B-Book brokers internalize client trades instead of sending them to the real market. Learn how this model works, why brokers use it, and what it means for your trading outcomes.
Introduction
A B-Book broker is a type of forex or CFD broker that takes the opposite side of a client’s trade rather than sending it to the open market.
It matters because it determines whether your broker profits when you lose or when you win. It is directly affecting the transparency and trust in trading execution.
Definition
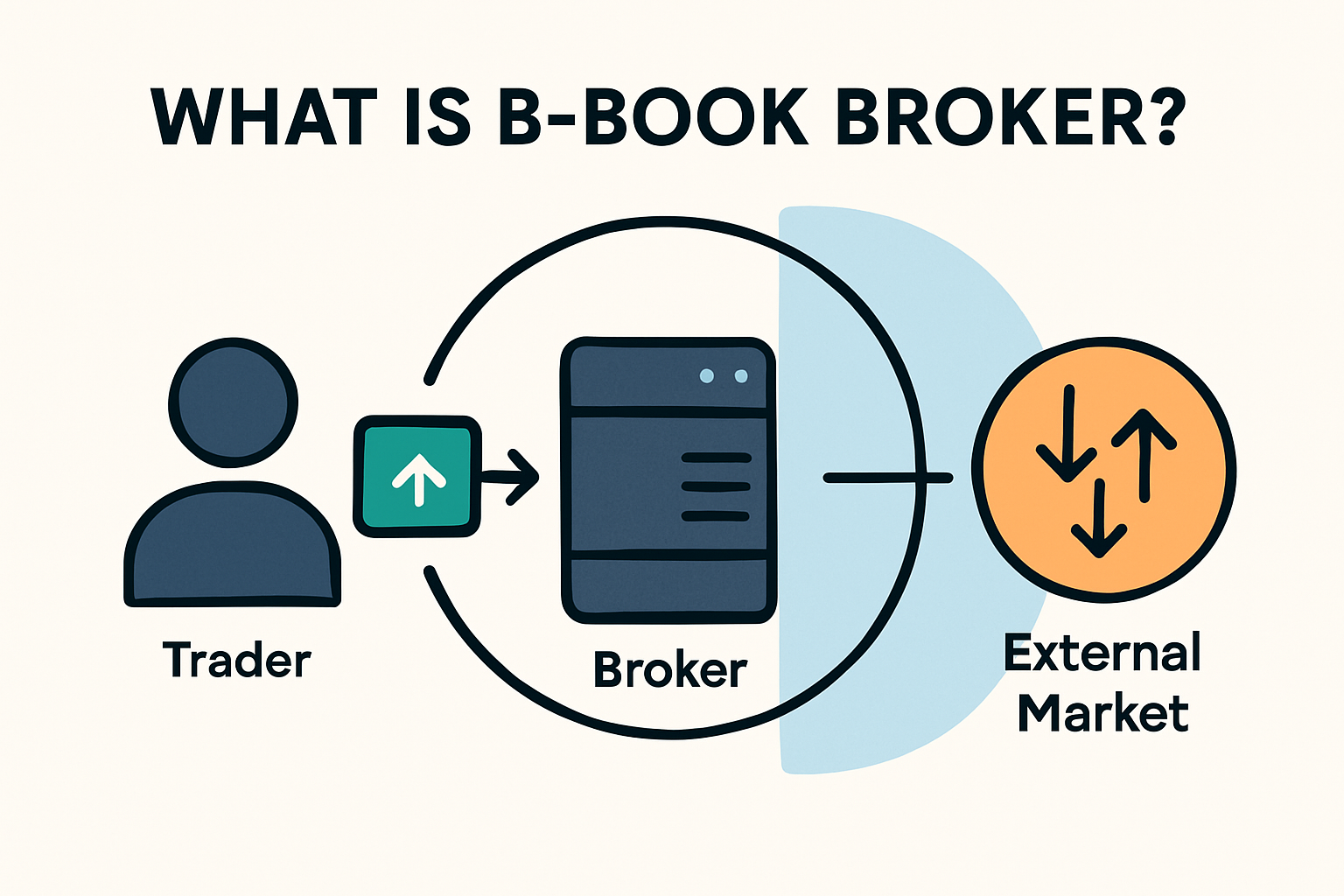
A B-Book broker is a market maker that handles trades internally instead of routing them to external liquidity providers.
In this model, the broker becomes the counterparty to the client’s trade so when a trader buys, the broker sells, and vice versa.
The broker’s profit or loss depends on the trader’s performance: if the trader loses, the broker gains; if the trader wins, the broker pays out.
This setup creates a potential conflict of interest, but it also allows brokers to offer fixed spreads, fast execution, and low trading costs for smaller accounts.
How a B-Book Broker Works
The B-Book model works by internalizing client trades through the broker’s own dealing desk:
Step 1: A trader places a buy or sell order.
Step 2: Instead of forwarding the order to a liquidity provider, the broker matches it internally or takes the opposite side.
Step 3: The broker manages overall risk by aggregating positions, offsetting exposure only when client trades become unbalanced or too large.
Step 4: If the trader loses, the broker earns that amount; if the trader wins, the broker pays the profit from its own funds.
To manage risk, many modern brokers operate a hybrid model, using both A-Book and B-Book execution. Profitable or high-volume clients are sent to the A-Book, while smaller or less consistent traders remain on the B-Book.
Example
Suppose a trader opens a $10,000 buy position on EUR/USD with a B-Book broker. Instead of sending the order to external liquidity providers, the broker takes the opposite sell position in-house.
If the EUR/USD pair drops and the trader loses $500, the broker earns that $500.
However, if the trader’s position moves in profit, the broker must pay out from its own account.
This means the broker’s earnings depend on the trader’s performance, aligning profits with client losses.
Advantages and Risks
| Advantages / Benefits |
Disadvantages / Risks |
| Fast execution and no rejection during high volatility |
Potential conflict of interest with client trades |
| Fixed spreads and lower trading costs |
Risk of price manipulation or stop-hunting by unethical brokers |
| Suitable for small-volume or retail traders |
Transparency depends on broker regulation and disclosure |
| Allows brokers to hedge or rebalance exposure efficiently |
Not ideal for consistent or high-profit traders |
Related Terms
A-Book Broker: A broker that sends trades directly to external liquidity providers, earning through spreads or commissions.
Market Maker: A broker or institution that provides bid and ask quotes and takes the opposite side of trades to maintain liquidity.
Dealing Desk (DD): The internal system a broker uses to process and manage client orders in a B-Book setup.
Hybrid Model: A broker setup that combines both A-Book and B-Book execution to balance transparency and profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why do brokers use the B-Book model?
It allows brokers to control risk, maintain liquidity, and offer competitive trading conditions like fixed spreads and quick execution.
2. Is B-Book trading legal?
Yes. It’s a regulated and common business model in forex and CFD trading, provided the broker is transparent and compliant with local financial authorities.
3. How can I tell if my broker is a B-Book broker?
Check if the broker is described as a market maker or dealing desk broker. Regulated firms must disclose their execution method in their terms or trading policy.
Summary
A B-Book broker internalizes trades and takes the opposite side of client orders, acting as the counterparty rather than routing them to the market.
B-Book forex brokers typically provide fixed spreads, meaning trading costs stay consistent regardless of market conditions. Whether you trade during peak volatility or quieter hours, a B-Book setup can offer more stable and predictable pricing.
Although, while it enables faster execution and fixed spreads, it introduces a potential conflict of interest that should be executed cautiously.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment, or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction, or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.





















