
How to Trade in Stocks by Jesse Livermore is more than a trading manual — it is a direct window into the mind of one of Wall Street's most legendary and enigmatic figures. First published in 1940. just a year before Livermore's death, the book distils decades of his hard-won experience, successes, and painful mistakes into a concise guide that still resonates in today's fast-paced financial markets.
Livermore's career was marked by spectacular wins, devastating losses, and a psychological resilience that allowed him to rise from a small-town boy trading bucket shops to a market operator whose moves could shift prices. In How to Trade in Stocks, he lays bare the methods, principles, and mindset that shaped his trading life — insights that remain astonishingly relevant for anyone navigating stocks, commodities, or currencies today.
The Making of a Market Legend

Before delving into the strategies outlined in How to Trade in Stocks, it is essential to understand Livermore's background. Born in 1877 in Shrewsbury, Massachusetts, he began trading at the age of fourteen in local bucket shops — speculative venues that mimicked stock market price movements without actual asset exchange.
These early years honed his skills in "tape reading," the meticulous observation of price and volume patterns via the ticker tape. Livermore quickly discovered that price movements often reflected the collective psychology of the market rather than purely fundamental news. This observation became the cornerstone of his trading philosophy.
His legendary trades — shorting the market before the Panic of 1907. the 1929 crash, and other major moves — were rooted in the principles he later codified in How to Trade in Stocks.
The Livermore Market Key System
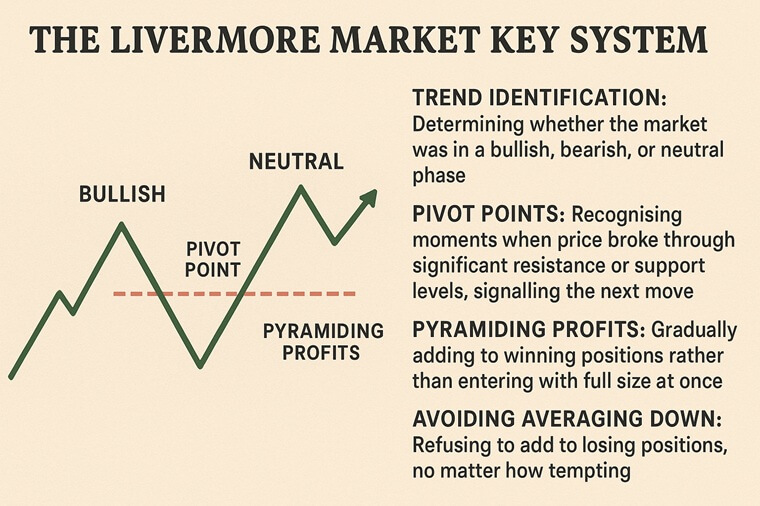
One of the central contributions of "How to Trade in Stocks" is the Livermore Market Key System, his structured approach to identifying market trends and deciding entry and exit points. While not a rigid mechanical system, it acted as a disciplined decision-making framework.
The Market Key System emphasised:
Trend Identification: Determining whether the market was in a bullish, bearish, or neutral phase.
Pivot Points: Recognising moments when price broke through significant resistance or support levels, signalling the next move.
Pyramiding Profits: Gradually adding to winning positions rather than entering with full size at once.
Avoiding Averaging Down: Refusing to add to losing positions, no matter how tempting.
Livermore cautioned that the system required patience and strict adherence, as the temptation to overtrade or chase market noise was ever-present.
Core Trading Principles and Rules
In How to Trade in Stocks, Livermore outlines a set of principles that remain pillars of trading discipline today:
Follow the Leaders: Focus on active, leading stocks rather than thinly traded issues.
Trade in the Direction of the Market: Never fight the dominant trend.
Wait for Confirmed Moves: Enter only when the market confirms your analysis.
Limit Losses Quickly: Set stop-loss orders to protect capital.
Let Profits Run: Resist the urge to take quick gains on winning trades.
These rules, while simple in appearance, require immense self-control — something Livermore admitted was the hardest part of trading.
The Psychological Battle

Perhaps the most enduring value of How to Trade in Stocks lies in its treatment of trader psychology. Livermore recognised that market speculation was as much a mental contest as a financial one.
He discussed the dangers of overconfidence after winning streaks, the paralysis caused by fear after losses, and the emotional exhaustion of constant decision-making. His advice — to wait for the right setup and act decisively — was rooted in the belief that emotional discipline separated successful traders from the masses.
Livermore also stressed the importance of solitude and independent thinking. He avoided market gossip and external opinions, preferring to make his own judgments based on price action.
Risk Management and Capital Preservation
In How to Trade in Stocks, Livermore repeatedly warns that survival is the first goal of any trader. He advised limiting position sizes, maintaining cash reserves, and never risking more than a small fraction of capital on any single trade.
His pyramid strategy — adding to positions only as they moved in his favour — was an early form of scaling in, designed to compound gains while protecting against catastrophic loss.
This focus on capital preservation allowed him to stay in the game through multiple market cycles, even after severe drawdowns.
Legacy and Modern Relevance

Although markets today are faster, more globalised, and technology-driven, the wisdom of How to Trade in Stocks remains strikingly relevant. The core truths about trend following, disciplined execution, emotional control, and risk management have not changed.
Modern traders can adapt Livermore's principles to algorithmic systems, swing trading, or even crypto markets — but the human element he emphasised still applies. The market remains, in his words, "never wrong," and traders still battle their own impulses as much as they battle the tape.
More than eight decades later, this book stands as both a practical manual and a philosophical reflection on speculation. For those willing to study it carefully and apply its lessons with discipline, it offers a timeless edge in an ever-changing financial world.
Disclaimer: This material is for general information purposes only and is not intended as (and should not be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by EBC or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person.

















