The USD to SGD exchange rate is a key focus for travellers, investors, and businesses trading between the United States and Singapore. But what really drives the value of the US dollar against the Singapore dollar?
Understanding the main factors that affect this exchange rate can help you make smarter decisions, whether you're sending money, planning a trip, or managing international investments.
What Is the USD to SGD Exchange Rate?
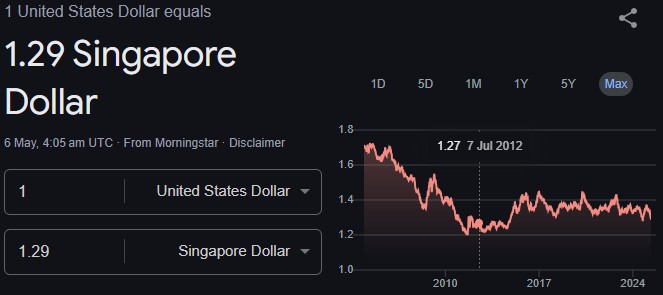
The USD to SGD exchange rate tells you how many Singapore dollars (SGD) are needed to buy one US dollar (USD). When the rate rises, the US dollar is stronger compared to the Singapore dollar; when it falls, the Singapore dollar is stronger.
This rate is constantly moving, reflecting a complex mix of economic, financial, and political factors.
Key Factors Affecting the USD to SGD Exchange Rate
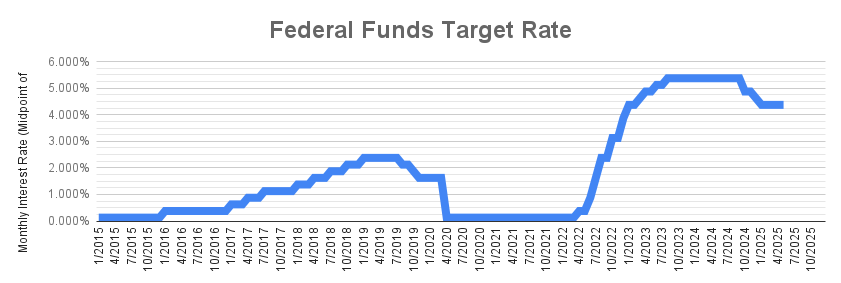
1. Monetary Policy
The decisions of central banks are among the most influential drivers of exchange rates. For USD/SGD, this means watching both the US Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS).
Federal Reserve: When the Fed raises US interest rates, the dollar typically strengthens as global investors seek higher returns, pushing the USD/SGD rate up.
Monetary Authority of Singapore: MAS manages the SGD using a unique exchange rate policy, rather than setting interest rates directly. If MAS allows the SGD to appreciate, the USD/SGD rate falls; if MAS lets the SGD weaken, the rate rises.
2. Interest Rates and Inflation
Interest rates and inflation are closely linked to currency values. Higher interest rates in the US or Singapore can attract foreign capital, boosting the respective currency. Conversely, higher inflation tends to weaken a currency over time.
If Singapore's inflation is lower than the US, the SGD may strengthen, lowering the USD/SGD rate.
If US interest rates rise faster than Singapore's, the USD may gain, raising the USD/SGD rate.
3. Trade Balance and Economic Growth
The balance of trade between the US and Singapore also plays a role. If Singapore exports more than it imports, demand for SGD increases, which can strengthen the currency and lower the USD/SGD rate. Strong economic growth in Singapore or the US can also move the exchange rate, as investors seek to invest in growing economies.
4. Capital Flows
Large movements of money in and out of Singapore or the US can impact the exchange rate. For example, if global investors buy Singaporean assets, demand for SGD rises, strengthening the currency. Conversely, if capital flows out of Singapore, the SGD may weaken.
5. Public Debt and Fiscal Health
Countries with high public debt may see their currencies weaken, as investors worry about inflation or default risk. If the US or Singapore increases its debt significantly, it could affect the USD to SGD rate.
6. Terms of Trade
This refers to the ratio of export prices to import prices. If Singapore's export prices rise faster than import prices, the SGD may strengthen, lowering the USD/SGD rate. The opposite is also true.
7. Market Sentiment and Political Stability
Market confidence and political events can cause rapid shifts in exchange rates. Singapore's reputation for political stability and sound financial management makes the SGD a “safe-haven” currency in Asia, often attracting investors during times of uncertainty.
How Do These Factors Interact?
Exchange rates are rarely driven by a single factor. For example, if the US raises interest rates but also faces high inflation or political uncertainty, the effect on the USD/SGD rate may be muted or even reversed. Similarly, Singapore's MAS may intervene to keep the SGD stable if global conditions become volatile.
Recent Trends in 2025
As of May 2025, the USD to SGD exchange rate has been influenced by steady US interest rates, Singapore's continued economic resilience, and global capital flows.
The SGD remains strong due to Singapore's robust trade surplus and safe-haven status, though any shift in US monetary policy or global economic sentiment could quickly change the outlook.
Final Thoughts
The USD to SGD exchange rate is shaped by a dynamic mix of monetary policy, interest rates, inflation, trade balances, capital flows, and market sentiment.
By understanding these factors, you can better anticipate currency movements and make more informed decisions, whether you're exchanging money, investing, or doing business internationally.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



























