Changes in the federal funds rate may affect the US dollar. When the Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate, it usually raises the overall economic interest rate. The higher yield has attracted capital from overseas investors, who are seeking higher returns on bonds and interest rate products. Investors sell investments denominated in local currency in exchange for investments denominated in US dollars.

Key points
1. When the Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate, it usually raises interest rates for the entire economy, which often leads to a stronger US dollar.
2. The higher yield has attracted investment capital from overseas investors, who are seeking higher returns on bonds and interest rate products.
3. The rise or fall of the federal funds rate is closely related to changes in the exchange rate of the US dollar against other currencies.
Understanding the Federal Funds Rate
Federal Funds Rate refers to the interest rate in the US interbank lending market, primarily the overnight lending rate. This change in interest rates can sensitively reflect the surplus or shortage of funds between banks, with some banks having excess cash while others may have short-term liquidity needs.
The Federal Funds Rate is a target interest rate set by the Federal Reserve Bank, usually the basis for commercial banks to borrow from each other. The Federal Reserve's targeting and adjustment of interbank lending rates can directly affect the cost of funds for commercial banks, and transmit the surplus and shortage of funds in the interbank lending market to industrial and commercial enterprises, thereby affecting consumption, investment, and the national economy.
The federal funds rate has a significant impact on the entire economy, and it is a key foundation of the interest rate market. It is closely related to setting the minimum loan rate that banks charge customers, as well as mortgage and savings rates.
The Federal Reserve adjusts interest rates based on economic demand through the FOMC or the Federal Open Market Committee. If the FOMC believes that the economy is growing too fast and there is a possibility of inflation or price increases, the FOMC will raise the federal funds rate.
On the contrary, if the FOMC believes that the economy is struggling or may fall into recession, the FOMC will lower the federal funds rate. Higher interest rates often slow down loans and the economy, while lower interest rates often stimulate loans and economic growth.
The task of the Federal Reserve is to use monetary policy to help achieve good employment rates and stable prices. During the 2008 financial crisis and Great Depression, the Federal Reserve maintained the federal funds rate around 0% -0.25%. In the following years, as the economy improves, the Federal Reserve will gradually increase interest rates further.
Inflation, Federal Funds, and USD
One way for the Federal Reserve to achieve full employment and stable prices is to set its inflation target at 2%. Since 2011, the Federal Reserve has officially set a target of raising the personal consumption expenditure price index by 2% annually.
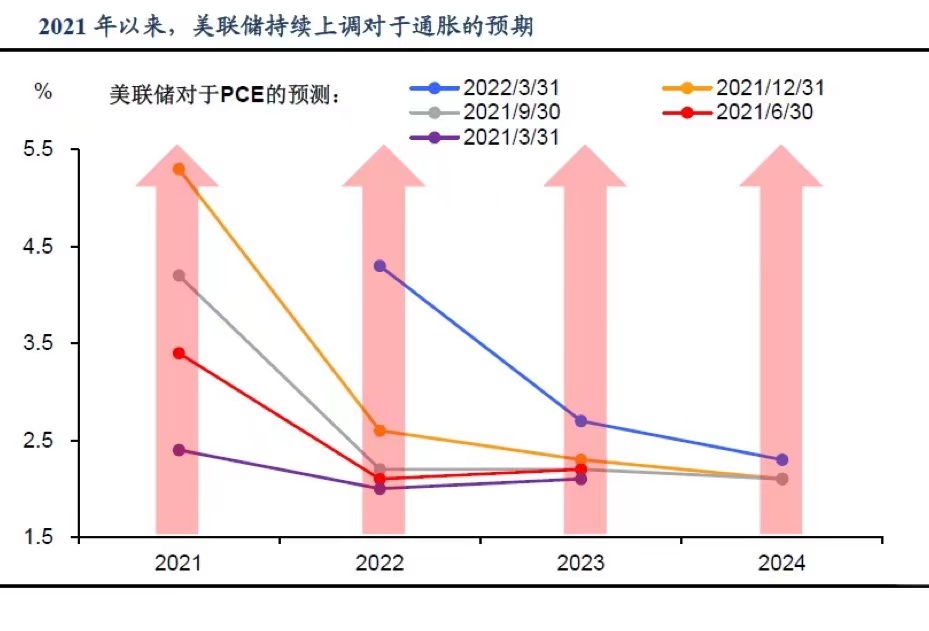
In other words, as the inflation index rises, commodity prices are also rising. If prices rise but wages do not increase, people's purchasing power will decrease. Inflation can also affect investors, for example, if investors hold fixed rate bonds that pay 3%, and the Inflation rate rises to 2%, the actual return for investors is only 1%.
When the economy is weak, the inflation rate decreases as the demand for goods decreases, driving down prices. On the contrary, when the economy is strong, wage increases will increase expenses, which may stimulate price increases. Maintaining an inflation rate of 2% helps the economy grow at a stable rate and allows for a natural increase in wages.
The adjustment of the federal funds rate will also affect inflation in the United States. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it encourages people to increase savings and reduce spending, thereby reducing inflationary pressure. On the contrary, when the economy enters a recession or grows too slowly and the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, it will stimulate spending and increase inflation.
How the US Dollar Helps the Federal Reserve Cope with Inflation
Of course, besides the Federal Reserve, there are many other factors that can affect inflation, and the US dollar exchange rate plays an important role in inflation. For example, due to the export of products from the United States to Europe, buyers need to convert euros into US dollars in order to make a purchase. If the US dollar strengthens, a higher exchange rate will cause Europeans to pay more for American goods based solely on the exchange rate. Therefore, if the US dollar is too strong, US export sales may decrease.
In addition, a strong US dollar makes foreign imports cheaper. If American companies purchase goods from Europe in euros and the euro weakens or the US dollar strengthens, then these imports will be cheaper. This leads to cheaper prices being sold in American stores, and these lower prices translate into low inflation.
Cheap imported products help maintain low inflation, as American companies producing goods domestically must maintain low prices in order to compete with cheap foreign imports. The strengthening of the US dollar helps make foreign imports cheaper and serves as a natural hedge against economic inflation risks.
It can be imagined that the Federal Reserve will closely monitor inflation and the strong level of the US dollar before making any decisions about the federal funds rate.
The Trend of the Federal Funds Rate and the US Dollar in Past History
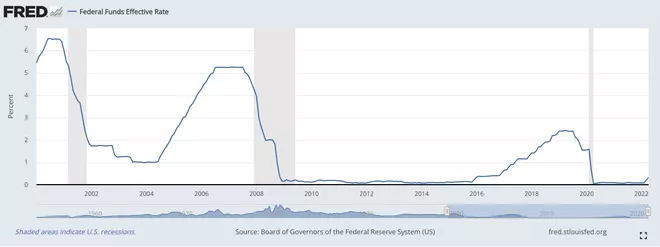
Below we can see the federal funds rate since the mid-1990s, with gray areas indicating economic recession:
In the mid-1990s, the federal funds rate rose from 3% to eventually exceed 6%;
In 2001, the federal funds rate dropped from over 6% a year ago to 1%;
In the mid-1900s, with the improvement of the economy, the federal funds rate increased;
In 2008, the federal funds rate once again dropped from over 5% to near zero and remained at zero levels for several years;
As the economy recovers from the Great Recession, the Federal Reserve gradually raises interest rates until 2018;
With the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve has taken emergency measures to lower interest rates to maintain economic operations;
Widely vaccinated with COIn the case of the VID-19 vaccine, the economy gradually recovered. However, the inflation rate has risen sharply. As of March 2022, the inflation rate measured by the consumer price index Index (CPI) is 8.5%, based on 12 months. In response, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates for the first time since 2018.
As the federal funds rate rises, the overall interest rate in the economy rises. If global capital flows are shifting towards assets denominated in US dollars in pursuit of higher returns, then the US dollar will strengthen.
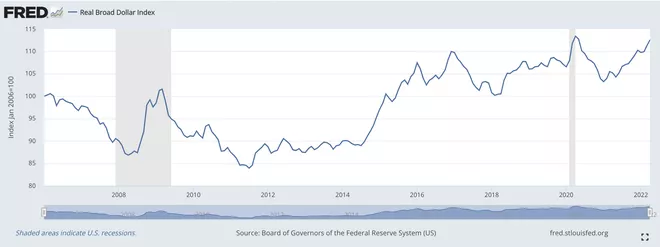
In the chart below, we can see the trend of the US dollar corresponding to different periods of interest rate hikes in the chart.
In the mid-1990s, when the Federal Reserve raised interest rates, the US dollar rose, measured by the us dollar index, which measures the exchange rate of a basket of currencies;
In 2002, when the Federal Reserve cut interest rates, the US dollar depreciated significantly;
The correlation between the US dollar and federal funds deviated in the mid-1900s. With economic growth and rising interest rates, the US dollar has not followed suit;
The US dollar began to rebound, only falling again in 2008 and 2009;
As the economy emerged from the Great Recession, the US dollar fluctuated for many years;
Against the backdrop of economic strength and the Federal Reserve's final interest rate hike, the US dollar began to rise again from 2014 to 2017 and stabilized in the spring of 2020;
During the global COVID-19 pandemic, the US dollar surged in 2020 as investors sought stability; As the world economy emerges from the pandemic, the US dollar gradually weakens from record highs;
In 2021 and 2022, with the Federal Reserve raising interest rates, the US dollar once again began to approach record highs.
Conclusion
Generally speaking, under normal economic conditions, an increase in the federal funds rate leads to an increase in interest rates for the entire US interest rate product. The result is usually an appreciation of the US dollar.
Of course, there is also a possibility of deviation in the correlation between the federal funds rate and the US dollar. The US dollar is also subject to other factors strengthening or weakening. For example, in turbulent times, the demand for US bonds as a safe haven investment can also strengthen the US dollar.