The Nigerian Naira (NGN) has experienced significant volatility over the past decade, influenced by various economic factors, including oil price fluctuations, inflation, and monetary policies. As of May 2025, the exchange rate is approximately ₦1,498.71 per US dollar.
As we look toward 2030, understanding the factors influencing the Naira's performance is crucial for investors. This comprehensive guide explores the current Dollar to Naira exchange rate, projections for its future, and the potential for a rebound by 2030.
Dollar to Naira Exchange Rate 2025
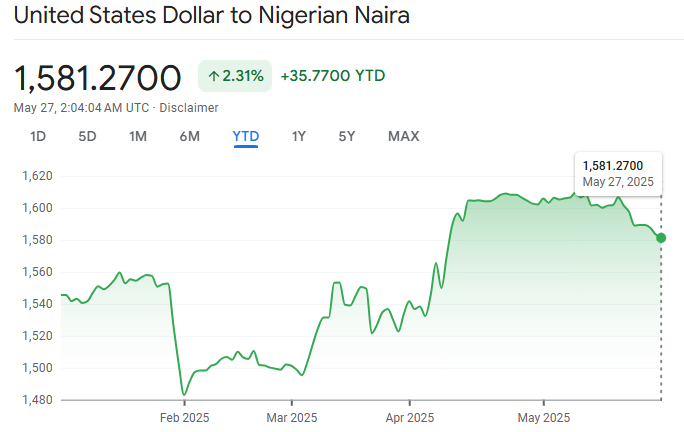
As of 27 May 2025, the Naira trades at approximately ₦1,581.27 per US dollar. It represents a substantial depreciation from previous years, attributed to declining oil revenues, inflationary pressures, and foreign exchange (FX) shortages.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has implemented various measures to stabilise the currency, including unifying exchange rates and removing fuel subsidies.
7 Factors Influencing the USD to NGN Exchange Rate in 2025
1. Oil Prices and Export Revenues
Over 90% of Nigeria's foreign exchange earnings come from oil.
When oil prices fall or production drops, Nigeria earns fewer dollars, reducing forex supply and weakening the Naira.
2. Inflation and Interest Rates
Nigeria's inflation has remained persistently high. When inflation rises, the Naira loses purchasing power, and demand for stable currencies like the dollar increases.
Higher inflation with relatively low interest rates disincentivises foreign capital inflow, reducing dollar availability.
3. Central Bank Policies and FX Management
The CBN has tightly controlled the exchange rate, creating disparities between official and black market rates.
Recent moves to liberalise the FX regime have increased volatility but may lead to long-term stability if consistently applied.
4. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Capital Flows
Investor confidence affects the demand and supply of forex. Policy uncertainty, security issues, and infrastructure deficits have reduced FDI in recent years.
A lack of investor inflow weakens the Naira, while inflow boosts it.
5. Political Stability and Governance
Political uncertainty and government spending policies (e.g., subsidy removals or public debt increases) impact investor confidence and currency strength.
Reforms, anti-corruption measures, and policy consistency help attract investment and support the Naira.
6. External Debt and Reserves
7. Government Fiscal Policies
Effective fiscal management by reducing budget deficits and controlling public debt can boost investor confidence and stabilise the Naira.
The Nigerian government's 2025 budget projects a deficit of 13.8 trillion Naira, equivalent to 3.87% of the estimated GDP, with an assumed exchange rate of 1,400 naira to the US dollar.
Dollar to Naira Historical Performance and Factors
| Year |
Official Rate (Approx.) |
Notes |
| 1980 |
₦0.60 – ₦1.00 |
Fixed exchange rate regime |
| 1993 |
₦22 |
After SAP reforms and devaluation |
| 2004 |
₦132 |
Managed float, oil prices improving |
| 2015 |
₦199 |
Oil crash, start of major depreciation |
| 2020 |
₦360 |
CBN interventions, wide black market gap |
| 2022 |
₦450 (official) / ₦700+ (parallel) |
Forex shortages widen disparity |
| 2023 |
₦700 – ₦1,000 |
Move toward unification of exchange rates |
| 2024 |
₦1,200+ |
Inflation, forex scarcity, market float |
| 2025 |
₦1,498.71 (official) |
Latest rate as of May 2025 |
1980s – Early 1990s: Fixed Regime and Early Devaluation
In the early 1980s, Nigeria maintained a fixed exchange rate system, where 1 USD was equivalent to about ₦0.60 – ₦1.00.
As oil prices fell and the Nigerian economy weakened, the government implemented the Structural Adjustment Program (SAP) in 1986, which led to the liberalisation of the exchange rate and a sharp devaluation.
By 1993, the rate had weakened to ₦22 per USD.
1994–2004: Multiple Exchange Rates and Managed Float
During this period, Nigeria adopted various systems, including dual and multiple exchange rates, resulting in wide disparities between official and parallel market rates.
By 2004, the exchange rate had depreciated to ₦132 per USD.
2005–2014: Oil Boom and Relative Stability
Thanks to high oil prices and strong foreign reserves, the Naira experienced relative stability.
The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) adopted a managed float regime and supported the Naira through interventions.
By 2014, the official exchange rate hovered around ₦165–₦170 per USD.
2015–2020: oil price crash and Policy Challenges
The collapse in oil prices in 2015 severely impacted Nigeria's foreign exchange earnings.
The Naira was devalued several times, with official rates moving from ₦199/USD in 2015 to ₦360/USD in 2020.
The parallel market (black market) often trades at a much higher rate than the official one.
2021–2023: Dual Rates, Inflation, and Reforms
Amid rising inflation and foreign exchange shortages, the Central Bank maintained multiple windows, but pressure mounted to unify the rate.
The official rate crossed ₦400/USD in 2021, while black market rates exceeded ₦700/USD by 2022.
In mid-2023, the Nigerian government and the Central Bank floated the Naira to unify the multiple exchange rates.
2024 and 2025: Volatility and Reforms
2024 Developments:
In 2024, inflation remained high (over 20%), while oil production was below quota due to theft and underinvestment.
Following exchange rate liberalisation, the official and parallel rates began to converge.
The Naira depreciated sharply after the float, reaching ₦1,000–₦1,200 per USD by the end of 2024.
2025 So Far:
As of May 2025, the official exchange rate is approximately ₦1,498.71 per USD, while parallel market rates may exceed ₦1,550–₦1,600/USD.
The depreciation reflects continued inflationary pressures, foreign investor concerns, and a shortage of forex supply.
Dollar to Naira Projection 2030: Will the Naira Rebound?

2025 Projections
Forecasts indicate that the USD/NGN exchange rate could reach ₦1,672.65 by May 2025, with fluctuations ranging between ₦1,268.16 and ₦1,672.65. By June 2025, the rate is estimated to average around ₦1,575, with potential highs of ₦1,604 and lows of ₦1,543.
Projections for May 2026 suggest the rate may climb to approximately ₦1,579.35, reflecting a continued upward trend in the USD/NGN exchange rate.
2026–2027 Outlook
The USD/NGN exchange rate is projected to follow a steady upward trend, indicating a gradual depreciation of the Naira. Forecasts suggest the rate will reach ₦1,867.80 by the end of 2025 and climb further to ₦1,583.23 by May 2026.
The rate is expected to hit ₦2,177.37 by the end of 2029, highlighting a consistent weakening trajectory over the coming years.
2028–2030 Long-Term Projections
Projections for the USD/NGN exchange rate by 2030 vary widely, reflecting the uncertainty surrounding Nigeria's economic outlook. One forecast predicts a significant depreciation of the Naira, with the exchange rate reaching ₦2,287.65 by May 2030.
In contrast, some long-term forecasts anticipate Naira's strengthening, with the USD/NGN rate potentially falling to ₦722.71 by 2030, indicating substantial appreciation.
Meanwhile, more conservative models place the rate at ₦2,297.67. These divergent estimates highlight the complexity of forecasting currency movements, which depend on economic, political, and fiscal factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Naira has undergone dramatic changes against the US dollar over the past 40 years, and the trend in 2025 continues to reflect the effects of inflation, forex policy shifts, and global economic pressures.
Regardless, the Naira could rebound by 2030, depending on the successful implementation of economic reforms, diversification of revenue sources, foreign investment, and inflation control.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.