Google Stock Price Jumps as AI Hardware Strategy Gains Attention
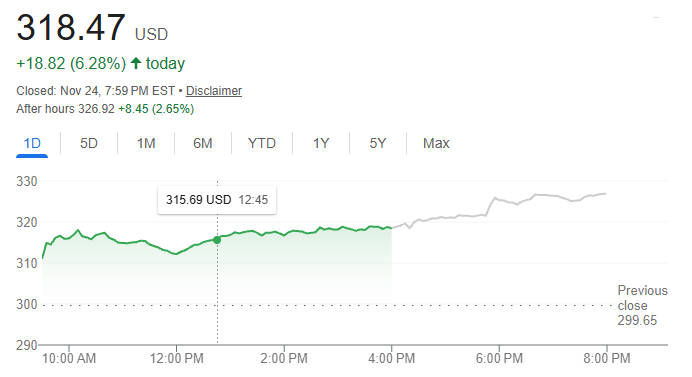
The Google stock price surged 6.28 percent to 318.47 USD, supported by renewed optimism around Alphabet's AI infrastructure strategy and the company's move to commercialise its Tensor Processing Units.
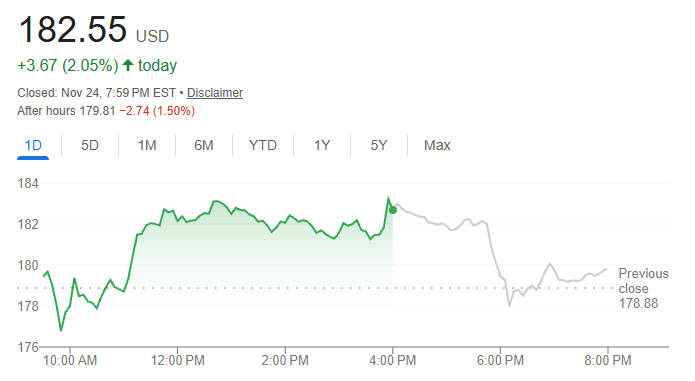
The Nvidia share price rose 2.05 percent to 182.55 USD during the session but slipped 1.50 percent to 179.81 USD in after market trading.
The sharp rise in the Google stock price reflects a shift in investor sentiment as markets reassess Alphabet's competitive positioning within the global AI hardware ecosystem.
What is a Google TPU and why it matters
Google created the Tensor Processing Unit as an application specific integrated circuit designed for operations found in machine learning and data driven models, which is one of the major drivers behind the recent climb in the Google Stock Price.
The hardware focuses on matrix and tensor computations that power deep learning workloads. Early TPU generations were built for internal use within Google and were made available to customers only through Google Cloud services.
By preparing to sell TPUs to external customers, Google is shifting from an inward facing optimisation strategy to a fully commercial hardware business. This move opens the possibility of direct competition with general purpose GPUs that dominate the market today.[1]
TPU vs GPU: performance, architecture and use cases
TPUs and GPUs both accelerate artificial intelligence but they perform differently. GPUs are highly flexible and support a large ecosystem of libraries and frameworks. TPUs specialise in tensor operations and often demonstrate superior efficiency for certain training and inference tasks.
Google's focus on TPU efficiency has given analysts new reasons to monitor Google Stock Price performance as competition in AI hardware intensifies.
| Feature |
TPU |
GPU |
| Primary purpose |
Tensor and matrix computations for machine learning |
Graphics rendering and general compute tasks |
| Architecture |
ASIC designed for deep learning operations |
Many core parallel processor for broad workloads |
| Typical strengths |
High throughput for neural network training and inference |
Versatility, wide software support, strong performance for varied tasks |
| Ideal users |
Enterprises with large scale AI models and consistent tensor workloads |
Users requiring flexibility and broad framework compatibility |
| Market leaders |
Google |
Nvidia and AMD |
Enterprises may choose TPUs for large, predictable workloads that benefit from high throughput and potentially lower long term costs. GPUs remain a preferred option for developers who need broad compatibility and for organisations that run many different types of models.
Why Meta is exploring Google TPUs
Reports suggest that Meta may rent TPU capacity from 2026 and could purchase large quantities from 2027. Meta operates some of the world's largest AI systems including recommendation algorithms and large language models. These workloads require consistent access to immense compute capacity.
This development has been closely watched by investors who believe it could have long term influence on the Google Stock Price, especially if major customers begin shifting away from a GPU-only architecture.
Meta's interest in TPUs centres on three strategic goals:
Meta wants to diversify its supplier base and reduce reliance on a single GPU provider.
Meta seeks to secure competitive pricing for large training clusters and high volume inference tasks.
Meta aims to evaluate whether TPU performance aligns more efficiently with specific tensor heavy workloads within its infrastructure.
A diversified compute strategy helps large technology firms manage costs, performance, procurement risk and long term planning.
Why Google TPU sales challenge Nvidia and AMD

Nvidia's share of the AI data centre market remains extremely strong. However the introduction of commercially available TPUs introduces a real alternative for hyperscalers and major enterprises.
Investors have already reacted to reports of Google's changing strategy because even a small shift in procurement patterns can influence revenue expectations for existing GPU suppliers, that said, many believe this shift may influence future performance of Google Stock Price as demand for semiconductor alternatives grows.
The potential effects include:
Reduced pricing power for Nvidia if major customers gain viable alternatives.
More balanced hardware strategies within global cloud providers.
A greater focus on software portability that allows models to shift between AI accelerators.
Increased competition in AI silicon development which may accelerate innovation.
Although GPUs will remain central to the AI industry, TPUs could claim a meaningful share of workloads that suit their architecture. Thus, it could be a sustained driver of Google Stock Price appreciation.
Broadcom's expanding role in TPU development
Broadcom is a long standing partner in the design of Google's TPUs. This partnership also indirectly supports Google Stock. If Google begins large scale sales to external customers, Broadcom stands to benefit from increased demand for design and manufacturing services.
The collaboration strengthens Broadcom's position in high value custom silicon and expands the addressable market for its semiconductor services.
Market participants have viewed this development favourably because it enhances Broadcom's role in next generation AI infrastructure.
How TPU availability may reshape data centre and cloud strategy
Enterprises that adopt TPUs in their own facilities gain a new set of strategic options. They may run high throughput tensor workloads on premises while continuing to use cloud services for variable or short lived tasks.
This shift supports the narrative that Google is positioned to capture more enterprise hardware spending, a trend that analysts believe could further influence Google Stock performance.
Potential benefits include:
Greater control over latency and performance for critical models.
Improved data governance for organisations that prefer to keep sensitive information on site.
Reduced long term compute costs for predictable workloads.
Combinations of TPUs, GPUs and specialised ASICs tailored to each application.
This flexibility may encourage more organisations to explore multi chip architectures rather than relying on a single class of accelerators.
Long term implications for the AI chip market
If Google moves forward with a full commercial rollout of TPUs, AI compute competition will intensify. Hyperscalers, cloud providers and large global enterprises may look for ways to reduce vendor concentration and incorporate multiple classes of specialised silicon.
The long term effects could include:
Growth in custom chip design across major platforms.
Expanded hardware ecosystems around Google TPUs.
New cross compatibility frameworks that allow models to run on mixed accelerators.
Stronger bargaining power for large customers when negotiating future procurements.
All of these developments could contribute positively to Alphabet's long term valuation and reinforce the case for continued strength in the Google Stock Price.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Why is the Google stock price rising today?
The Google stock price is rising because investors are optimistic about Alphabet's decision to commercialise TPUs. This move expands its AI hardware strategy, diversifies revenue potential and intensifies competitive pressure on long-established GPU suppliers.
Q2: Could TPUs reduce Nvidia's dominance?
TPUs will not replace GPUs but could reduce Nvidia's pricing power if large customers adopt a more diversified accelerator strategy. This may gradually reshape the competitive dynamics in AI hardware.
Q3: Will Meta's interest in TPUs impact the market?
Meta's potential adoption is important because major hyperscalers influence hardware standards globally. Even partial migration to TPUs may encourage other enterprises to explore non-GPU alternatives.
Q4: Are TPUs suitable for all AI workloads?
TPUs are highly efficient for large language model training and inference but GPUs still offer greater versatility. Most companies will adopt hybrid or multi-accelerator strategies.
Sources:
[1] https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/compute/performance-per-dollar-of-gpus-and-tpus-for-ai-inference
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.





























