable GPU setups, and some case studies show 50 to 65 percent lower inference cost when workloads move from Nvidia GPU clusters to TPUs.
The real shift in 2025 is commercial:
Reports say Meta is in talks to spend billions of dollars on Google’s TPUs from 2027, and may rent TPUs via Google Cloud as early as next year.
Market reaction has been sharp. After these headlines, Nvidia’s market value dropped by more than 100 billion dollars in a day, while Alphabet shares rose to fresh highs.
If even one or two hyperscalers shift 10 percent of their future AI capex away from Nvidia toward TPUs, it could slow Nvidia’s data center growth and compress its valuation multiple.
4. Broadcom (AVGO): Custom AI ASICs And Networking
Broadcom is not a GPU vendor, but it co-designs AI accelerators and networking chips with hyperscalers, including components linked to Google’s TPU platforms.
Its position as a custom silicon and high-speed networking supplier gives big cloud customers an alternative path: instead of buying Nvidia systems end-to-end, they can design their own ASICs with Broadcom and rely on its switches and interconnect to scale clusters.
That reduces Nvidia’s chance to capture every dollar of AI hardware spending, even if GPUs remain at the core of many systems.
5. Marvell Technology (MRVL): The AI Interconnect Specialist
Marvell focuses on the plumbing of AI data centers: optical interconnects, custom ASICs and networking silicon that link thousands of GPUs or XPUs.

Company material and recent analysis highlight a growing AI-related total addressable market around 55 billion dollars for custom silicon and interconnects, and note that Marvell’s ASIC business has roughly doubled as hyperscalers ramp AI.
For Nvidia, Marvell is not a direct rival, but it makes it easier for cloud providers to build tailored systems where Nvidia is only one element among many. That can limit Nvidia’s ability to lock in full-stack designs across networking, switches and accelerators.
6. Qualcomm (QCOM): Shifting AI To The Edge
Qualcomm’s Snapdragon platforms, including the latest 8 Gen 5 and X-series PC chips, integrate powerful NPUs for on-device AI.
As more AI workloads run directly on phones and PCs, fewer light-to-medium tasks may need to hit cloud GPUs. Over time this splits demand between data center accelerators and edge compute.
That does not remove the need for Nvidia GPUs, but it can slow the pace at which cloud inference requirements grow, especially for smaller or latency-sensitive models.
7. Arm Holdings (ARM): The Architecture Behind AI CPUs and NPUs
Arm does not sell finished chips at scale. Instead it licenses CPU and NPU architectures used inside many AI-capable processors.
New platforms such as Arm’s Lumex compute subsystems and Armv9.7-A focus on higher AI throughput, better matrix operations and security, spanning devices, vehicles and data centers.
The more widely Arm’s AI-optimized cores spread, the easier it becomes for OEMs to design their own AI silicon rather than rely entirely on Nvidia’s ecosystem.
8. TSMC (TSM): Critical Supplier and Quiet Strategic Force
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing is not a direct competitor, but it manufactures most of Nvidia’s advanced GPUs, along with chips for AMD, Apple and others.
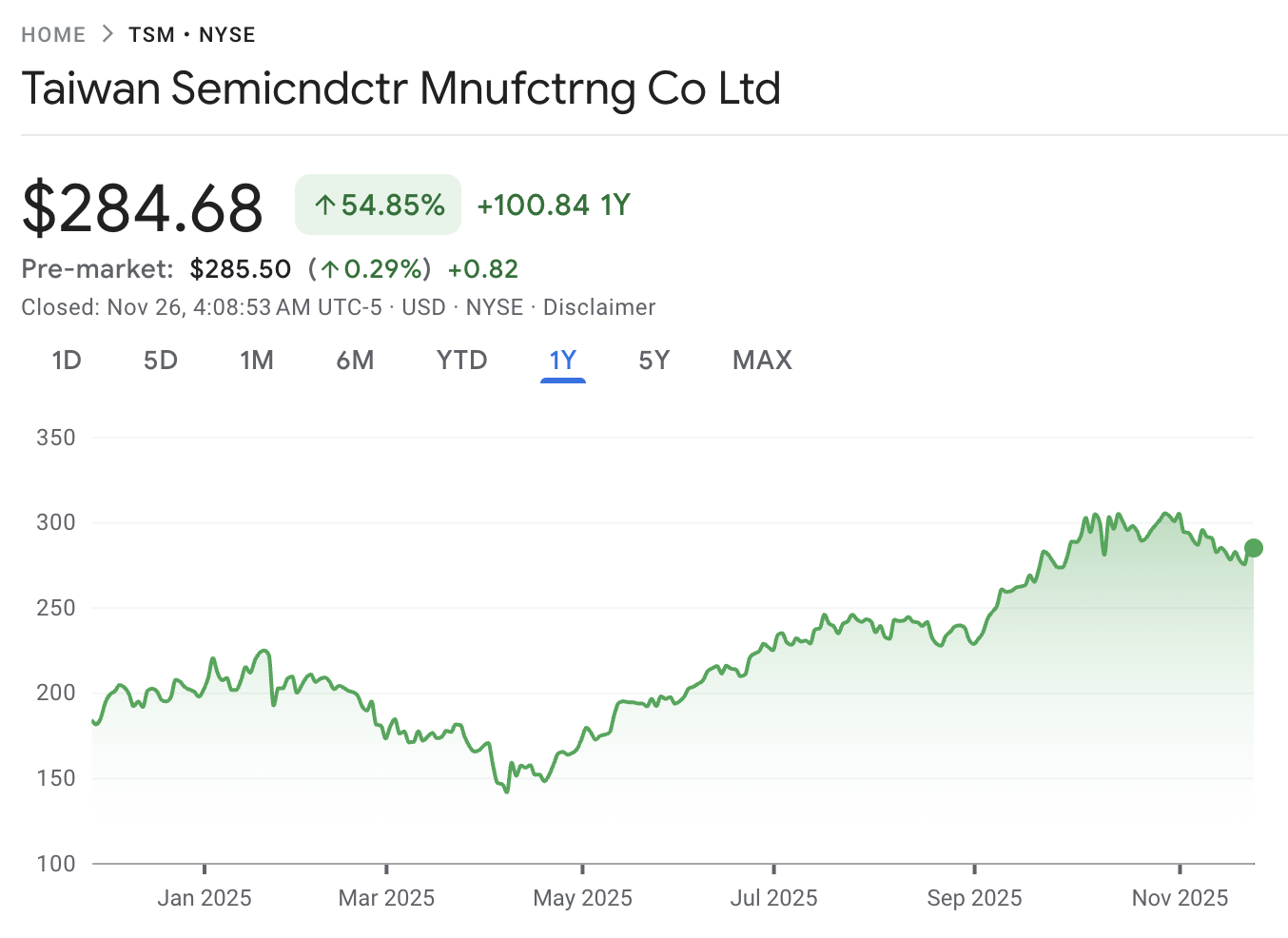
It produces more than 90 percent of the world’s most advanced chips and expects record sales driven by AI demand.
Recent comments from both Nvidia’s and TSMC’s CEOs suggest Nvidia is pushing for more wafers to keep up with AI orders. The way TSMC allocates cutting-edge capacity between rivals directly affects Nvidia’s ability to grow unit shipments.
9. Micron Technology (MU): High-bandwidth Memory Leader
Micron sits at the heart of AI hardware through high-bandwidth memory (HBM), which is stacked directly next to AI accelerators. Its HBM3E products deliver over 1.2 TB/s of bandwidth per cube and are already designed into leading AMD Instinct platforms.
SK Hynix and Micron together dominate AI-grade HBM, and recent analysis points to annual AI memory growth near 30 percent through 2030, with signs of tightening supply and rising prices.
Higher memory costs can squeeze Nvidia’s system margins or push customers to explore alternative architectures that use memory more efficiently.
Technical Picture: Nvidia And Key Peers
From a market perspective, Nvidia is still the reference name that sets the tone for AI chips.
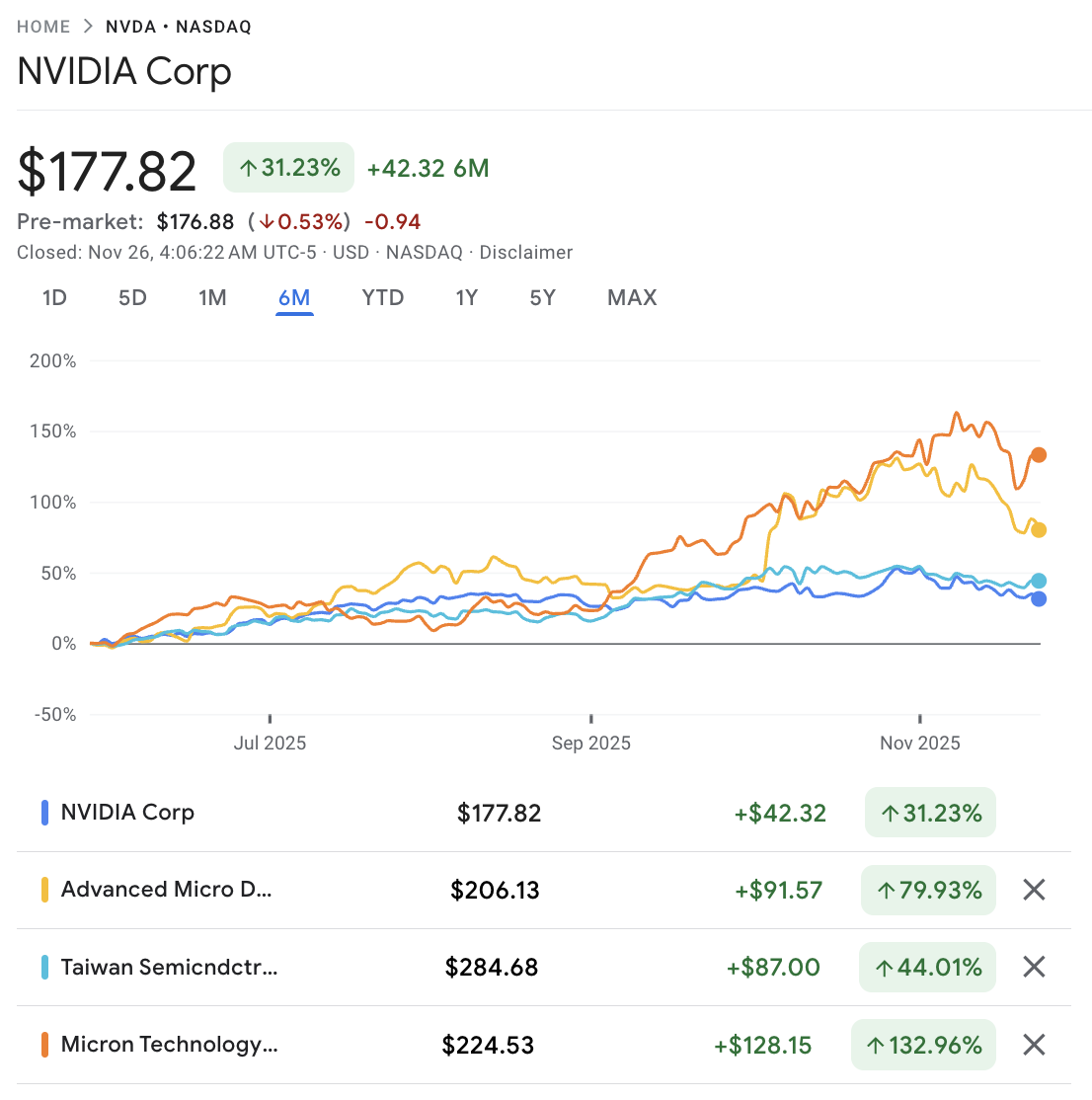
Recent price and range statistics, as of late November 2025:
| Stock |
Latest Close (USD) |
52-Week Range (USD) |
Distance from 52-Week High |
Approx 1-Year Performance |
| Nvidia (NVDA) |
177.82 |
86.62 – 212.19 |
~16% below high |
~+31% |
| AMD (AMD) |
206.13 |
76.48 – 267.08 |
~23% below high |
~+51% |
| TSMC (TSM) |
284.68 |
134.25 – 311.37 |
~9% below high |
~+57% |
| Micron (MU) |
224.53 |
61.54 – 260.58 |
~14% below high |
~+115% |
A few technical takeaways:
Nvidia is still in a broad uptrend on the 1-year view, but the stock is consolidating below its 52-week high. That reflects both huge prior gains and rising concern about competition and valuation.
AMD and Micron have stronger 12-month price performance, which gives traders liquid alternatives when sentiment sours on Nvidia.
Forward valuation remains rich across the group. Latest data shows Nvidia and AMD trading on higher forward P/E multiples than TSMC and Micron, which sit closer to the low-20s and mid-teens respectively.
When news hits about Google’s TPUs or Meta’s potential chip choices, the market often reacts first to Nvidia, then resets prices across AMD, Broadcom, TSMC and Micron depending on which side of the trade looks more exposed.
How Traders Can Position With EBC Financial Group
For traders, the story is less about picking a single winner and more about understanding where capital might rotate next.
With EBC Financial Group, clients can:
Trade Nvidia and its main competitors alongside major indices, FX pairs and commodities.
Use advanced charting tools to track ranges, breakouts and relative strength across AI chip names.
Manage risk with stop loss and take profit orders when trading volatile semiconductor stocks.
Combine stock and index CFDs to hedge portfolio exposure to the broader tech sector.
Trading leveraged products involves a high level of risk and may not be suitable for all investors. You can lose more than your initial investment. Consider your objectives and seek independent advice if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Which stock is Nvidia’s closest AI chip competitor?
In data center GPUs, AMD is the closest like-for-like rival through its Instinct accelerator line, which is already shipping at scale into cloud providers. Intel’s Gaudi accelerators and Google’s TPUs are also important, but they target a narrower set of workloads today.
2. How do Google’s TPUs affect Nvidia’s growth story?
Google’s TPUs offer cheaper performance for some AI tasks, and large buyers like Meta may adopt them from 2027. That raises the risk of future AI spending shifting partly away from Nvidia.
3. Are AI chip valuations stretched?
Recent analysis shows tech’s share of S&P 500 market value has risen faster than its share of earnings, and the Nasdaq trades well above its long-term average forward P/E. Nvidia, AMD and other AI leaders are among the most expensive names, which increases sensitivity to any earnings disappointment or sign of competition.
4. Do memory and foundry stocks compete with Nvidia?
They’re partners but still vie for AI hardware dollars. TSMC controls advanced chip capacity, while Micron and SK Hynix dominate HBM supply, so their pricing and output shape Nvidia’s costs and growth.
5. Can I trade these AI chip stocks with EBC Financial Group?
Yes. EBC Financial Group offers access to Nvidia and many of its key competitors through stock or CFD products, alongside major indices and FX. Always check the product specifications for your region and remember that trading on margin carries significant risk.
Final Thoughts
Nvidia remains the benchmark AI chip stock, with a dominant share of AI accelerators and strong earnings growth.
At the same time, the list of credible competitors is growing, from AMD’s GPUs and Intel’s Gaudi accelerators to Google’s TPUs, Broadcom and Marvell in custom silicon, and suppliers such as TSMC and Micron in manufacturing and memory.
For traders, that means the AI chip story is no longer a single-stock trade. It is a sector exposed to competition, valuation risk and very large capital flows.
Tracking how these names trade against each other can help identify rotation, hedge risk and spot new opportunities as the AI hardware cycle evolves.
If you are considering trading Nvidia or its competitors, use clear risk limits, monitor news flow closely and work with a regulated broker such as EBC Financial Group.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.