In global finance, exchange rates are more than just numbers; they shape economies, influence trade, and impact our daily lives. One of the most widely used and debated exchange rate systems is the floating exchange rate. But what is it exactly, how does it work, and why does it matter so much?
In this article, we will define a floating exchange rate, compare it to fixed systems, provide real-world examples, and discuss its benefits and drawbacks. We'll also explain why traders, investors, and policymakers pay close attention to this topic.
Understanding Exchange Rates

Before diving into floating systems, let's define exchange rates more broadly. An exchange rate is the value of one country's currency in terms of another country's currency. For example, if 1 US dollar equals 18 South African rand, that's the USD/ZAR exchange rate.
Exchange rates influence:
International trade
Travel costs
Investment returns
Monetary policy
There are two main types of exchange rate systems: floating and fixed (or pegged). Countries may adopt one or a hybrid approach, depending on their economic strategy.
What Is a Floating Exchange Rate?
A floating exchange rate is a system for valuing a currency in which its price is set by market dynamics, particularly supply and demand within the foreign exchange (forex) market. There is no predetermined target or peg, allowing the exchange rate to fluctuate freely.
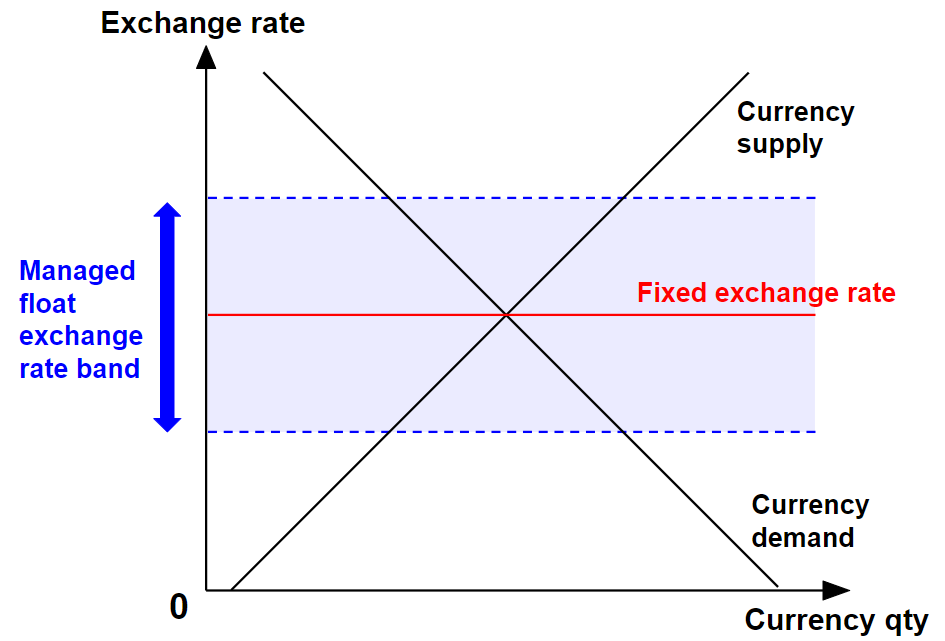
Governments or central banks do not actively intervene to maintain a set rate. However, in extreme conditions, they may step in to stabilise the economy—a system known as a managed float.
Key Features:
Currency value changes daily (or even hourly)
Influenced by trade balances, interest rates, inflation, political stability, and speculation
Used by most developed nations, including the US, UK, Japan, Canada, and Australia
How Does a Floating Exchange Rate Work?
Let's say the demand for the euro (EUR) increases relative to the US dollar (USD). More investors or traders want euros to invest in European assets or trade European goods.
It pushes the EUR/USD exchange rate higher, meaning the euro strengthens and the dollar weakens.
If demand for euros falls, the opposite happens: the euro weakens, and the dollar strengthens. These movements happen continuously due to:
The floating exchange rate reflects real-time assessments of a country's economic health and outlook.
Floating Exchange Rate Examples
United States (USD)
The US dollar is a classic example of a floating currency. It is influenced by Federal Reserve policy, economic data (such as inflation and jobs), and global investor sentiment. Events such as interest rate hikes or geopolitical tensions can cause significant movement.
Japan (JPY)
The Japanese yen floats freely, but the Bank of Japan occasionally intervenes when volatility spikes. For example, if the yen appreciates too much, it hurts exports, prompting temporary action.
South Africa (ZAR)
The South African rand is a floating currency, highly responsive to commodity prices, political developments, and global risk sentiment. When markets are nervous, emerging-market currencies such as the rand often weaken.
United Kingdom (GBP)
The British pound is another example. Brexit-related news led to significant fluctuations in the GBP/USD exchange rate as markets reevaluated economic risks.
Floating vs Fixed Exchange Rate
| Floating Exchange Rate |
Fixed Exchange Rate |
| Market-determined through supply and demand |
Pegged to another currency or basket of currencies |
| High volatility and frequent fluctuations |
Stability and predictability |
| Adjusts automatically to economic conditions |
Requires intervention by central banks |
| Used by US, UK, Japan, Canada |
Used by Hong Kong, saudi arabia, UAE |
| Exposed to speculative trading risks |
Prone to black market rates if peg is unrealistic |
Many countries opt for a hybrid or managed float system, intervening occasionally to correct excessive volatility while letting the market play a leading role.
Floating Exchange Rate and Forex Trading
The floating exchange rate system is the foundation of the global forex market, the largest and most liquid financial market in the world.
Why Traders Like Floating Rates:
Volatility: More price movement means more trading opportunities
24/5 Access: Forex is open around the clock, overlapping with major trading sessions (London, New York, Tokyo)
Diverse Strategies: Traders use technical analysis, trend-following, or news-based trading in floating currency pairs
Popular floating pairs include:
EUR/USD
GBP/USD
USD/JPY
USD/ZAR
AUD/USD
Platforms like EBC Financial Group offer access to these pairs with real-time spreads, deep liquidity, and robust charting tools suitable for both beginners and professionals.
Recent Examples
COVID-19 Pandemic
During the early months of 2020, panic and uncertainty led to a massive flight to safety. The US dollar surged against many currencies, while oil-exporting nations like Russia and Nigeria saw their currencies plummet. Floating rates adjusted quickly to reflect this turmoil.
Brexit
The UK pound declined after the Brexit vote in 2016. Floating exchange rates allowed the GBP/USD rate to absorb the shock and reflect new trade risks.
US Interest Rate Hikes (2022–2023)
As the Federal Reserve raised interest rates to combat inflation, the dollar strengthened against floating currencies such as the euro and yen. This shift had a global impact on trade and capital flows.
Should Countries Adopt Floating Exchange Rates?
There's no one-size-fits-all answer. Floating exchange rates offer flexibility and autonomy, making them ideal for economically stable and developed countries.
However, they might not be suitable for smaller or developing economies, as volatility can lead to social and economic instability.
When choosing a system, countries consider:
Benefits and Risks
| Benefits |
Risks |
| Adjusts automatically to economic changes, balancing trade deficits/surpluses |
Prone to volatility and sharp fluctuations due to market speculation |
| Allows independent monetary policy decisions without needing to defend a peg |
Creates uncertainty for importers, exporters, and investors |
| Reflects real-time supply and demand, improving market efficiency |
A weak currency can lead to imported inflation |
| Reduces need for maintaining large foreign currency reserves |
Emerging markets may suffer from capital flight during global shocks |
| Encourages fiscal discipline and long-term structural reforms |
Sudden shifts in investor sentiment can destabilize weaker economies |
Conclusion
In conclusion, a floating exchange rate system adjusts currency values to supply and demand, accurately reflecting a country's economic performance in real-time.
While it introduces volatility and uncertainty, it also offers flexibility, transparency, and autonomy in today's interconnected world.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.