LEAP options are long-term equity anticipation securities, commonly known as long-dated options. These contracts allow traders and investors to benefit from price movements in underlying assets, but with much longer timeframes than standard options. Where regular options expire within weeks or months, LEAP options can have expiration dates as far as two years into the future.
To put it simply, LEAP options function the same way as shorter-term options but give traders more time for their strategies to develop. That makes them particularly popular among investors who want exposure to long-term market moves without having to tie up as much capital as they would with outright stock ownership.
What Are LEAP Options?
LEAP stands for Long-Term Equity Anticipation Securities. These are standardised options contracts with expiration dates that extend beyond one year. In most cases, LEAP options can go out as far as 24 to 36 months, though availability depends on the underlying security.
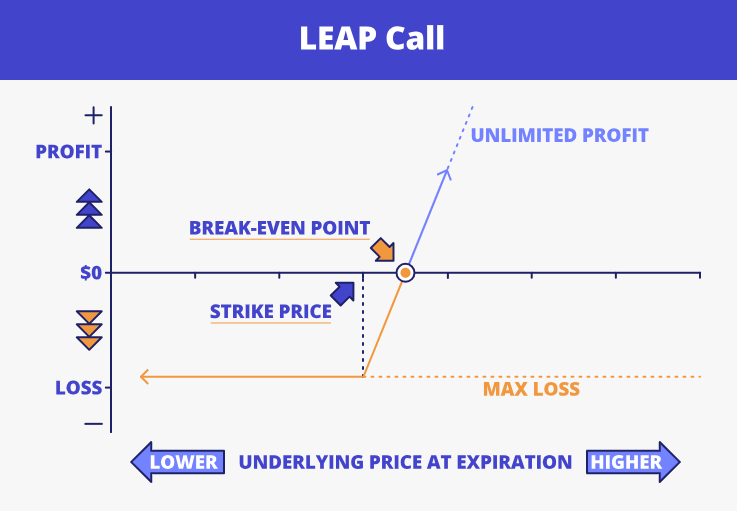
Just like regular options, LEAP options come in two forms: calls and puts. A LEAP call option gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase the underlying stock at a predetermined price (known as the strike price) before the option expires. A LEAP put option, on the other hand, gives the buyer the right to sell the underlying stock at the strike price before the expiry date.
These contracts are listed and traded on major options exchanges and can be bought or sold just like shorter-dated options. The main difference lies in the time element. The extended expiration window gives investors more flexibility and a longer time horizon to play out their expectations of future stock movements.
Why Investors Use LEAP Options
LEAP options are often used by investors who have a long-term view on a particular stock or index but prefer not to tie up large sums of capital. Buying 100 shares of a company can be expensive, particularly for high-value stocks. A LEAP call option on the same stock allows a trader to control those shares for a fraction of the cost.
The appeal lies in the leverage. A relatively small premium gives the buyer exposure to the stock's long-term performance. If the price moves in the anticipated direction, the option can increase significantly in value over time. If the trade goes wrong, the maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for the option.
Another reason investors use LEAP options is to hedge existing positions. For example, a shareholder who wants downside protection can purchase a LEAP put option. If the share price drops, the put gains in value and helps offset the losses in the underlying asset.
LEAP options can also be used to generate income by selling them, particularly in covered call strategies. Because they are long-dated, they contain more time value, and that translates into higher premiums for sellers.
LEAP Options vs Short-Term Options

One of the biggest differences between LEAP options and short-term options is how they respond to the passage of time. All options lose value over time due to time decay, but LEAP options decay much more slowly. This gives traders more time for a thesis to play out without worrying as much about rapid erosion of value.
In addition, LEAP options are less sensitive to short-term volatility. Because they are priced with a longer time frame in mind, day-to-day swings in the market tend to have a smaller impact on their value compared to short-term contracts.
However, because of their longer duration, LEAP options are generally more expensive in terms of premium. Investors need to consider whether the potential gain justifies the higher cost and whether they have the patience to wait for the position to develop.
When LEAP Options Make Sense
LEAP options are best suited to traders and investors with a clear long-term view. For example, if an investor believes a particular company is undervalued and likely to rise substantially over the next 18 months, a LEAP call option could be a more cost-effective way to gain exposure.
These options also make sense for those looking to build structured strategies such as diagonal spreads or long-term hedges. A portfolio manager who wants to reduce downside risk during uncertain economic conditions might use LEAP put options to limit losses over the next year or more.
It is important to understand that while the longer expiry gives more breathing room, LEAP options still carry risk. If the anticipated move does not occur before expiry, the option may expire worthless.
Risks Involved in LEAP Options
Like any financial instrument, LEAP options involve risks. The most obvious is the potential loss of the premium paid. Even with more time, the market may not move in the expected direction, and the option may end up with no intrinsic value.
Liquidity can also be an issue. While many LEAP options are traded on large-cap stocks and indices, the further out the expiry date, the fewer the number of contracts typically available. This can make it harder to enter or exit positions at desirable prices.
Another risk is the misjudgement of time. Having more time is not always a guarantee of success. If the market conditions shift dramatically or the fundamental outlook for the stock changes, the long time horizon might not provide the expected benefit.
Choosing the Right LEAP Option

Selecting the right LEAP options contract involves several considerations. Strike price selection is crucial. Deep in-the-money options provide more intrinsic value and are more expensive but behave more like the underlying stock. Out-of-the-money options are cheaper and offer greater percentage returns if successful, but they also carry higher risk.
Time to expiry is another factor. Longer expiries give more flexibility but cost more. Some traders choose expirations 12 to 18 months out, balancing cost with time. Those building complex strategies may opt for full 24- to 36-month contracts.
Ultimately, it depends on the investor's objective. Are they looking for aggressive returns, downside protection, or steady income generation? LEAP options offer tools to support each of these goals, but strategy and risk management remain key.
Conclusion
LEAP options offer a flexible and efficient way to gain exposure to long-term market trends without committing large amounts of capital. They can be used for directional bets, portfolio hedging, or income generation, depending on how they are structured. With longer durations and slower time decay, LEAP options give traders time for their strategies to mature.
However, like any investment tool, they require a solid understanding of how they work and what risks are involved. Used properly, LEAP options can be a powerful part of a well-rounded trading strategy, especially for those with a long-term outlook.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.