Nikkei futures are among the most popular ways for traders worldwide to gain exposure to the Japanese stock market. As Japan's economy continues to play a major role in global finance, understanding Nikkei futures can open up new opportunities for both hedging and speculation.
If you're new to trading or just curious about how these contracts work, this guide will walk you through the essentials, from contract types to trading strategies and risk management.
What Are Nikkei Futures?
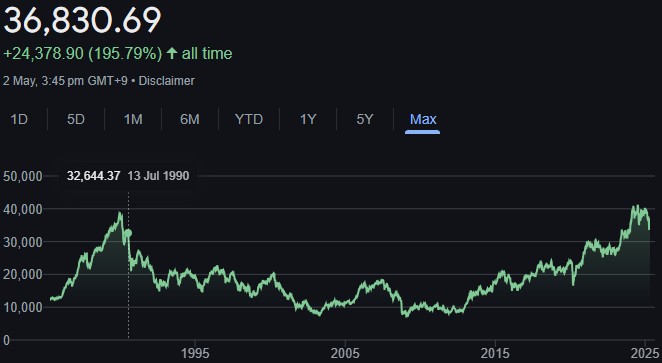
Nikkei futures are financial contracts that allow traders to buy or sell the Nikkei 225 index at a predetermined price on a future date. The Nikkei 225 is Japan’s primary stock market index, tracking the performance of 225 top companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
By trading futures, you can speculate on whether the index will rise or fall-without owning any actual shares.
Key Features
Underlying Asset: Nikkei 225 index
Settlement: Cash-settled (no physical delivery of stocks)
Contract Months: March, June, September, December
Trading Hours: Nearly 24-hour trading, including night sessions
Leverage: Trade a large notional value with a fraction of the capital (margin)
Types of Nikkei Futures Contracts
To suit different trading needs, Nikkei futures are available in various contract sizes and currencies:
Standard Nikkei 225 Futures: Large contracts, typically JPY-denominated, with a contract size of Nikkei 225 × 1,000.
E-mini and Micro Nikkei Futures: Smaller contract sizes, available in both JPY and USD denominations, ideal for retail traders or those seeking more flexibility.
Mutual Offset System: Allows positions to be opened on one exchange (e.g., CME or SGX) and closed on another, boosting liquidity.
How Does Nikkei Futures Trading Work?
When you buy or sell a Nikkei futures contract, you agree to exchange the value of the index at a set price on the contract’s expiration date. If the index moves in your favour, you profit; if not, you incur a loss. Since these contracts are cash-settled, no actual stocks change hands-your gains or losses are paid in cash.
Example
Suppose the Nikkei 225 is trading at 30,000. You buy one standard contract (Nikkei 225 × 1,000 = ¥30,000,000). If the index rises to 31,000 by expiry, your profit is:
(31,000−30,000)×1,000=¥1,000,000
If the index falls, you'd incur a loss of the same calculation.
Margin and Leverage
One of the main attractions of futures trading is leverage. You only need to deposit a margin-a small percentage of the contract's notional value-to control a much larger position.
For example, a margin of ¥1,700,000 might let you control a contract worth ¥30,000,000, giving you about 18 times leverage. However, leverage amplifies both gains and losses, so risk management is crucial.
Trading Hours and Expiry
Day Session: 8:45–15:45 (Japan time)
Night Session: 17:00–6:00 (next day)
Contract Expiry: The business day before the second Friday of the contract month.
New contracts begin trading the day after the previous contract expires, and up to 19 contract months can be traded at once.
Why Trade Nikkei Futures?
Broad Market Exposure: Capture the performance of Japan's top 225 companies in a single trade.
Leverage: Control large positions with less capital.
Hedging: Offset risks in Japanese stocks or portfolios.
Liquidity: High trading volumes and tight spreads, especially in major contracts.
Global Access: Trade in JPY or USD, and use international exchanges like CME and SGX.
Key Strategies for New Traders
Trend Following: Use technical analysis to identify and ride market trends.
Spread Trading: Exploit price differences between JPY- and USD-denominated contracts or between different contract months.
Hedging: Protect your Japanese stock holdings from market downturns by selling futures contracts.
Risk Management: Always set stop-loss orders and monitor your margin to avoid forced liquidations.
Risks and Considerations
Leverage Risk: While leverage can boost profits, it also magnifies losses. Never risk more than you can afford to lose.
Market Volatility: Futures prices can swing sharply, especially around major economic news or earnings releases.
Margin Calls: If your account falls below the required margin, you may need to deposit more funds or have your position closed at a loss.
Contract Expiry: Be aware of contract expiration dates and roll over positions if you want to maintain your exposure.
Final Thoughts
Nikkei futures offer an efficient, flexible way to trade Japan's leading stock index, whether you're seeking growth, hedging risk, or simply diversifying your portfolio.
By understanding contract types, trading mechanics, and risk management, new traders can confidently navigate this dynamic market. Remember, start small, use leverage wisely, and always keep learning as you build your futures trading skills.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.