Closing position refers to the act of futures investors buying or selling stock index futures contracts with the same variety, quantity, and delivery month as their stock index futures contracts, but with opposite trading directions, in order to settle stock index futures trading. It can also be understood as: closing a position refers to the trading behavior of a trader to close their position, and the method of closing is to make opposite hedging transaction in the opposite direction of the position.
In futures trading, closing positions mirror selling in stock trading. This process involves two types: buying to close (matching selling to open) and selling to close (matching buying to open). The bidirectional nature of futures trading dictates these actions, crucial for managing positions effectively.

1、 Classification of Closing Positions
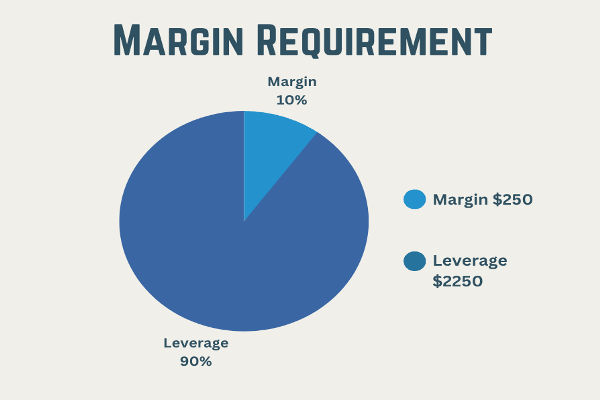
Closing positions in futures trading can be categorized into hedging and mandatory closing positions. Hedging involves futures investment firms buying and selling contracts of the same delivery month within the same exchange to settle previously held contracts. Mandatory closing, on the other hand, occurs when a third party, such as a futures exchange or brokerage, forcibly closes a position due to reasons like insufficient margins or policy violations.
Forced position closures in futures trading are common due to factors like delayed margin payments, breaches of position limits, or sudden regulatory changes. In regulated futures markets, forced liquidation occurs when a brokerage closes a client's positions to cover margin shortfalls, mitigating further losses amid unfavorable market conditions.
2、 The Difference Between Hedging and Compulsory Liquidation
During trading, futures exchanges enforce mandatory closing measures in compliance with regulations, with any resulting losses borne by members or customers. If forced closure of positions occurs due to member or customer violations, resulting profits are categorized as non-operating income for the exchange and not returned to the violators. Conversely, positions closed due to national policy changes or limit fluctuations are transferred back to the members or customers.
【 EBC Platform Risk Reminder and Disclaimer 】: There are risks in the market, and investment needs to be cautious. This article does not constitute investment advice.