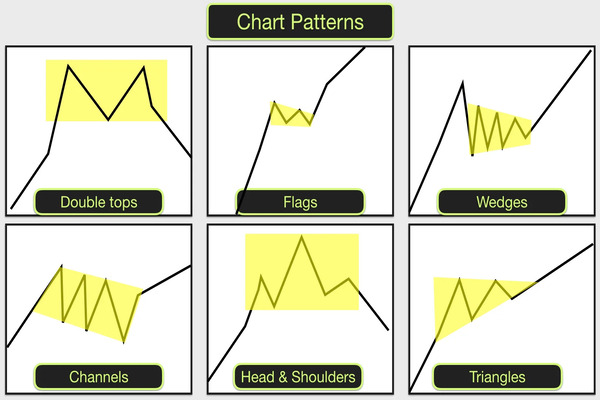
In technical analysis, patterns speak louder than predictions. Among the many formations traders look for, the triangle chart pattern stands out for its clarity and potential. Just as a triangle is one of the most stable shapes in geometry, the triangle chart pattern offers structure in an often chaotic market. It represents consolidation before a breakout and provides insight into whether a trend is likely to continue or reverse.
Understanding this pattern is key for those aiming to make more informed trading decisions. Let's explore five essential types of triangle chart pattern every trader should know and how each can help guide entry and exit strategies.
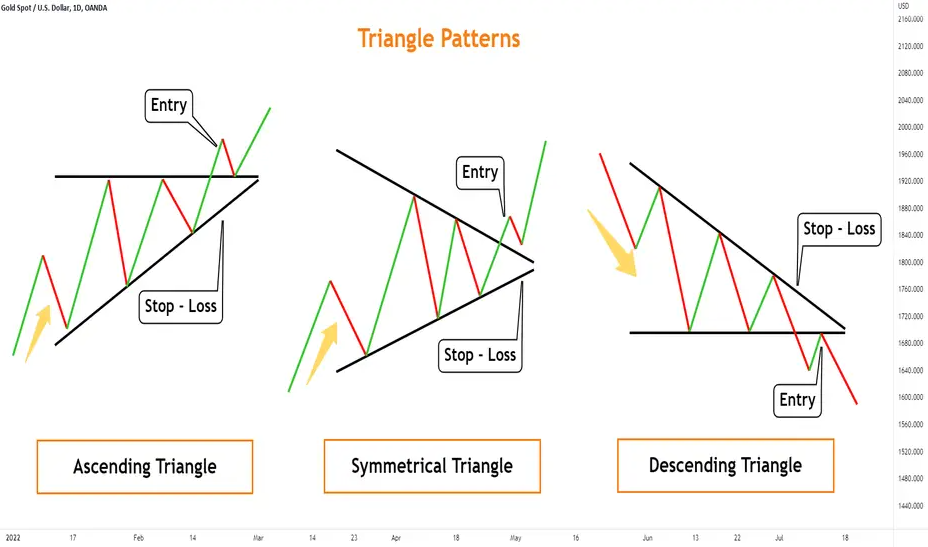
1. Symmetrical Triangle
The symmetrical triangle is one of the most commonly observed triangle chart patterns. It occurs when the price forms lower highs and higher lows, with both trendlines sloping toward a point. This pattern signals market indecision and typically appears during periods of consolidation.
Although it doesn't inherently suggest a direction, the symmetrical triangle often leads to a continuation of the existing trend. Traders usually wait for a breakout above or below the converging lines, using volume as confirmation.
How to Trade It:
Enter a trade once the price breaks out and closes beyond either trendline. Set your stop-loss just outside the opposite side of the triangle and target a profit based on the widest part of the pattern.
2. Ascending Triangle
The ascending triangle chart pattern is characterised by a flat upper trendline and a rising lower trendline. This structure suggests that buyers are becoming more aggressive, repeatedly pushing the price higher and putting pressure on a resistance level.
This bullish pattern generally leads to an upward breakout, especially when accompanied by rising volume. It is often found in uptrends and is considered a continuation pattern.
How to Trade It:
Look for a clean breakout above the flat upper resistance line. Enter on a close above this level, and place a stop-loss just below the rising trendline.
3. Descending Triangle
The descending triangle chart pattern is the opposite of the ascending triangle. It features a flat support line and a descending upper trendline. This pattern reflects a weakening of buying interest, with sellers gradually driving prices lower.
It's commonly viewed as a bearish continuation pattern and is most reliable in downtrending markets. The breakout usually happens below the support level, with increasing volume supporting the move.
How to Trade It:
Once the price breaks below the flat support line, consider entering a short position. Use the height of the triangle to estimate your profit target and set a stop-loss just above the descending trendline.
4. Expanding Triangle
Also known as a broadening formation, the expanding triangle is identified by diverging trendlines, where the highs get higher and the lows get lower. This triangle chart pattern reflects heightened volatility and market indecision.
Unlike symmetrical, ascending, or descending triangles, the expanding triangle doesn't favour a particular breakout direction. It shows uncertainty, often followed by sharp movements once a breakout occurs.
How to Trade It:
Trading this pattern requires patience. Watch for a confirmed breakout with strong volume. Depending on the direction, enter long or short and be cautious with wider stop-losses due to the increased volatility.
5. Right-Angled Triangle
The right-angled triangle chart pattern resembles either an ascending or descending triangle but forms a 90-degree angle between one flat line and one sloped line. The pattern highlights a standoff between buyers and sellers, with one side gradually overpowering the other.
Its breakout direction depends on the prevailing trend and momentum. As with other triangle types, volume plays a key role in confirming the move.
How to Trade It:
Wait for a clear breakout. Enter on confirmation, placing a stop just beyond the opposite boundary. Project a price target using the pattern's height.
Why Triangle Chart Patterns Matter
Triangle chart patterns are essential tools in technical trading because they capture the psychological battle between bulls and bears. Whether symmetrical, ascending, descending, expanding or right-angled, each variation of the triangle chart pattern offers insights into price action and potential breakouts.
The simplicity of these patterns belies their power. They can provide not only entry and exit signals but also clarity in periods of consolidation. However, like any technical indicator, they work best when used in conjunction with other tools such as volume, support and resistance levels, and moving averages.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While triangle chart patterns can be highly effective, there are some pitfalls traders should be wary of:
Acting Before Confirmation: Many traders enter positions before the breakout occurs. Always wait for confirmation to reduce the risk of false signals.
Ignoring Volume: Breakouts accompanied by low volume are often unreliable. Volume helps validate the strength of a move.
Setting Stops Too Tight: Triangles can produce fakeouts. Giving your trades breathing room can help avoid premature exits.
Final Thoughts
The triangle chart pattern is not a magic solution, but it remains a staple in the toolbox of savvy traders. Understanding the nuances of each triangle variation can provide a significant edge in technical analysis.
By learning to recognise these patterns and apply them within broader strategies, traders can improve their ability to anticipate market moves and act with greater confidence.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.