Margin requirements play a pivotal role in the world of trading. For many traders, understanding margin requirements is the difference between sustainable success and facing an unexpected margin call. However, misconceptions around margin requirements continue to cause confusion and lead to costly mistakes.
This article will uncover the real truths about margin requirements, explain how they work, and show you how to manage them effectively in your trading journey.
What Are Margin Requirements?

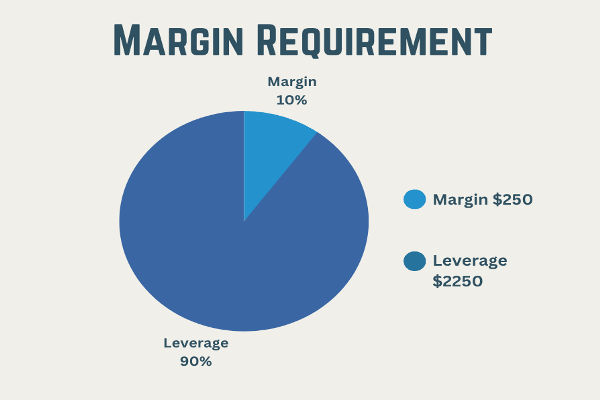
Margin requirements refer to the minimum amount of capital that a trader must deposit to open and maintain a leveraged position. In simple terms, margin acts as a security deposit. Brokers set margin requirements to ensure that traders have enough funds to cover potential losses in volatile markets.
For example, if a broker requires a 5% margin, a trader must put down £500 to control a £10,000 position. The concept allows traders to access larger market positions with relatively smaller amounts of their own money. However, while leverage can amplify profits, it can just as easily magnify losses.
Why Do Margin Requirements Matter?
Many new traders underestimate the importance of margin requirements. Meeting these obligations is not just a formality; it is a fundamental part of responsible trading. When you understand margin requirements properly, you can better manage your exposure, avoid forced liquidation of positions, and plan your trades with a clear view of risk.
Regulators like the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) enforce strict margin requirements to protect traders from excessive risk. Especially in markets such as forex, commodities, and indices, margin requirements are critical to maintaining financial stability both for the individual trader and the broader system.
How Margin Requirements Are Determined
Several factors influence margin requirements:
Firstly, asset class plays a major role. More volatile instruments often have higher margin requirements to account for the increased risk. Trading indices or cryptocurrencies usually requires higher margins than trading major currency pairs.
Secondly, the type of account affects margin requirements. Professional trading accounts may offer lower margin requirements but involve greater risk, while retail accounts are subject to stricter margin rules under FCA regulations.
Lastly, market conditions impact margin. During periods of heightened volatility, brokers often adjust margin requirements upward to shield both the broker and the trader from rapid, unpredictable price movements.
The Misconceptions About Margin Requirements
A major misconception is that low margin requirements automatically benefit the trader. Some believe that lower margins mean they can trade more aggressively with minimal risk. In reality, using too much leverage based on low margin requirements often leads to rapid losses. Margin is not free money; it is borrowed exposure that must be handled with care.
Another myth is that margin requirements never change. In truth, brokers frequently update margin policies in response to economic news, market volatility, or regulatory shifts. Staying informed about these updates is vital to avoiding unpleasant surprises.
Finally, some traders assume that margin requirements protect them entirely from losses. While they limit excessive trading, they do not eliminate risk. Traders are still responsible for monitoring positions and maintaining sufficient funds in their accounts.
Margin Calls: The Reality of Not Meeting Requirements
Failing to meet margin requirements can trigger a margin call. This occurs when the value of a trader's account falls below the required maintenance margin. When this happens, the broker demands additional funds to bring the account back into compliance. If the trader cannot deposit the necessary funds quickly, the broker may close positions automatically to limit further losses.
Margin calls are stressful and often result in forced closures at unfavourable prices. Understanding margin requirements and monitoring account equity closely helps traders avoid these situations.
Managing Margin Requirements Responsibly
Managing margin requirements starts with maintaining a comfortable buffer above the minimum levels. Relying on the bare minimum is risky. Traders who leave extra funds in their accounts create a cushion that allows positions to breathe, especially during periods of market volatility.
Using appropriate position sizing is another key strategy. Instead of taking the maximum size allowed by margin requirements, prudent traders risk only a small percentage of their account on each trade. This approach helps maintain financial stability even when the market moves against them.
Keeping informed about scheduled economic events, earnings announcements, and political developments can also help manage margin risks. These events can lead to sharp price movements that increase the likelihood of margin calls.
The Future of Margin Requirements
Margin requirements have evolved significantly over the years. In response to market crises and periods of high volatility, regulators worldwide, including the FCA, have introduced stricter rules to protect retail traders. It is likely that margin policies will continue adapting to market realities, technological changes, and shifts in trader behaviour.
For traders, this means staying adaptable. Building a habit of checking broker communications, reading regulatory updates, and reassessing margin practices regularly will be increasingly important.
Conclusion
The truth about margin requirements is simple but powerful: they are a tool designed to protect both traders and brokers from catastrophic losses, but only when used with understanding and discipline. Margin requirements are not a shortcut to larger profits. They are part of a comprehensive risk management framework that every trader must respect.
By understanding how margin requirements work, recognising common misconceptions, and managing trades responsibly, you can navigate the challenges of leveraged trading with greater confidence. Mastering margin is not just about meeting a number; it is about trading smarter and securing your long-term success.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.