This principle has long been seen as a cornerstone of trading education. A simple, structured formula that promises steady long-term success when applied with discipline.
However, real-world markets are rarely predictable. Prices move fast, volatility changes, and not every setup can deliver a perfect 1:3 outcome. So, does the rule still hold up in today’s dynamic environment?
And more importantly, how can traders apply it effectively to real trading situations?
What Is the Risk-Reward Ratio?
The risk-reward ratio is one of the most important concepts in trading. It measures how much potential profit (reward) you expect to earn for every unit of risk (loss) you take on a trade.
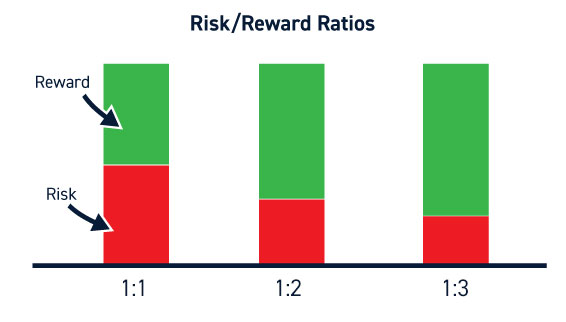
The formula is straightforward:
For example:
If you risk $100 to potentially make $300, your risk-reward ratio is 1:3.
If you risk $100 to gain $200, your ratio is 1:2.
In simple terms, a 1:3 risk-reward ratio means you stand to make three times what you risk.
This ratio helps traders plan trades rationally, instead of emotionally, and ensures that even a few winning trades can offset multiple losses.
Why the 1:3 Risk-Reward Ratio Is So Popular
The 3:1 rule gained traction because it theoretically allows traders to be profitable even if they win only 25 to 30 percent of the time. In this setup, one winning trade can cover three losses, reducing the pressure on having a high win rate.
Traders appreciated its simplicity, discipline, and psychological clarity. However, markets are rarely this clean-cut.
| Win Rate |
Risk-Reward Ratio |
Profitability |
| 30% |
1:3 |
Break Even |
| 40% |
1:3 |
Profitable |
| 50% |
1:3 |
Strongly Profitable |
Beyond math, the 1:3 ratio also builds discipline. It teaches traders to wait for high-quality setups rather than chasing every opportunity.
How to Use the 1:3 Risk-Reward Ratio in Forex Trading
The 1:3 risk-reward ratio is based on a simple principle: for every unit of risk, your potential reward should be three times greater.
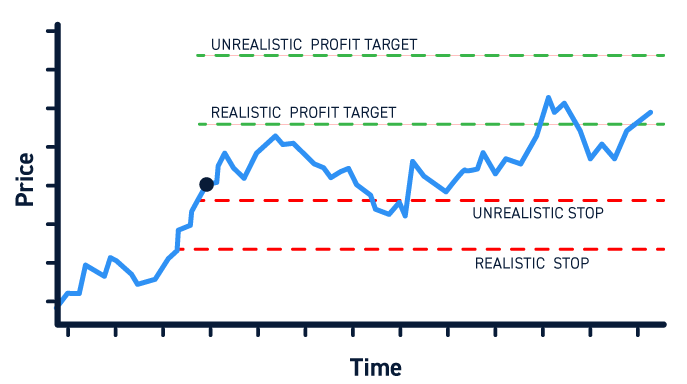
For example, if you risk 20 pips in a forex trade, your take-profit target should be 60 pips. This creates a profit potential large enough to offset multiple smaller losses over time.
Even with a win rate of only 30 to 40 percent, traders can still remain profitable if they maintain this ratio consistently. It focuses on risk management rather than prediction, which is the foundation of long-term success in trading.
When used correctly, the 1:3 risk-reward ratio allows traders to trade smarter, not harder, by keeping losses controlled and letting winners grow.
When the 1:3 Ratio Doesn’t Work Perfectly
The 1:3 risk-reward ratio is a useful guide, but it’s not a guaranteed formula. Real markets rarely move in straight lines, and rigid targets can backfire.
Here’s where traders often struggle:
High Volatility: Sudden price swings can trigger your stop-loss before the trade reaches its goal.
Sideways Markets: In tight ranges, aiming for 1:3 may be unrealistic or force poor entries.
Frequent Trading: For scalpers and short-term traders, smaller ratios like 1:1.5 or 1:2 are often more practical.
What truly matters is consistency, not just the ratio.
A 1:3 setup with a 25% win rate can underperform compared to a 1:2 setup with a 60% win rate. Balance both risk and probability to build steady, sustainable results.
Adjusting the Ratio to Match Market Conditions
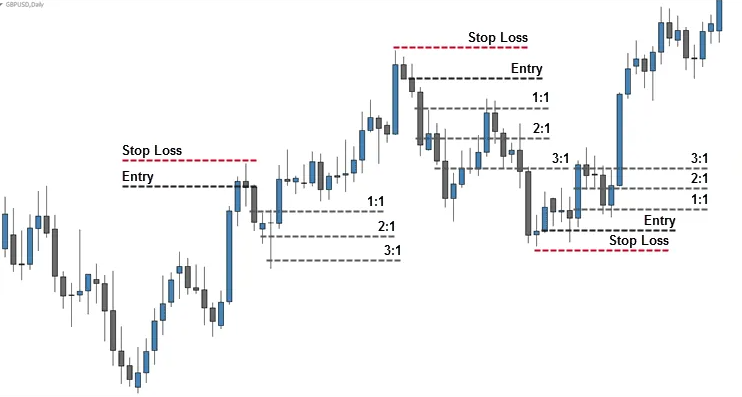
Expert traders don’t blindly stick to one ratio. They adapt based on context:
| Market Type |
Ideal Ratio |
Reason |
| Trending Market |
1:3 or higher |
Strong momentum supports bigger rewards |
| Range-Bound Market |
1:1.5 to 1:2 |
Price moves are smaller, need faster exits |
| Volatile Market |
Flexible |
Focus on risk control, not big targets |
The key is to understand your probability of success and market structure.
If your win rate is high, you can afford smaller ratios.
If your win rate is low, aim for higher rewards to offset losses.
Finding the Balance Between Risk and Probability
Your risk-reward ratio should always reflect market structure, volatility, and your personal trading style. If your trades have a high probability of success, slightly smaller ratios can still deliver solid profits.
If your setups are more selective but less frequent, aiming for larger rewards helps offset potential losses.
The Psychology Behind the Risk-Reward Ratio
The risk-reward ratio is not just about numbers; it strongly influences how traders think and behave in the market.

Aiming for higher rewards can develop patience and discipline, but it can also test your emotions when trades take longer to reach their targets.
You may feel frustrated if the market reverses before hitting your profit level, yet this approach encourages better trade selection because you will focus on setups with clear potential.
On the other hand, smaller ratios provide quicker results and more frequent wins. However, they can create complacency if the profits are too small to offset future losses.
The key is to understand your own psychological comfort zone and adjust your ratio to match it.
Practical Tools to Manage Your Risk-Reward Ratio
Modern trading platforms make ratio management easy:
Charting Tools: Draw your entry, stop, and target visually to see your ratio instantly.
Risk Calculators: Determine position size and risk exposure accurately.
Backtesting Software: Analyse historical results to find which ratio works best for your strategy.
Consistency in applying these tools is what turns a concept into a repeatable trading edge.
Pro Tips for Mastering the 1:3 Risk-Reward Ratio
Don’t force every trade to fit 1:3 and evaluate the market context first.
Use technical confluence (trendlines, support/resistance, moving averages) to justify targets.
Avoid moving your stop-loss impulsively, it ruins the ratio’s effectiveness.
Let winning trades run; don’t cut profits early out of fear.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
1.What does a 1:3 risk-reward ratio mean in trading?
It means for every $1 you risk, you aim to make $3 in profit, a powerful way to balance risk and reward.
2.Is the 1:3 risk-reward ratio always the best?
Not always. It works best in trending markets, but in range-bound conditions, smaller ratios like 1:2 may perform better.
3.How do I calculate the risk-reward ratio in forex?
Divide your potential reward (target distance in pips) by your risk (stop-loss distance). Example: 60 pips reward ÷ 20 pips risk = 1:3.
4.Can you make money with a 1:3 risk-reward ratio even with low accuracy?
Yes. You only need to win about 30–35% of trades to stay profitable with a 1:3 setup.
Final Thoughts
The 1:3 risk-reward ratio remains one of the most effective tools for traders seeking steady and disciplined growth.
Successful traders focus on precision and discipline rather than luck. They rely on calculated setups, consistent execution, and emotional control to achieve long-term results.
Use the 1:3 ratio as your compass. Let it guide your decisions, not restrict them. Profitability in trading does not come from chasing perfect numbers but from consistent performance, proper planning, and smart risk management.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.