As of 30 October 2025, the euro trades at approximately ¥173.5 per €1, maintaining one of its strongest levels against the Japanese yen since 2008. In reverse, this means 1 ¥ ≈ 0.00576 €, highlighting the yen’s relative weakness versus the euro.
The widening gap between European Central Bank (ECB) and Bank of Japan (BoJ) policies continues to drive this trend.
Understanding these dynamics is essential for anyone managing money transfers, investments, or trade between Japan and the Eurozone.
Current Japanese Yen to Euro Value (30 October 2025)
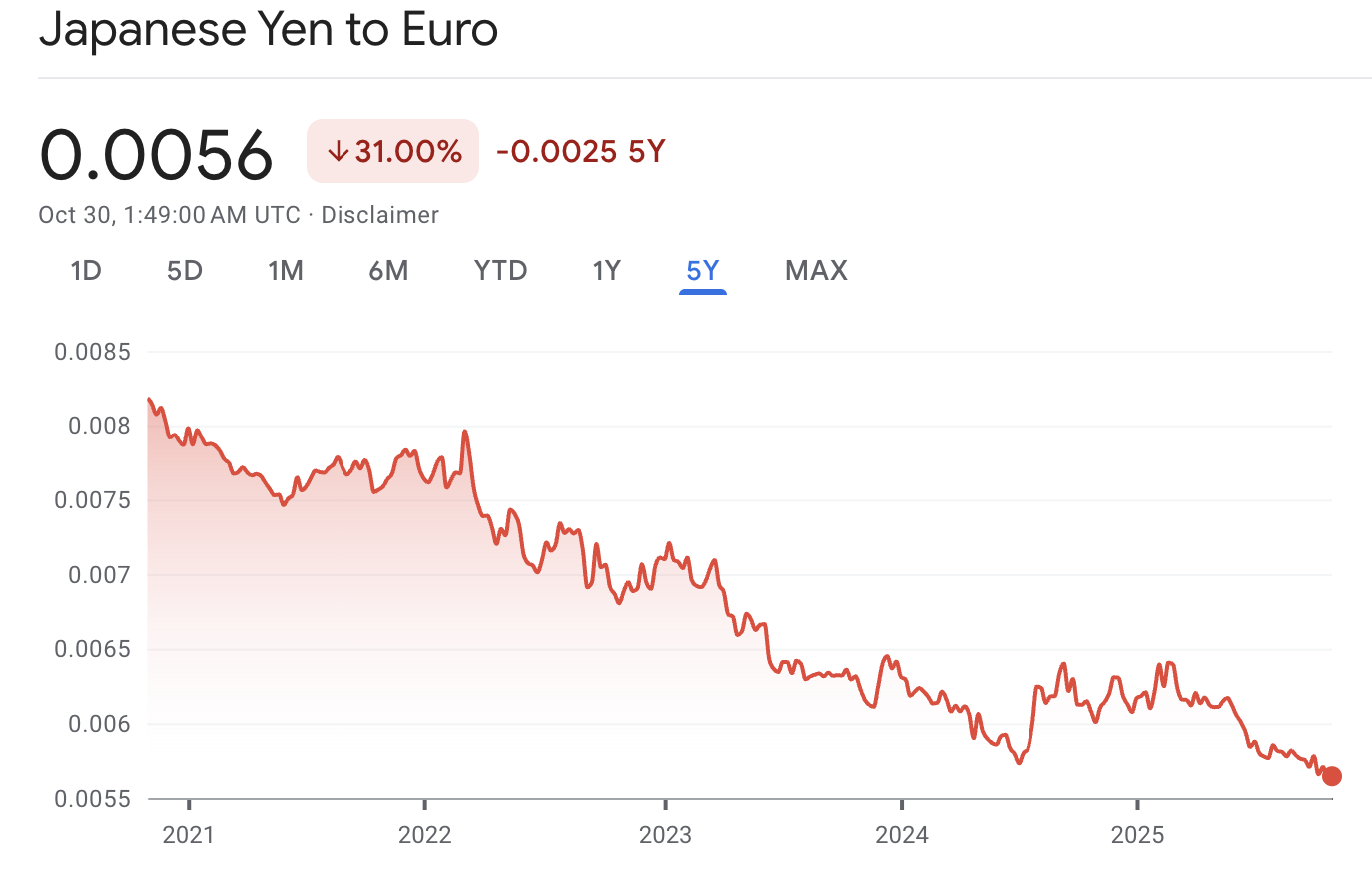 As of 30 October 2025, 1 JPY ≈ 0.00576 EUR, reflecting continued yen weakness. The trend shows the euro strengthening against the yen, driven by higher ECB rates and Japan’s ongoing monetary easing.
As of 30 October 2025, 1 JPY ≈ 0.00576 EUR, reflecting continued yen weakness. The trend shows the euro strengthening against the yen, driven by higher ECB rates and Japan’s ongoing monetary easing.
Let's explore the core factors that influence this currency pair and how they interact in today's dynamic economic environment.
Key Factors Influencing the Yen to Euro Exchange Rate
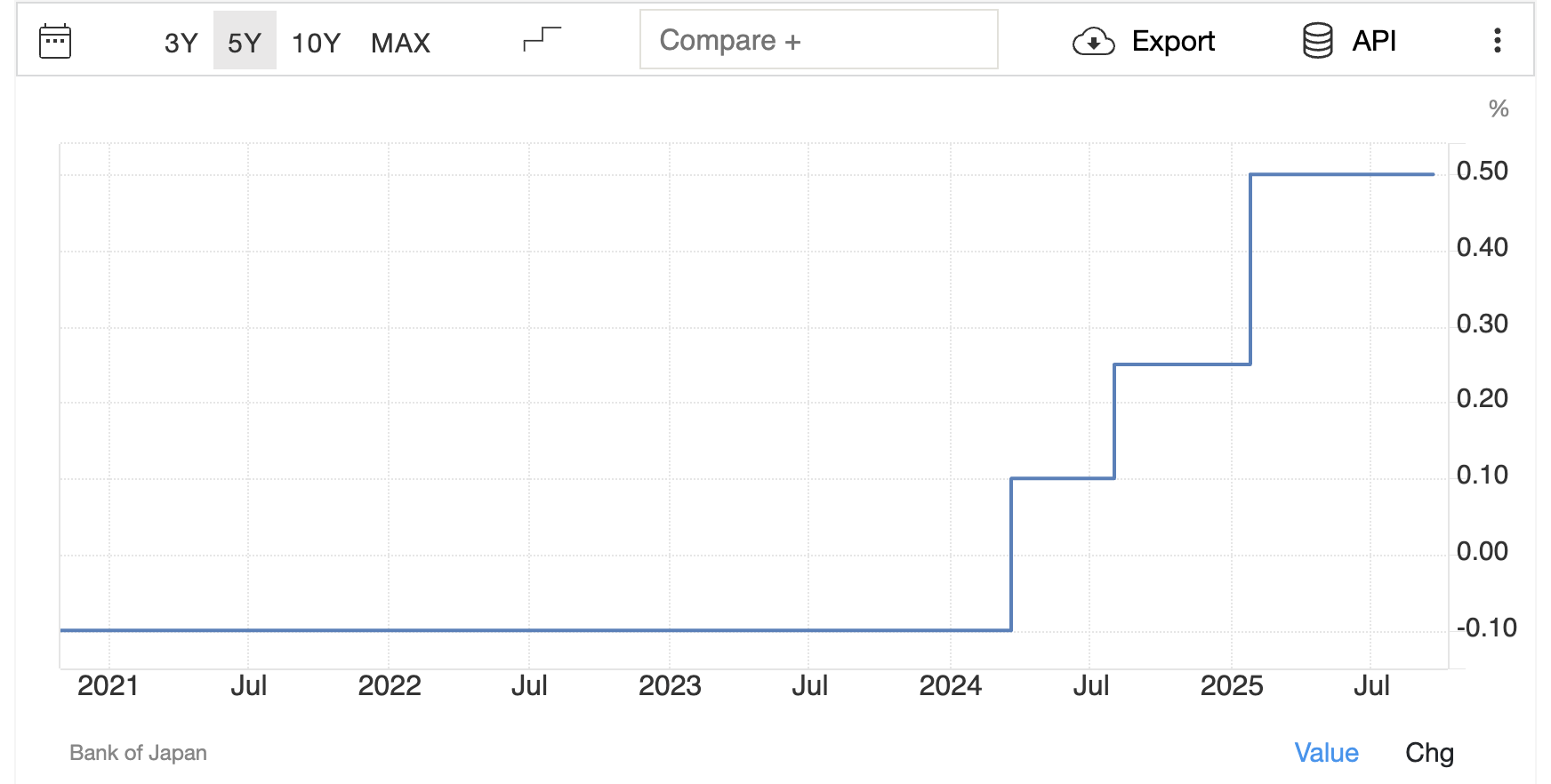
1. Interest Rate Differentials
The European Central Bank’s key deposit facility rate stands at approximately 2.00%, while the Bank of Japan’s policy rate remains at 0.50%, with markets expecting a possible rise to 0.75% in the near term.
This sizable yield gap continues to encourage capital flows into the Eurozone, thereby supporting the euro.
2. Inflation and Growth Performance
In the European Central Bank (ECB)‑jurisdiction, annual inflation stood at 2.2% in September 2025, up from about 2.0% the previous month.
In Japan, core consumer prices rose about 2.9% year‑on‑year in September 2025, keeping pressure on the monetary‑policy front.
Economic‑growth momentum is modest: The IMF projects Japan’s real GDP growth at about 1.1% for 2025.
3. Central Bank Policies and Interventions
Despite signs of pressure, the BoJ maintains yield curve control and bond purchases. Any hint of policy normalization could trigger a stronger yen, though markets see this as unlikely before mid-2026.
4. Trade Balances and Global Flows
Japan’s energy imports have widened its trade deficit, while the Eurozone’s export resilience especially in machinery and autos supports euro demand.
5. Political Stability and Market Sentiment
Political stability across the Eurozone continues to support investor confidence, while Japan’s slower growth and demographic challenges weigh on market sentiment. This divergence contributes to sustained euro strength versus the yen.
6. Safe-Haven Flows
The yen remains a safe-haven asset, often strengthening briefly during global uncertainty. However, these moves have been short-lived amid steady euro demand.
7. Carry Trade Dynamics

Japan’s low rates continue to make the yen a funding currency for global carry trades. When risk appetite is high, the yen weakens as investors seek higher yields abroad.
8. Commodity Prices and Terms of Trade
Both economies rely on imported energy. Elevated oil prices pressure Japan’s yen, while Europe’s diversified sourcing provides relative stability.
9. Natural Disasters and External Shocks
Japan’s exposure to natural events, such as summer typhoons in 2025, caused minor short-term volatility in the yen.
10. Economic Data Releases
Ongoing releases of GDP, CPI, and employment data from Japan and the Eurozone continue to influence short‑term JPY/EUR market movements.
In the Eurozone, preliminary Q3 2025 GDP growth was reported at 0.3% quarter-on-quarter, with September inflation at 2.2%.
In Japan, Q3 2025 GDP growth came in at 0.2% q/q, while core CPI remained elevated at 2.9%, keeping market attention on potential BoJ policy adjustments.
These reports frequently trigger volatility in the yen-to-euro rate, especially when they diverge from expectations.
Pros and Cons Of Investing In Japanese Yen
The Japanese yen remains a strategic defensive asset, useful for diversification and crisis protection, but it’s not a high-yield play. Investors considering exposure should view the yen as a stability anchor, not a short-term growth engine.
| Benefits of Investing in Japanese Yen |
Risks of Investing in Japanese Yen |
| Seen as a safe-haven currency during global uncertainty |
Very low interest rates mean limited returns |
| Helps diversify and balance investment portfolios |
Yen can stay weak for long periods |
| Japan has a strong, stable financial system |
Aging population and slow growth limit upside |
| May rise if Bank of Japan tightens policy |
Policy changes or global shifts can cause volatility |
Yen to Euro: Outlook for Late 2025 and Beyond
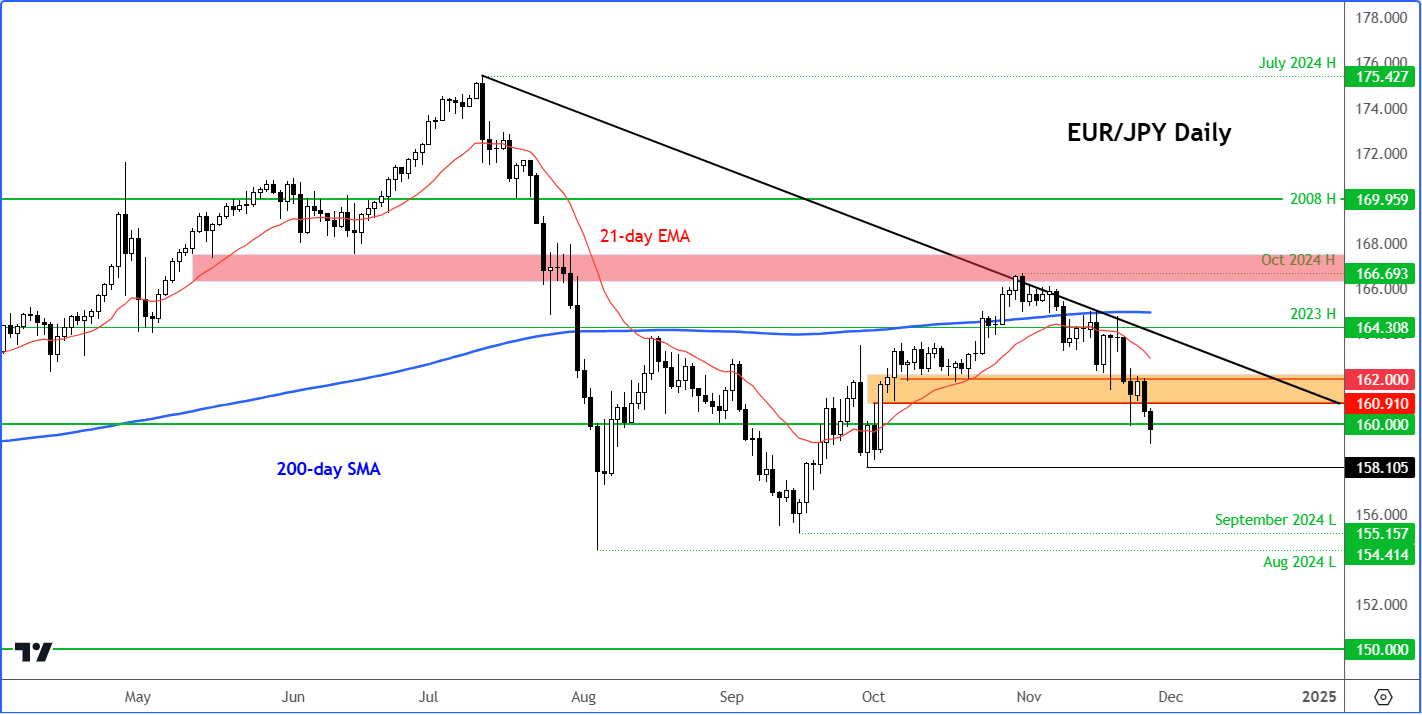
Market consensus suggests the EUR/JPY pair will stay within the 170–175 range through year-end. A meaningful yen recovery is unlikely until the BoJ raises rates or inflation in Japan stabilizes.
Forecast Summary (as of 29 Oct 2025):
Short-Term Range: ¥172–¥175
Year-End Target: Around ¥174
2026 Outlook: Gradual yen strengthening possible if BoJ tightens policy
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) directly affects the yen’s value through its monetary policy decisions. When it lowers interest rates or implements quantitative easing, the yen tends to weaken because returns for holding yen decrease and liquidity rises.
Conversely, raising rates or tightening policy attracts capital inflows, strengthening the currency. Tools like yield curve control and forward guidance further influence market expectations, with even hints of tightening capable of boosting the yen.
Inflation and economic growth outlooks also guide BoJ actions, so markets closely watch announcements, knowing they can sway the EUR/JPY pair significantly.
Key Investors Takeaway
Euro strength favors EUR-denominated assets: With the euro near ¥173.5, European investments may offer currency gains when converted to yen.
Hedging is crucial: For Japanese investors or businesses exposed to EUR payments, using FX hedges can reduce volatility risk.
Monitor policy divergence: ECB rate stability versus BoJ easing is likely to keep the yen under pressure, affecting short‑term and medium‑term currency positions.
Opportunities in trade and arbitrage: Companies importing from the Eurozone or engaging in cross-border transactions can benefit from strategic timing of conversions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the current yen to euro rate?
As of 30 October 2025, 1 JPY ≈ 0.00576 EUR, or 1 EUR ≈ ¥173.5.
2. Why is the yen weak against the euro?
The euro benefits from higher ECB rates, while the BoJ continues monetary easing, widening the interest-rate gap.
3. When might the yen strengthen again?
A meaningful yen recovery is unlikely until the BoJ raises rates or inflation in Japan stabilizes, possibly in 2026.
4. How can investors manage currency risk?
Using FX hedges, monitoring central bank policy, and strategically timing conversions can reduce exposure to JPY/EUR volatility.
5. What factors most influence the JPY/EUR pair?
Interest rates, inflation, BoJ/ECB policy, trade balances, global risk sentiment, and key economic data releases.
Final Thoughts
The yen to euro exchange rate is shaped by a complex mix of factors, including interest rates, inflation, central bank policy, trade balances, political stability, and global risk sentiment.
By understanding these drivers, you can better anticipate currency movements and make informed decisions-whether you're exchanging money, investing, or managing international business in 2025.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.