In forex trading, most eyes chase the dollar and euro, and occasionally the yen. But when it comes to the pound, many people, consciously or unconsciously, ignore it. After all, its trading volume is much lower than that of several other forex trading currencies. But remember, before the dollar, it was actually the currency that the sun never set Empire used to dominate the world. So what is the status of the pound in the markets today? Let's delve deeper into this.
 What is the Currency of British?
What is the Currency of British?
Its full English name is Pound Sterling and the currency symbol is £. It is the official legal tender of the United Kingdom and is also used as official or unofficial currency in many other countries and territories. It is divided into coins and notes, including 1. 2. 5. 10. 20. 50. 1. 2. and 5. 10. 20. and 50 pound notes.
It is one of the major reserve currencies in the international financial market and one of the most active currencies in the global foreign exchange market. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) gives it the currency code GBP for ease of trading, and its exchange rate is affected by a variety of factors, including the state of the UK economy, monetary policy, international trade and fluctuations in global financial markets.
It has the longest history of any currency still in use. It officially became the standard monetary unit in the United Kingdom in 1821 and remained the most important international means of payment and reserve currency in the capitalist world until the early 20th century. By the end of World War I, the Empire's economy was in decline, and its position was slowly declining and gradually being replaced by the dollar.
With the emergence of the forex market, it is not only a currency, but also as an investment object. As the most valuable basic forex variety in history, although its value has been greatly reduced, it is still one of the five basic foreign exchange currencies. It ranks third in global foreign exchange reserves and is the fourth most traded currency after the dollar, euro and yen.
Britain's financial sector accounts for a large proportion of the overall economy, and London has the world's largest foreign exchange market. So when some economic or financial event happens, it is very vulnerable to its impact and fluctuate greatly. In 2008. due to the impact of the financial crisis, it saw a sharp decline in value far more than other currencies.
In the forex market, the currency is little more than a small cake, with trading volume alone lagging behind the euro by several streets. Just as small-cap stocks in the stock market are prone to ups and downs because of speculation, their volatility is relatively strong, especially short-term volatility. Therefore, if you have not practiced in the foreign exchange market for three or five years and summarized some of your own routines, you need to be more cautious about investing in the currency.
In general, the pound sterling is not only the former king of the currency world, but also the hottest in the foreign exchange market. But to make money on an investment, you need a deeper understanding and analysis of the species.
Base foreign exchange currencies
|
Forex Currency
|
Currency Code
|
Currency Unit
|
Country/Region
|
|
US Dollar
|
USD |
United States Dollar |
United States of America |
|
Euro
|
EUR |
Euro |
Eurozone |
|
Japanese Yen
|
JPY |
Japanese Yen |
Japan |
|
British Pound
|
GBP |
Pound Sterling |
United Kingdom |
|
Swiss Franc
|
CHF |
Swiss Franc |
Switzerland |
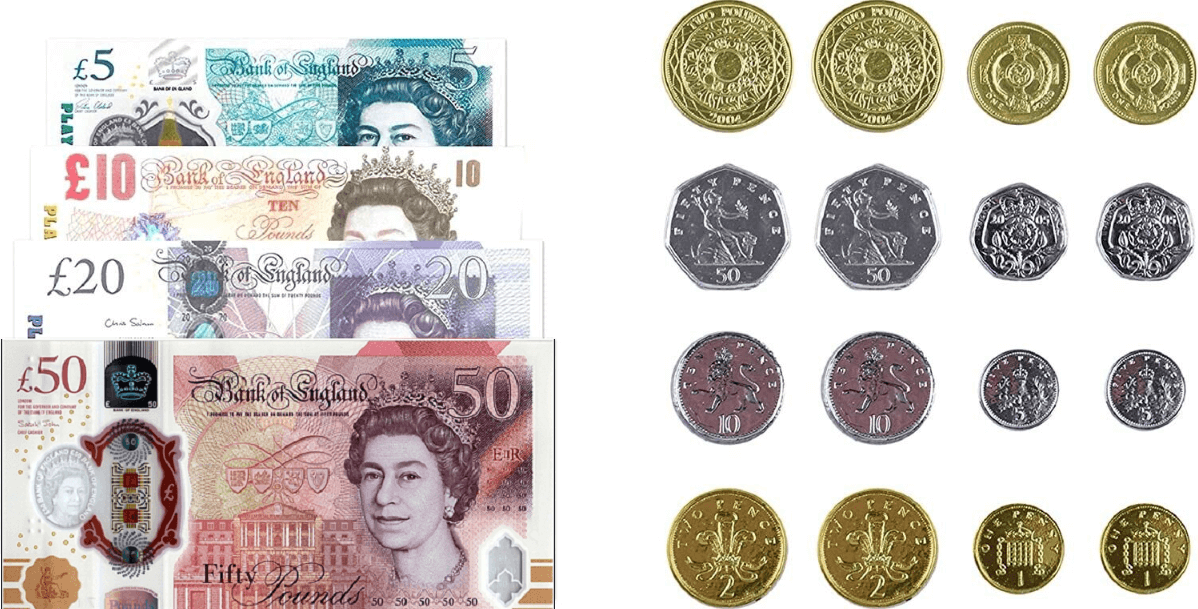
Sterling Notes and Coins
It is the native currency and official monetary unit of the United Kingdom, issued by the Bank of England, and is commonly referred to as Quid in British slang. It is the currency of the Bank of England and is issued and managed by the Bank of England. In addition, Scotland and Northern ireland also have their own bank-issued notes, and their legal tender is also the British pound sterling, but the design and some aspects may be slightly different.
British banknotes are printed by De La Rue, the world's largest banknote printing company, which has been printing money for the UK since 1860. In its development process, it has experienced a total of nine editions from the initial white currency similar to checks to the current circulation of the FG series of banknotes, as well as the king banknotes being issued.
There are 5. 10. 20 and 50 pound notes in circulation, 1. 2. 5. 10. 20 and 50 pence and 1 and 2 pound coins. One pound (Quid) is equal to 100 pence. Notes are mostly used for big purchases such as shopping or paying rent, while coins are mostly used for transportation, inserting coins or making change.
Although currency, especially paper money, is a sign of wealth, the patterns depicted on it are often unrelated to money and wealth, but to highlight the spiritual civilization of a country.
The same is true for British currency, which since 1960 has featured the late Queen Elizabeth II on the front of all UK banknotes, whether they are £5. £10. 20 or 50 notes. Born in 1926. she ascended the throne in 1952. was crowned in 1953. and died in 2022. having reigned for 69 years, making her the longest reigning monarch in British history.
In line with the Queen, a symbol of British history, culture and national spirit, the reverse character of the British banknote selects a variety of representative figures that make the British people proud. Unlike Queen Elizabeth II, who has occupied the front of the British banknotes for nearly 60 years because of her long standby, her small partner on the back has changed one batch after another.
On the front, it was King Charles III until the Queen's death. The latest King's note will not enter circulation until mid-2024. gradually replacing the Queen's head. The latest version of the king banknote in addition to changing the head, coupled with a transparent security window and a relief of the king's image. The rest of the design is the same as before, and the denominations are still £5. £10. £20 and £50.
Coins in the United Kingdom are minted and issued by the Royal Mint. The coins are divided into different denominations, each with a unique design and size. The pennies and twopence are made of copper, the fives, tenths, twenties, and fifties are made of nickel-cadmium alloy, and the pounds and twopence are made of magnesium-aluminum alloy.
Although there are different designs, the front usually shows the head of the British monarch. The two pound coins are usually used to commemorate special occasions, either the current monarch or other important historical figures. The head of the king is usually centered and may have text such as "ELIZABETH II" and the year of issue of the coin. In the past, the head of the Queen of England faced to the right, but now the head of the king faces to the left.
The image on the back of the coin varies according to the year of issue and the specific event. A penny coin may have an oak branch on the reverse, a two penny coin may have a shield on the reverse, a five penny coin may have a small fishing boat on the reverse, a ten penny coin may have an oak branch on the reverse, a twenty penny coin may have a crown on the reverse, and a fifty penny coin may have an eagle on the reverse.

Factors Influencing the Value of the British Pound Sterling
The Sterling exchange rate is the exchange rate of the British currency against the currencies of other countries, which is determined by the supply and demand in the forex market and reflects the market's overall assessment of the British economy and currency. Its formation is determined by buyers and sellers in the market based on expectations for the UK economy and currency, as well as a range of other factors. In other words, changes in supply and demand directly affect the value of the currency.
Macroeconomic indicators and UK economic data, such as GDP growth rate, employment rate, inflation rate, etc., have a direct impact on the market's view of the health of the UK economy. Good economic performance usually increases investor confidence in the UK currency, which affects the exchange rate.
The level of interest rates is a very key factor in the forex market, which affects the attractiveness of investment. If interest rates are relatively high in the UK, it could attract more money into the country, raising demand for the UK currency and thus pushing up the conversion ratio.
Politics also plays a big role in exchange rates, as it relates to the level of investor confidence. Political stability usually increases investor confidence in a country's economy and helps the local currency appreciate. Conversely, political instability could trigger investor concerns about the currency, leading to a devaluation.
Trade surplus or deficit, import and export data, etc., will also have an impact on the British currency, resulting in exchange rate fluctuations. If the UK economy runs a trade surplus, when it exports more than it imports, the value of its currency will rise. Because foreign countries need to use their own currency to buy their own goods and services, this increases the demand for their own currency. Conversely, if the UK economy runs a trade deficit, in which it imports more than it exports, it can cause the national currency to depreciate as foreign investors may reduce their holdings of the local currency due to reduced demand.
Monetary policy initiatives by central banks, such as quantitative easing or tightening, affect the money supply and market confidence, which in turn affects the value of that currency. As a major reserve currency, its value is also affected by the state of the global economy. Global economic uncertainty could cause investors to seek safety, raising demand for more stable currencies such as theirs.
Historical and Recent Trends Affecting the Pound Sterling's Exchange Rate
The combination of these factors leads to the formation of the pound exchange rate. In today's foreign exchange market, its exchange rate trend has been in a state of depreciation, especially in its exchange against the US dollar. Because there are many factors affecting the exchange rate in the foreign exchange market, according to the comparison between historical events and the current situation, it can be seen that the overall economic situation, inflation and the benchmark interest rate are three key factors.
In 1990 Britain was in recession, house prices were falling and the Bank of England's base rate was high. This then led to higher inflation and a booming German economy, so the Deutschmark gradually strengthened against the pound. In order to maintain the currency's international status, the British government has little choice but to raise interest rates further to entice investors to buy it. But interest rates were already over 10% and British households were struggling to pay their home mortgages.
British businesses are not performing well, and high unemployment is adding fuel to the fire. Soros saw the difference between the United Kingdom and Germany, so he concluded that it would depreciate against the mark, and began the preparatory work of shorting Quid. This was followed by Black Wednesday in 1992. when the British government was forced to withdraw from the ERM(Exchange rate Mechanism) system after George Soros' massive short selling of the British currency led to its devaluation.
Then came Brexit, which cost the British economy £100 billion a year. Also after Brexit, the United Kingdom experienced a certain shortage of labor. This is mainly due to the end of the free movement of Labour between the UK and Europe after Brexit, which has caused some industries, especially services and agriculture, to face the challenge of insufficient personnel supply. Many businesses reported difficulty recruiting enough workers, which affected the normal functioning of production and services.
There is also the issue of interest rates, which are currently 5.25% in the UK, compared with 4.5% in the EU. At the same time, the global economy has slowed down, with both the UK and EU economies stagnating. But eurozone inflation has fallen to 2.9% in October 2023. while UK inflation has only fallen back to 4.9%. In other words, its depreciation rate is 1.6 times that of the euro.
For example, because of inflation, £100 today will have only £95 of purchasing power a year from now, and €100 today will be equivalent to €97 a year from now. With £100 earning £5.25 a year and €100 earning €4.50 a year, you can see that the euro is still a better deal.
After Russia's invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. there was a flood of money flowing into the dollar because it was seen as a safe haven for global investors. From March 2022. the United States took the lead in raising interest rates, and other Western countries followed suit. The currencies of other Western countries fell by an average of 20% against the dollar over the course of the rate rise, with the British currency particularly vulnerable.
Because the British Prime Minister Truss introduced a tax reduction policy in September 2022. the tax cut increased the financial burden of the government. As a result, financial markets began to sell British currency and gilts, causing British pension funds to nearly collapse. Only then did the Bank of Britain come out and buy gilts, sending them to their lowest level against the dollar since 1985. It took two months to recover, with gains of 20 percent against the dollar.
Similarly, in recent years, the UK's inflation rate has been higher than that of the EU, resulting in a faster depreciation of its currency against the euro. As a result, international investors prefer the euro, and as a result the currency has recovered less than the euro.
Based on these circumstances, the direction of the pound sterling in the coming years will also be influenced by a number of factors, including the government's efforts to curb inflation, interest rate policy and the economic recovery. Therefore, when investors want to invest in the currency, they must be considered in many ways.
GBPUSD exchange rate December 2023
|
Dates
|
Market Close
|
Opening Bell
|
Supreme
|
Lowest
|
Rise Or Fall In Price
|
| 2023/12/29 |
1.2694 |
1.2698 |
1.2735 |
1.2664 |
0.01% |
| 2023/12/28 |
1.273 |
1.2797 |
1.2829 |
1.2711 |
-0.50% |
| 2023/12/27 |
1.2794 |
1.2719 |
1.2804 |
1.2697 |
0.53% |
| 2023/12/26 |
1.2726 |
1.2693 |
1.2732 |
1.2683 |
0.29% |
| 2023/12/25 |
1.2689 |
1.2709 |
1.2728 |
1.2682 |
-0.09% |
| 2023/12/22 |
1.27 |
1.2687 |
1.2746 |
1.2672 |
0.09% |
| 2023/12/21 |
1.2688 |
1.2639 |
1.2697 |
1.2611 |
0.40% |
| 2023/12/20 |
1.2637 |
1.2731 |
1.2737 |
1.2624 |
-0.73% |
| 2023/12/19 |
1.273 |
1.2645 |
1.2763 |
1.2639 |
0.70% |
| 2023/12/18 |
1.2642 |
1.2679 |
1.2706 |
1.2628 |
-0.26% |
| 2023/12/15 |
1.2675 |
1.2765 |
1.2792 |
1.2667 |
-0.71% |
| 2023/12/14 |
1.2766 |
1.2617 |
1.2796 |
1.2611 |
1.17% |
| 2023/12/13 |
1.2618 |
1.2563 |
1.2636 |
1.2499 |
0.45% |
| 2023/12/12 |
1.2561 |
1.2556 |
1.2616 |
1.2513 |
0.06% |
| 2023/12/11 |
1.2553 |
1.2543 |
1.2592 |
1.2531 |
0.06% |
| 2023/12/8 |
1.2546 |
1.2594 |
1.2603 |
1.2501 |
-0.35% |
| 2023/12/7 |
1.259 |
1.256 |
1.2614 |
1.2543 |
0.25% |
| 2023/12/6 |
1.2559 |
1.2601 |
1.2615 |
1.255 |
-0.27% |
| 2023/12/5 |
1.2593 |
1.2629 |
1.2653 |
1.2576 |
-0.31% |
| 2023/12/4 |
1.2632 |
1.2714 |
1.2727 |
1.2603 |
-0.54% |
| 2023/12/1 |
1.27 |
1.2623 |
1.2718 |
1.2613 |
0.62% |
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.



 What is the Currency of British?
What is the Currency of British?