The global economy is complex and ever-changing, shaped by inflation, employment, production, and geopolitical shifts. One of the most perplexing and feared economic phenomena is stagflation, which puzzles economists and spooks investors.
As we move through 2025, questions about stagflation have resurfaced due to persistent inflation, sluggish growth, and geopolitical instability. But what exactly is stagflation? Why does it matter? And should you be concerned this year?
In this article, we'll explain stagflation, what causes it, how it affects the average person, and how to protect your investments and financial well-being if stagflation becomes a reality in 2025.
What Is Stagflation?
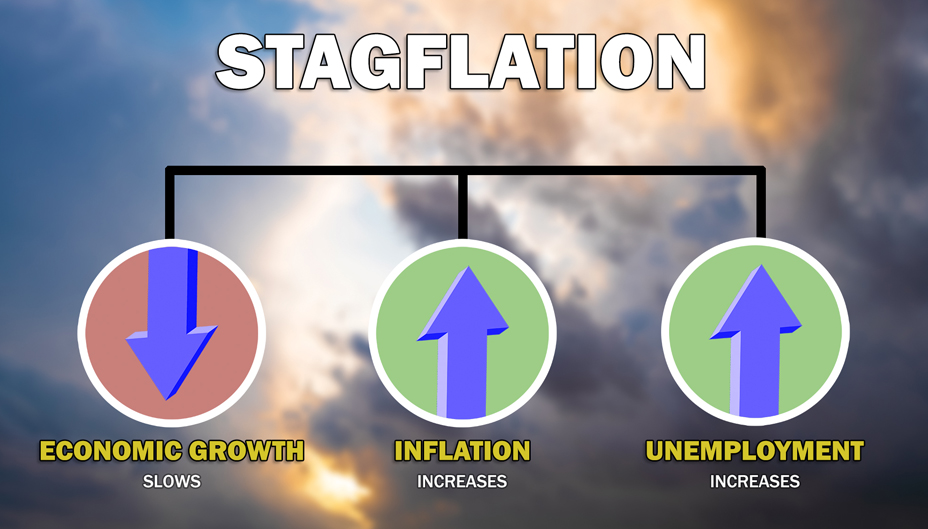
The word stagflation combines two economic terms: stagnation and inflation. It refers to high inflation occurring with slow economic growth and high unemployment simultaneously. It is unusual because inflation and unemployment typically move in opposite directions.
Under normal economic theories like the Phillips Curve, high inflation coincides with low unemployment and vice versa. Stagflation defies this logic, making it a rare and troubling anomaly for policymakers, economists, and investors.
Stagflation's Brief History
The most well-known instance of stagflation occurred during the 1970s, especially in the United States. A series of oil shocks triggered by geopolitical tensions caused energy prices to soar, which led to widespread inflation. At the same time, economic growth stalled, and unemployment increased due to tightening monetary policy and a decline in manufacturing competitiveness.
During this time, central banks were caught in a bind: raising interest rates could fight inflation, but increase unemployment and reduce economic output. On the other hand, lowering rates to stimulate growth could worsen inflation. It was a difficult balancing act with few good options.
This historical experience left a lasting impact and has shaped how economists and governments think about inflation control and economic management today.
What Causes Stagflation?
1. Supply Shocks: A sudden disruption in the supply of essential goods, like oil, food, or energy, can raise prices dramatically. This type of inflation isn't caused by demand but by shortages, which also slow production.
2. Poor Economic Policy: Overreliance on expansionary monetary policies, such as prolonged low interest rates or excessive government spending, can contribute to inflation while failing to stimulate real economic growth.
3. Wage-Price Spirals: When workers demand higher wages to keep up with inflation and businesses pass these costs on to consumers, a self-reinforcing loop of rising prices and wages can develop.
4. Declining Productivity: If businesses are unable or unwilling to invest in innovation, infrastructure, or human capital, productivity stagnates, leading to slower economic growth even as prices continue to rise.
5. Geopolitical Uncertainty: Wars, trade disruptions, and political instability can drive up costs, reduce investor confidence, and impair global supply chains—all ingredients for stagflation.
Rising global tensions, energy price volatility, persistent inflation, and slowdowns in manufacturing are present in 2025, contributing to growing concerns about a stagflationary environment.
Stagflation in 2025: Is It Happening?
So, is the world actually experiencing stagflation in 2025? Economists are split. While not every country is currently facing a textbook case of stagflation, several worrying trends suggest we may be moving in that direction.
Inflation remains high in many developed economies, partly due to elevated energy prices, persistent supply chain issues, and wage pressures. At the same time, GDP growth has slowed, particularly in Europe and parts of Asia, while unemployment has begun to tick upward in sectors like manufacturing and tech.
Central banks, including the U.S. Federal Reserve, are grappling with taming inflation without choking off growth. Interest rates remain relatively high compared to the previous decade, which dampened consumer spending and business investment.
The effects are even more pronounced in emerging markets. Rising interest rates in developed economies have led to capital outflows from developing nations, depreciating their currencies and increasing the cost of imports, specifically energy and food. This creates inflationary pressures and hampers growth simultaneously.
Although not officially declared, many economists argue that pockets of stagflation are emerging, especially in economies where inflation remains elevated above target levels while growth falters.
How Stagflation Affects You
Declining Purchasing Power: As prices rise but incomes stay flat or decline due to weak economic conditions, your purchasing power erodes. Every day, items become more expensive, and your money doesn't go as far.
Job Insecurity: High unemployment means fewer job opportunities, less job security, and potentially lower wages. Employers are less likely to hire or increase pay during economic stagnation.
Lower Investment Returns: Stock markets typically struggle during stagflation. Corporate profits decline as input costs rise and consumer demand weakens, leading to increased volatility and reduced equity valuations.
Housing Market Volatility: High interest rates can hold real estate demand. Mortgage payments rise, affordability drops, and property prices may stagnate or fall.
In short, stagflation can squeeze your finances from multiple angles —costs go up, income growth slows, and investment returns become harder to come by.
How to Protect Your Finances During Stagflation
If stagflation becomes more entrenched in 2025 and beyond, it's essential to take steps to protect your financial position.
1) Diversify Your Investments: In a stagflationary environment, traditional assets like stocks and bonds may underperform. Consider diversifying into commodities, gold, real estate, and inflation-protected securities (TIPS).
2) Reassess Your Budget: With prices rising and incomes potentially stagnant, it's crucial to track your spending and cut back on non-essential expenses. Focus on maintaining an emergency fund.
3) Reduce Variable Debt: Rising interest rates can make variable-rate debt more expensive. Consider refinancing to fixed rates or paying off high-interest debt as quickly as possible.
4) Invest in Skill Development: Job markets can be shaky during stagflation, so upgrading your skills can make you more competitive and resilient in a tough employment environment.
5) Stay Informed and Adaptive: Economic conditions can change rapidly. Monitor inflation reports, central bank statements, and employment trends to adjust your strategy as needed.
While stagflation presents challenges, a well-prepared investor and consumer can navigate it successfully with the right mindset and strategy.
Conclusion
While the signs of stagflation—high inflation, slowing growth, and rising unemployment—are concerning, it's not inevitable that the global economy will experience full-blown stagflation in 2025. Much depends on the direction of energy prices, central bank decisions, geopolitical developments, and consumer confidence.
However, vigilance is required. If inflation remains stubbornly high and economic growth continues to slow, the risk of stagflation will persist and may require painful adjustments in policy and behaviour.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.